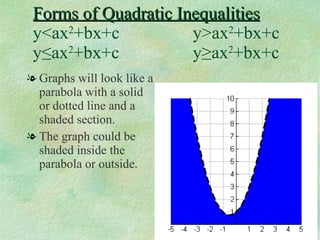
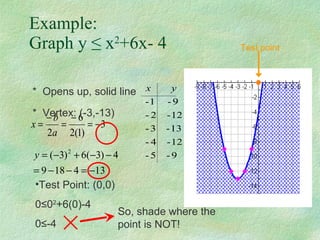
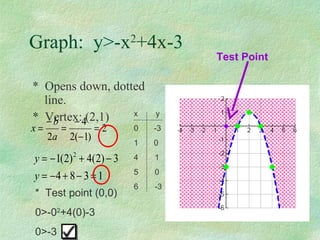
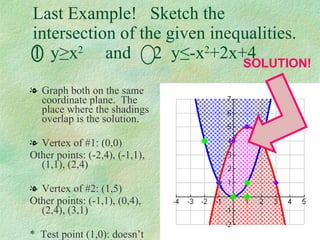
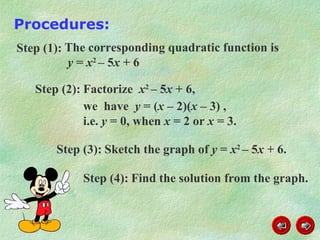
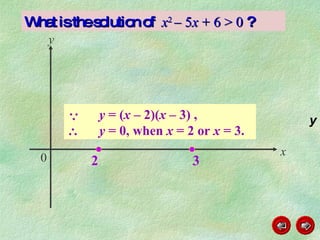
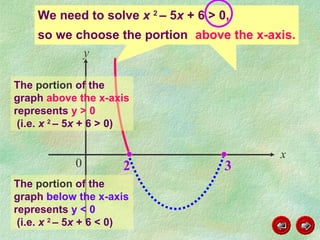
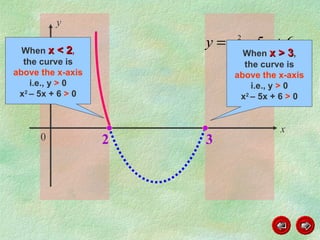
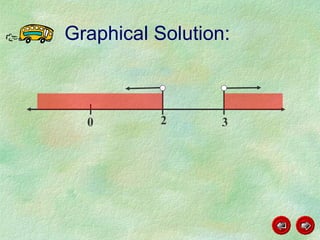
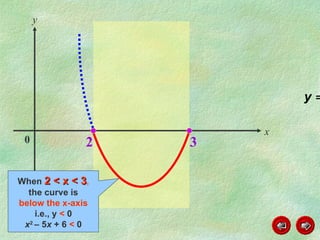
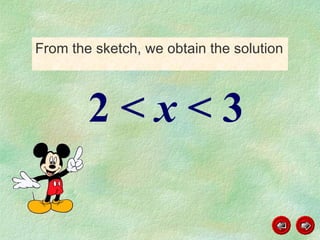
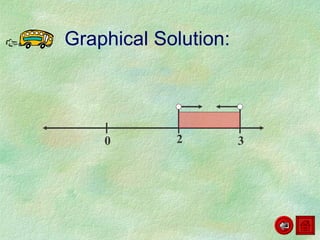
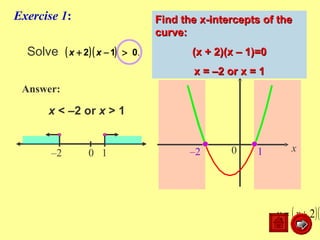
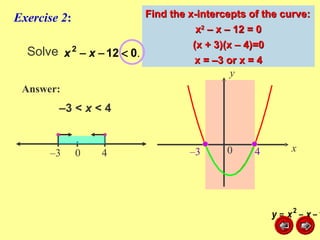
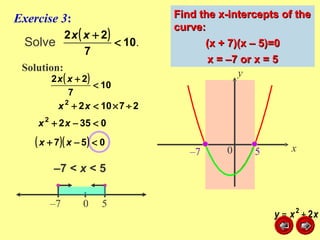
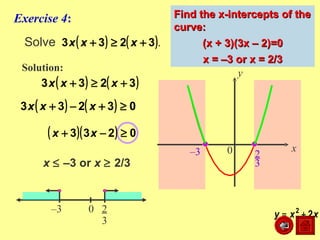
This document discusses how to graph and solve quadratic inequalities. It provides steps for graphing quadratic inequalities by sketching the parabola and shading the appropriate region based on a test point. Examples are given of solving quadratic inequalities graphically by determining the portions of the graph above or below the x-axis and obtaining the solution intervals. Exercises are also worked through to practice solving quadratic inequalities graphically.