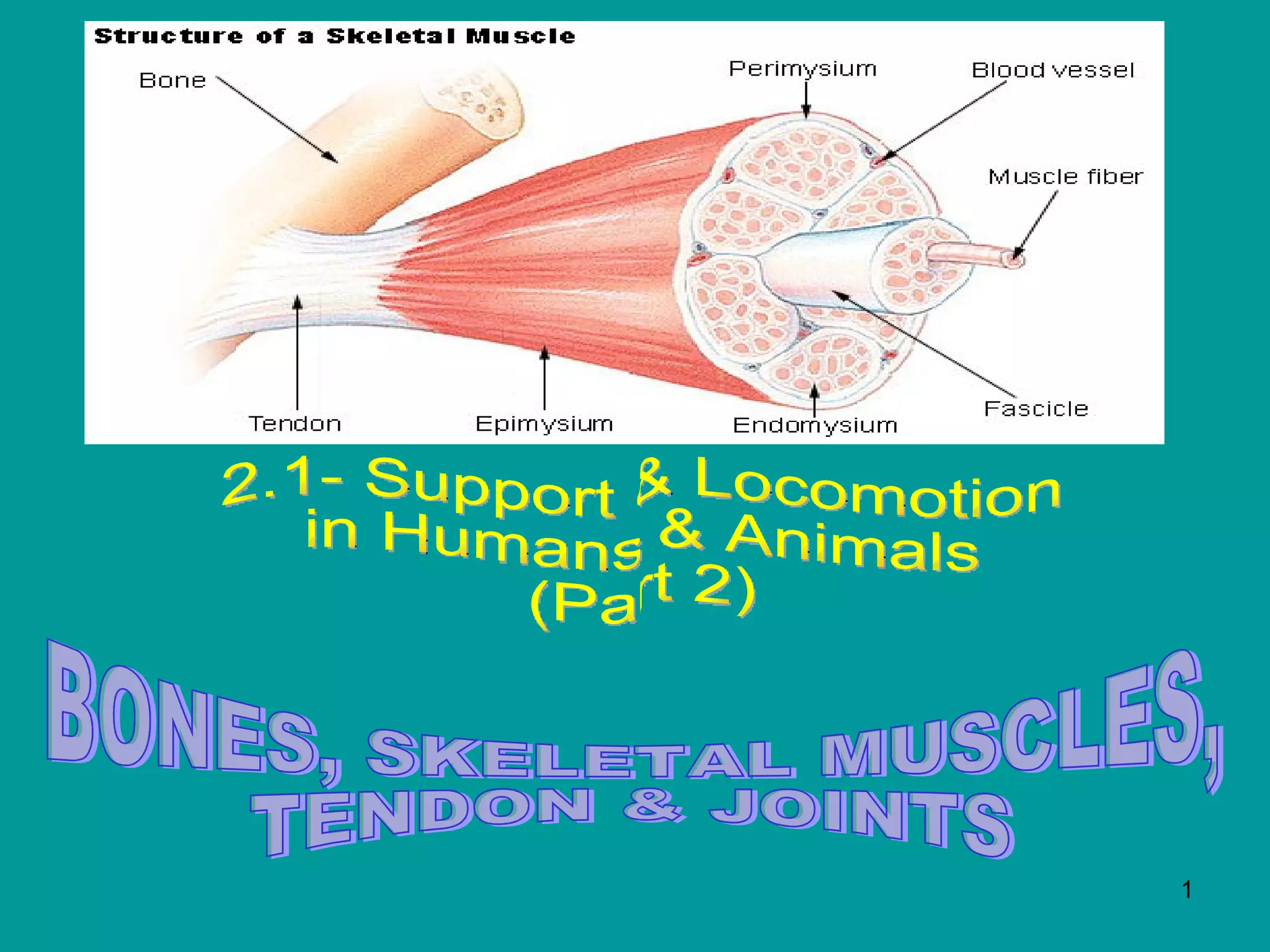
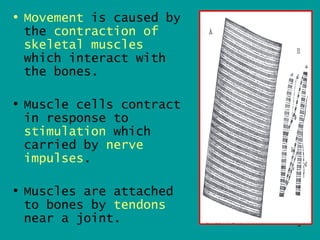
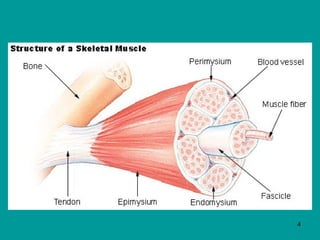
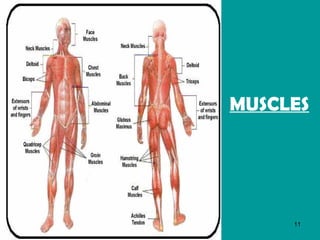
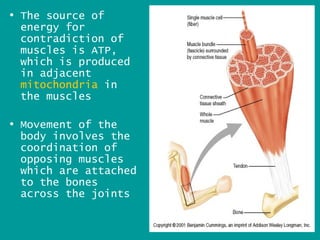
1. Skeletal muscles contract when stimulated by nerve impulses, pulling on bones via tendons near joints to cause movement.
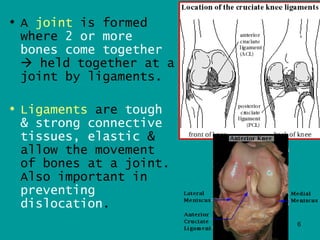
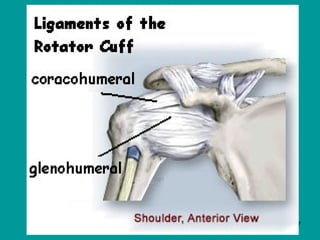
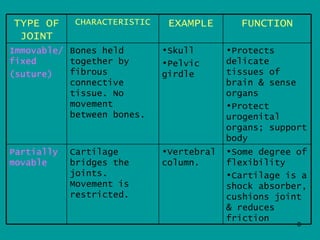
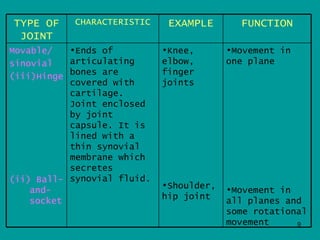
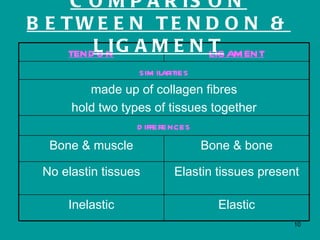
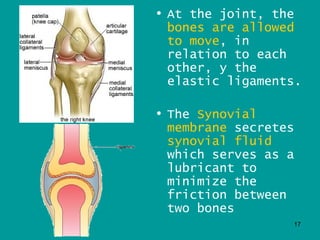
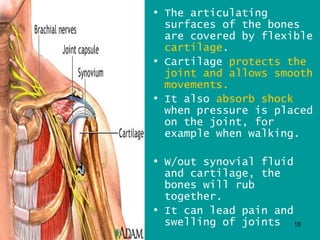
2. Joints are where bones meet, connected by ligaments which allow movement. Cartilage and synovial fluid act as shock absorbers and lubricants at joints to reduce friction between bones.
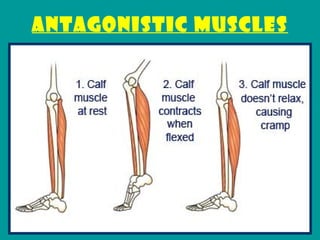
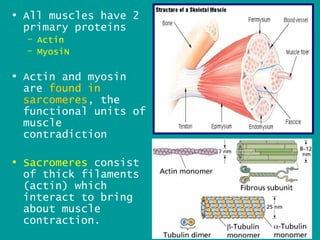
3. Antagonistic muscles like the biceps and triceps work in opposition to flex and extend joints, with actin and myosin fibers interacting in sarcomeres to power muscle contraction through ATP energy.