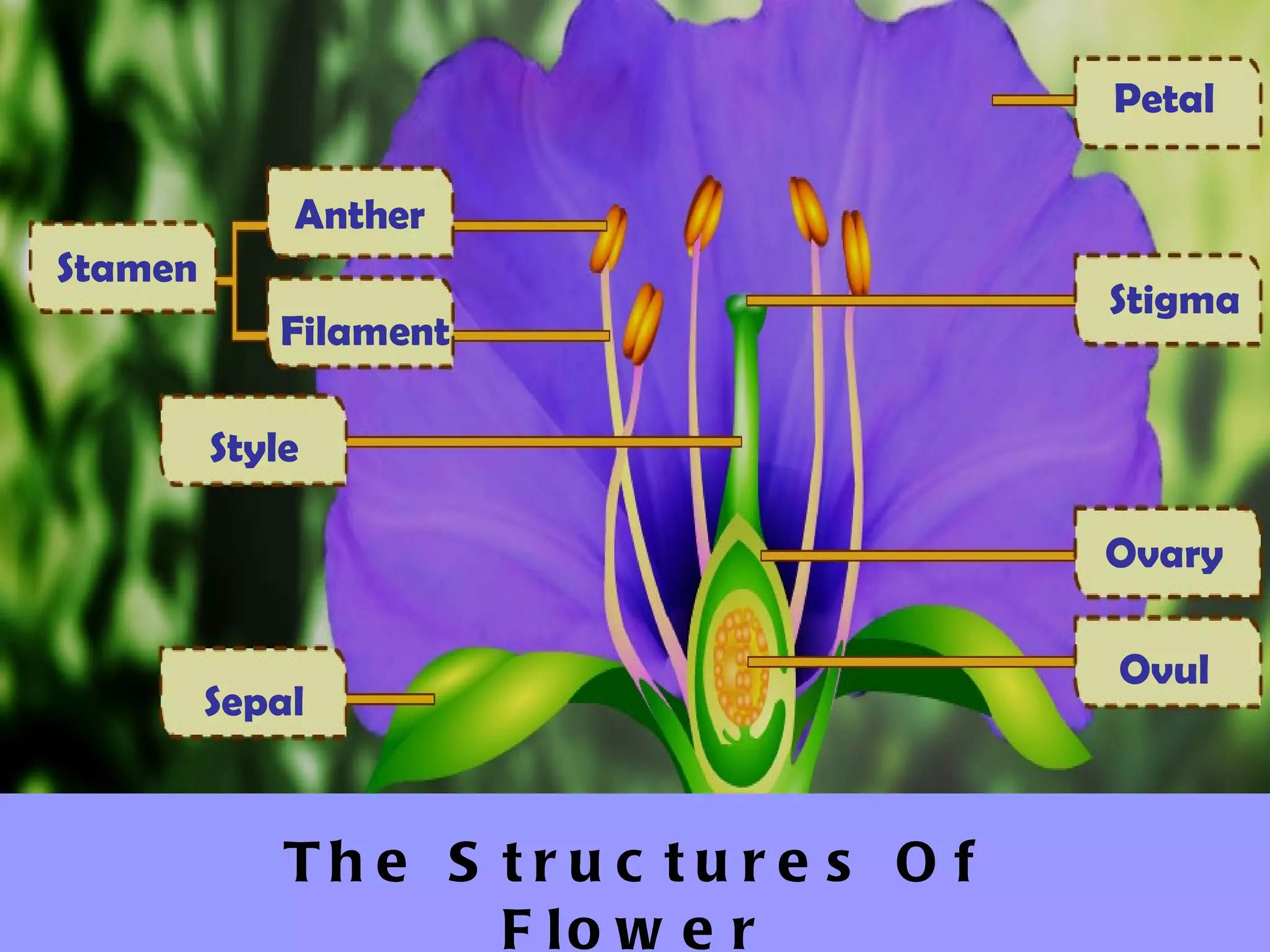
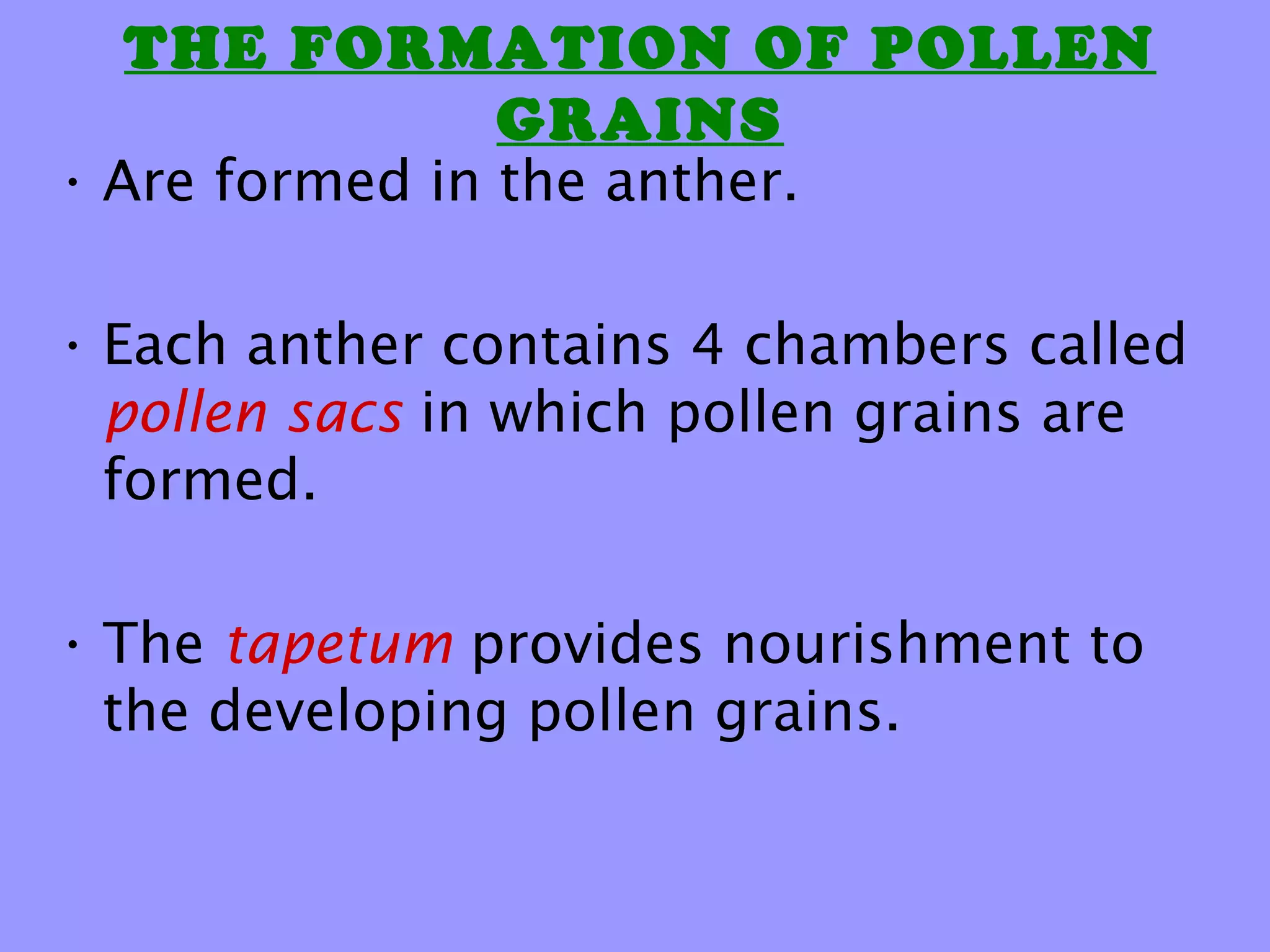
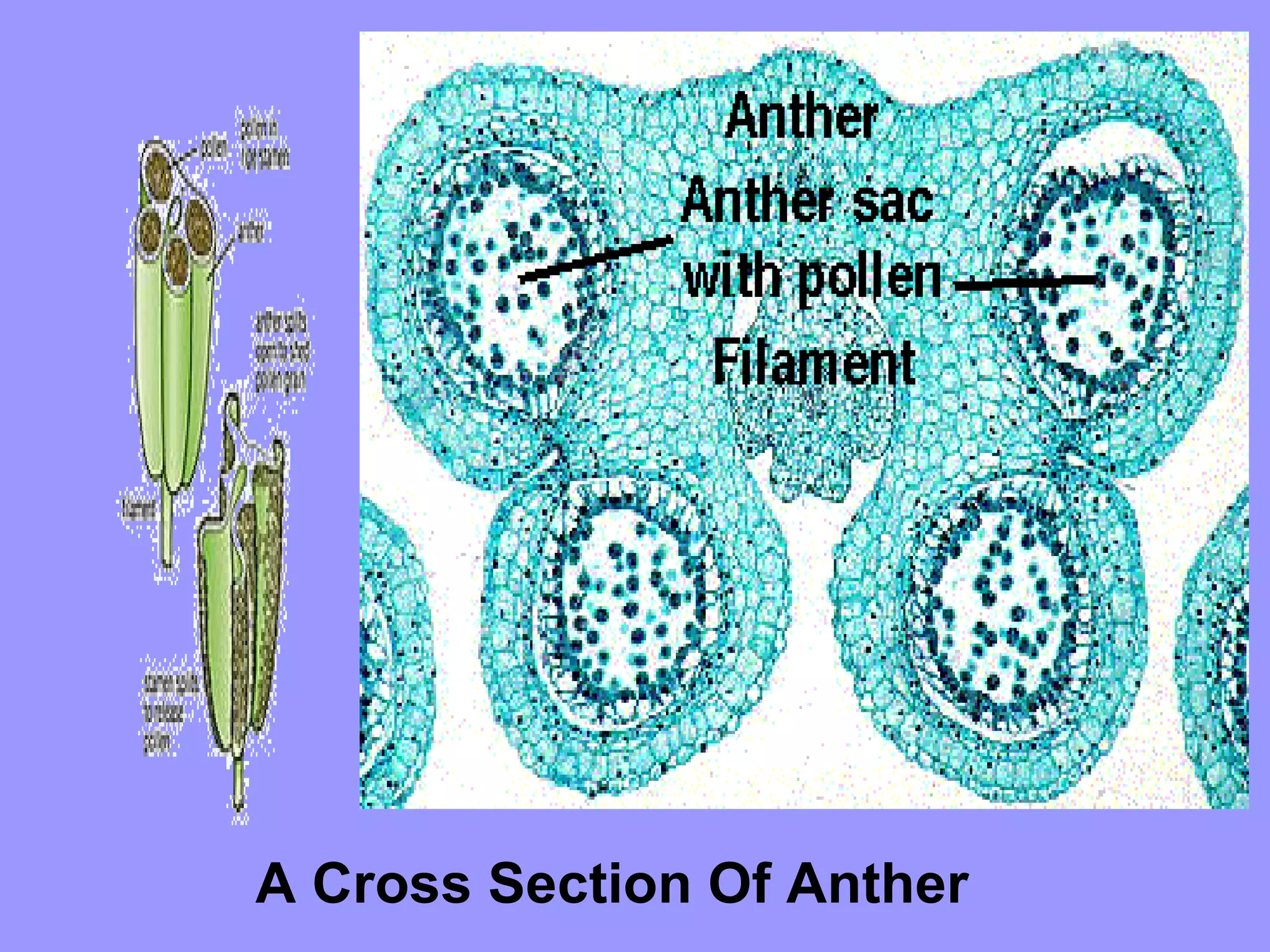
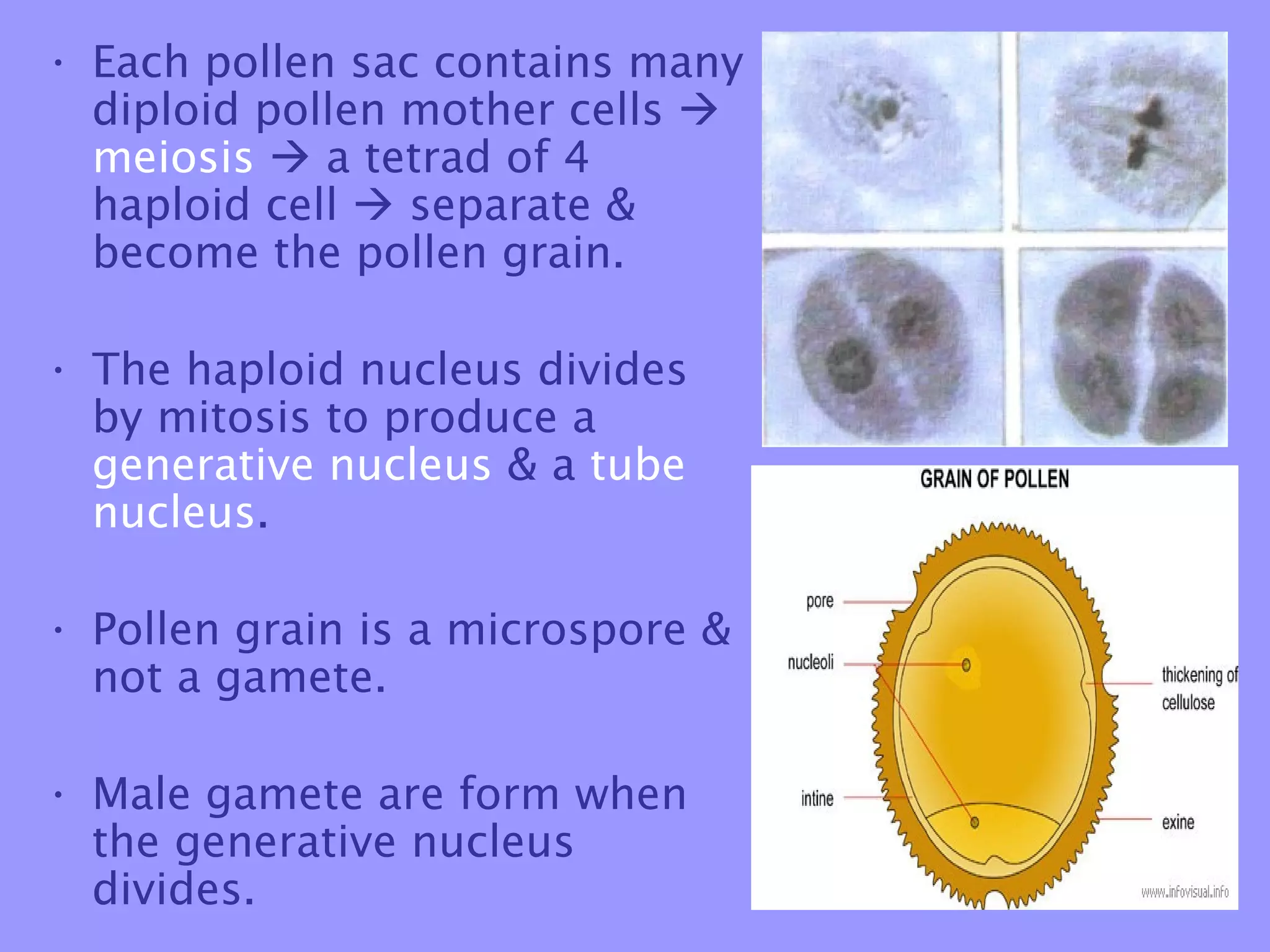
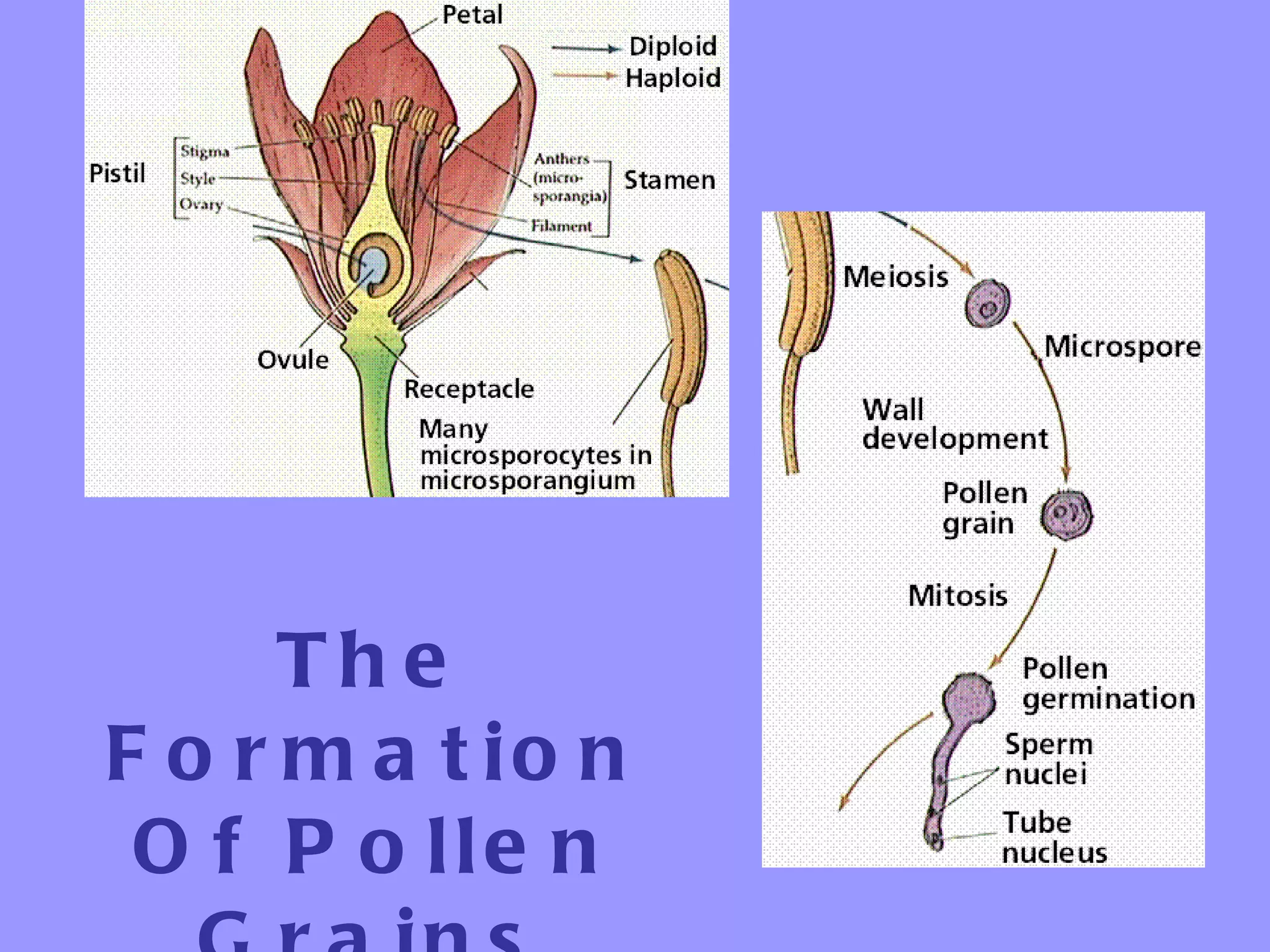
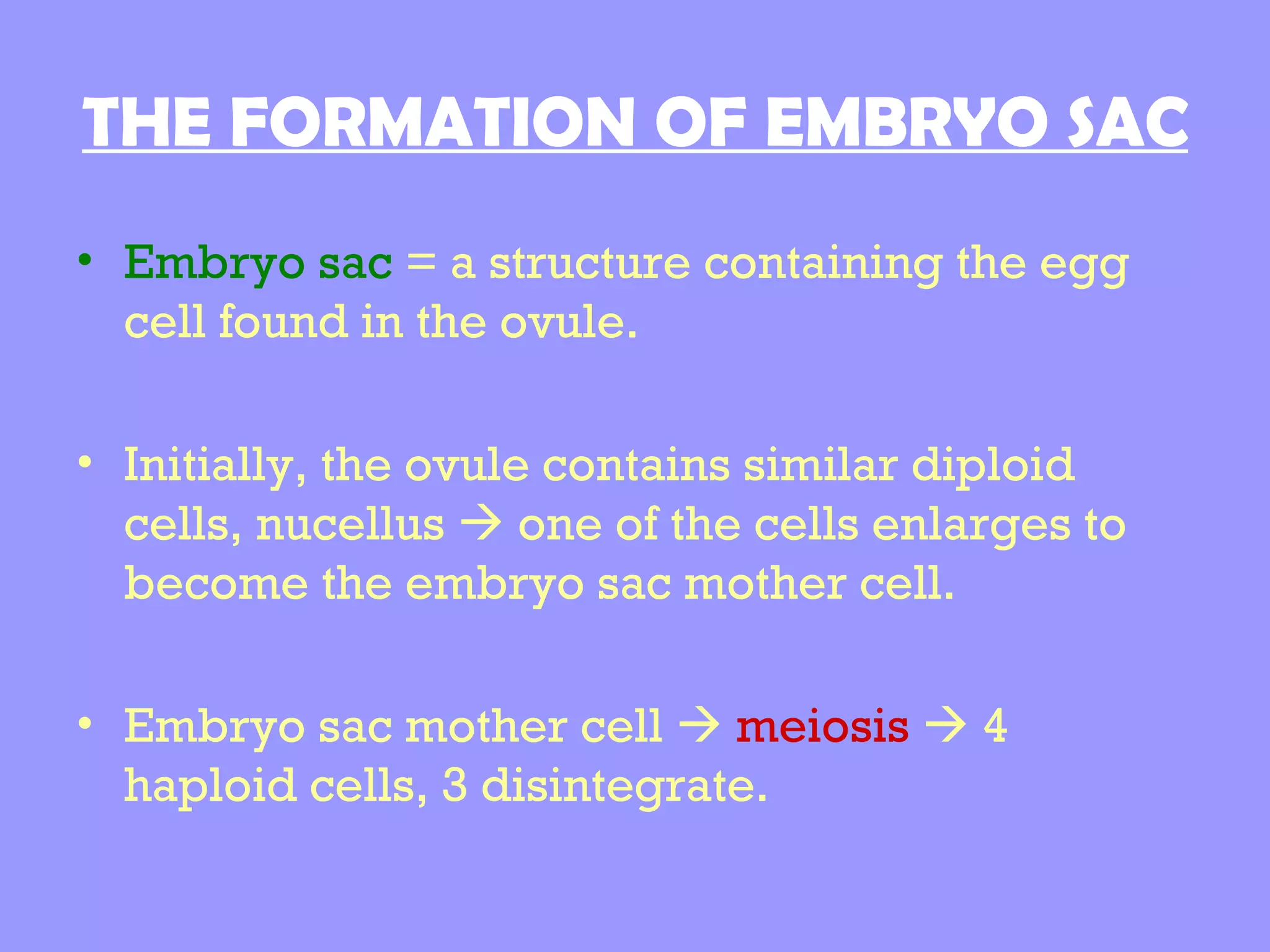
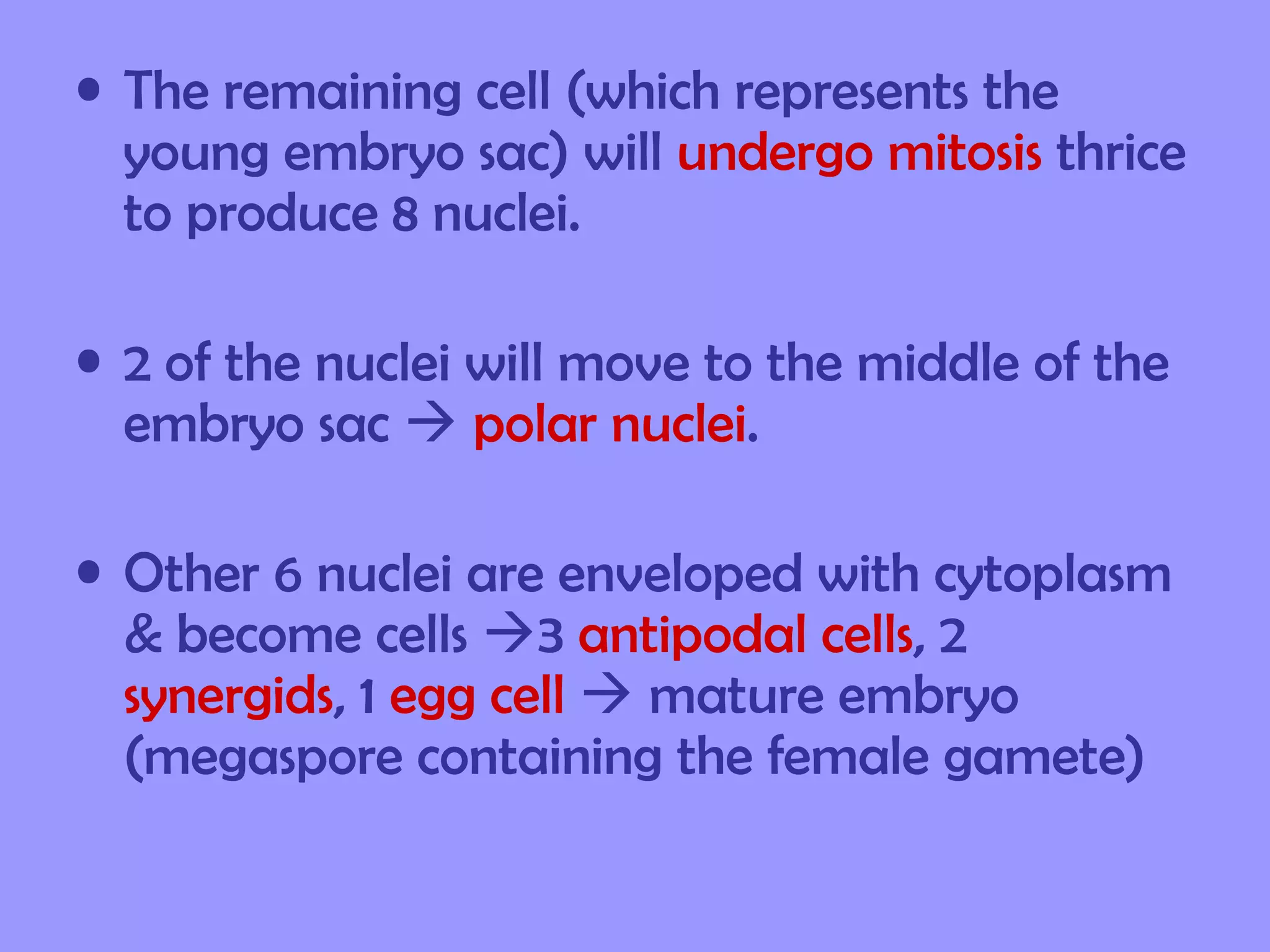
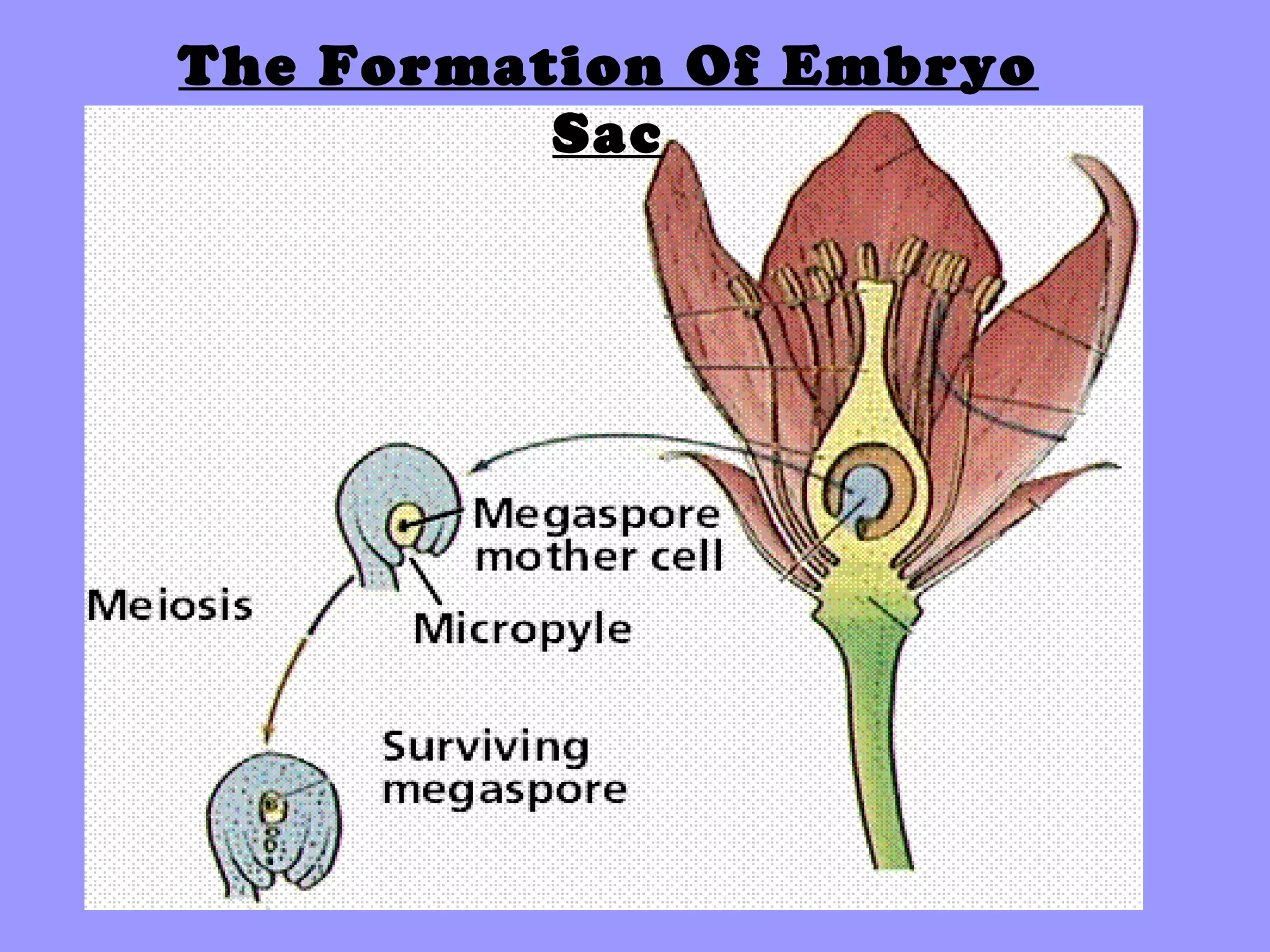
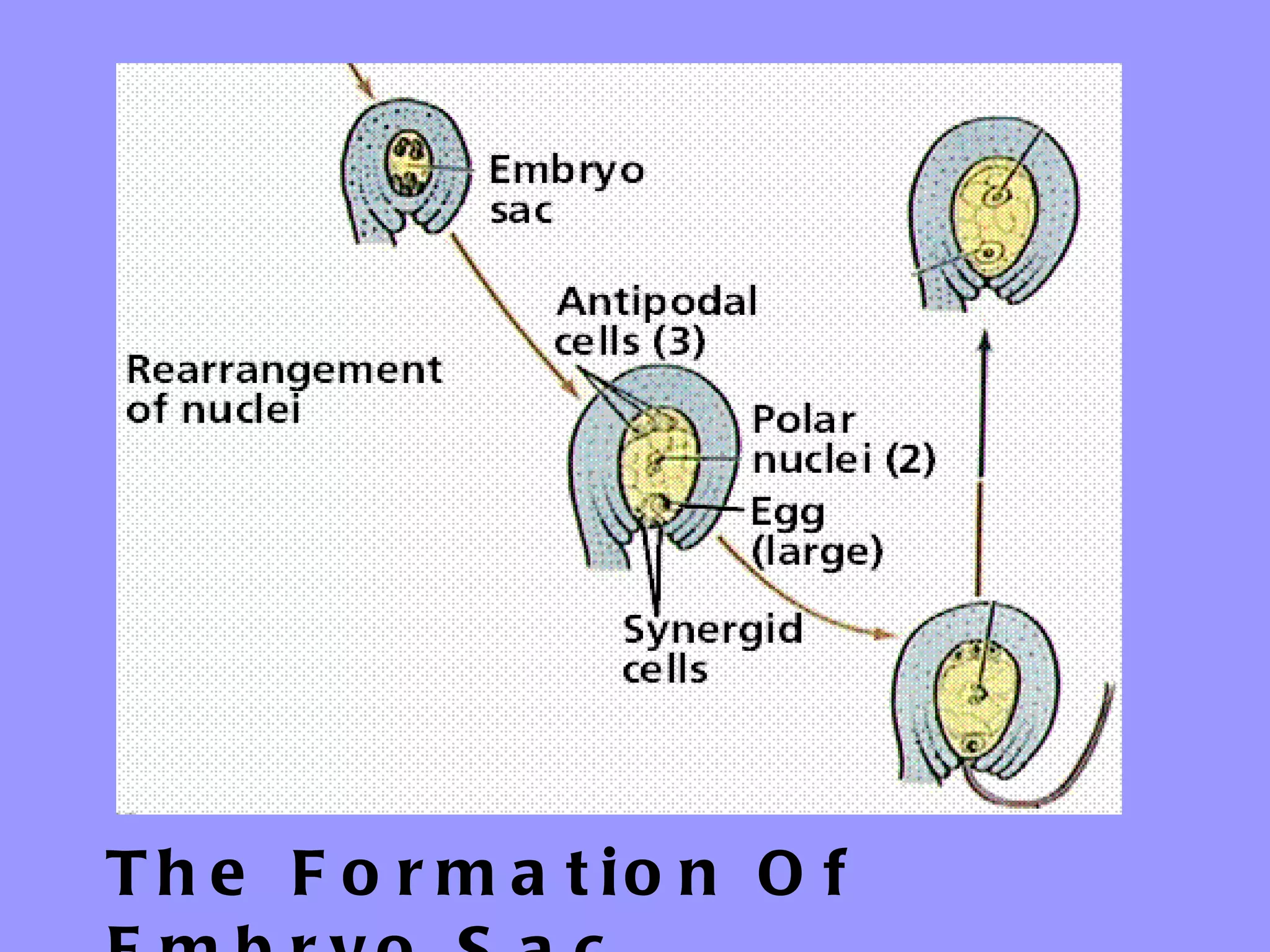
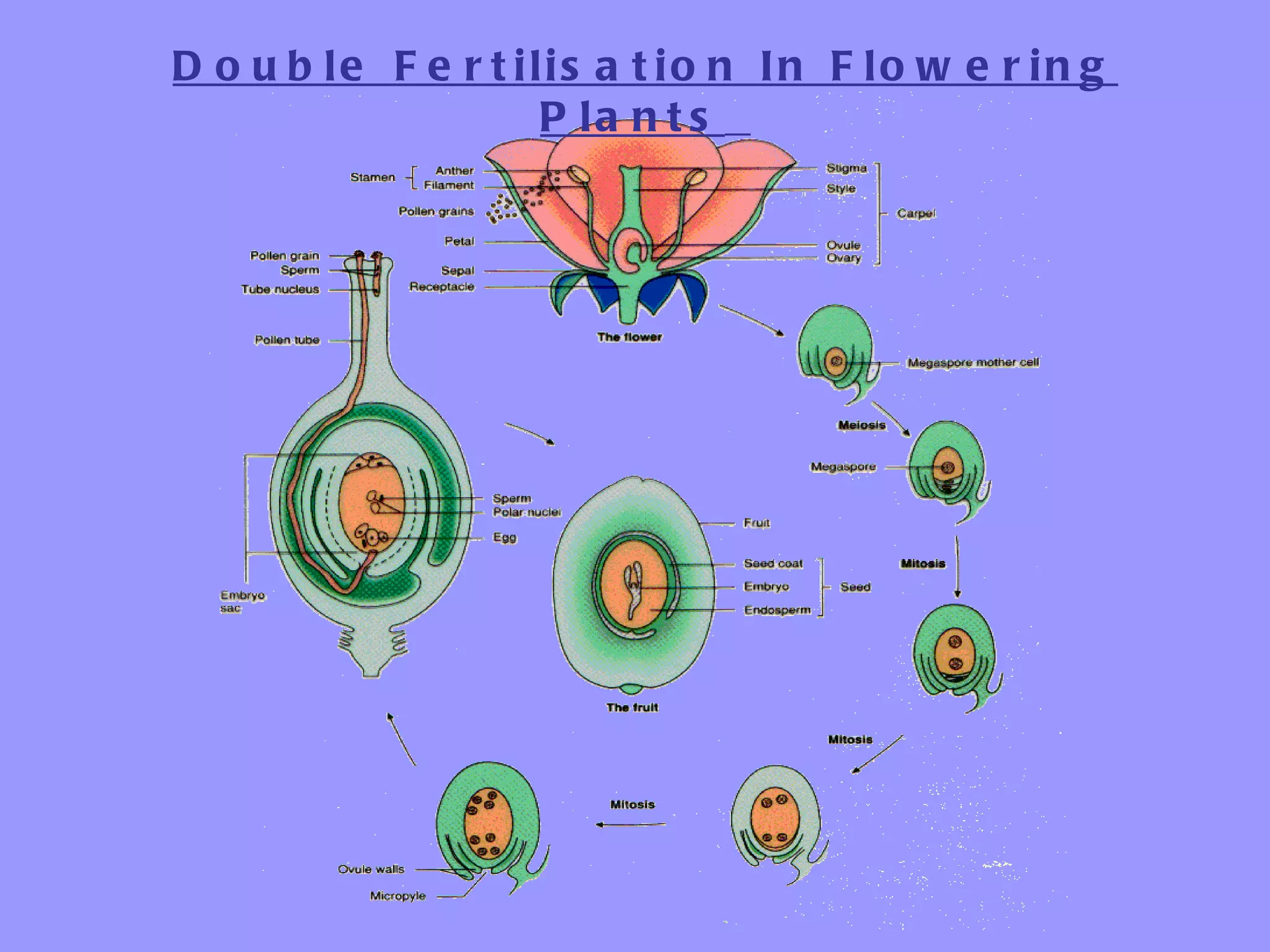
This document summarizes the process of sexual reproduction in flowering plants. It describes the male and female structures in flowers, including the formation of pollen grains and embryo sacs. The key stages discussed are pollination, fertilization, and double fertilization. Double fertilization is important because it ensures the nutritive endosperm tissue forms to provide food for the developing embryo, allowing seeds to survive unfavorable conditions until germination.