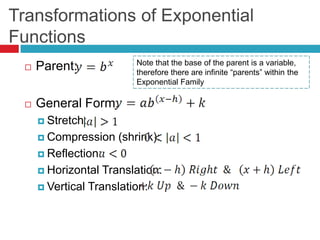
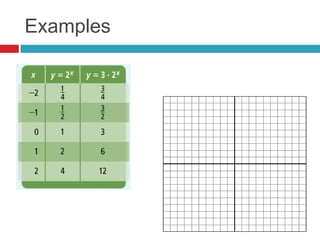
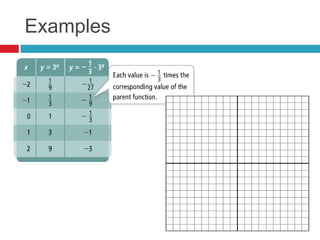
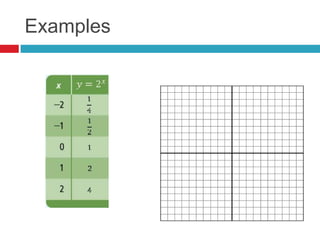
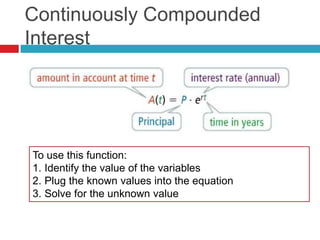
This document discusses properties and transformations of exponential functions, including stretch, compression, reflection, and horizontal and vertical translation. It also discusses the number e as the base for natural exponential functions and using the function A=Pe^rt to model continuously compounded interest. Examples are provided to demonstrate graphing transformations of exponential functions and using the continuously compounded interest formula.