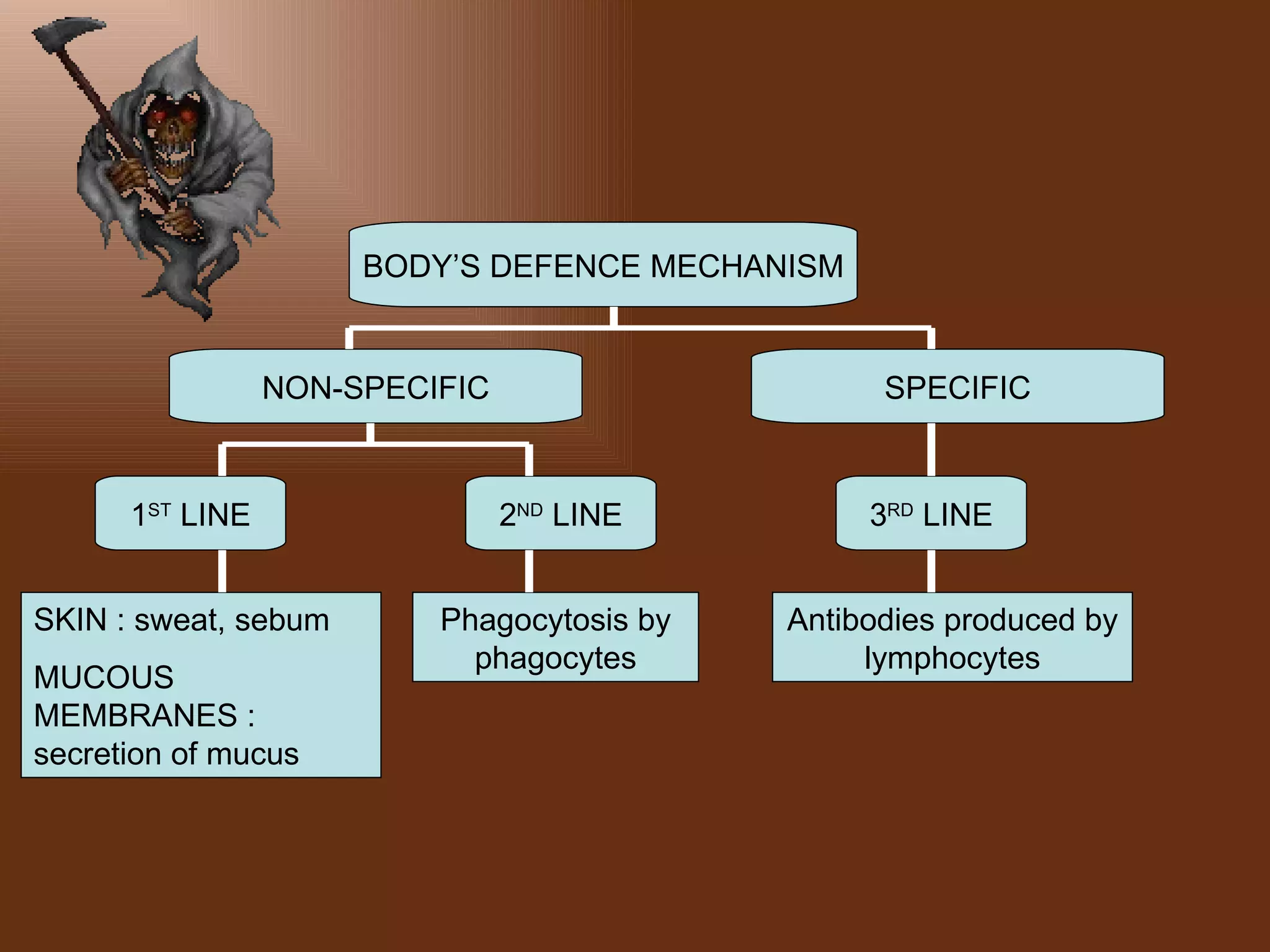
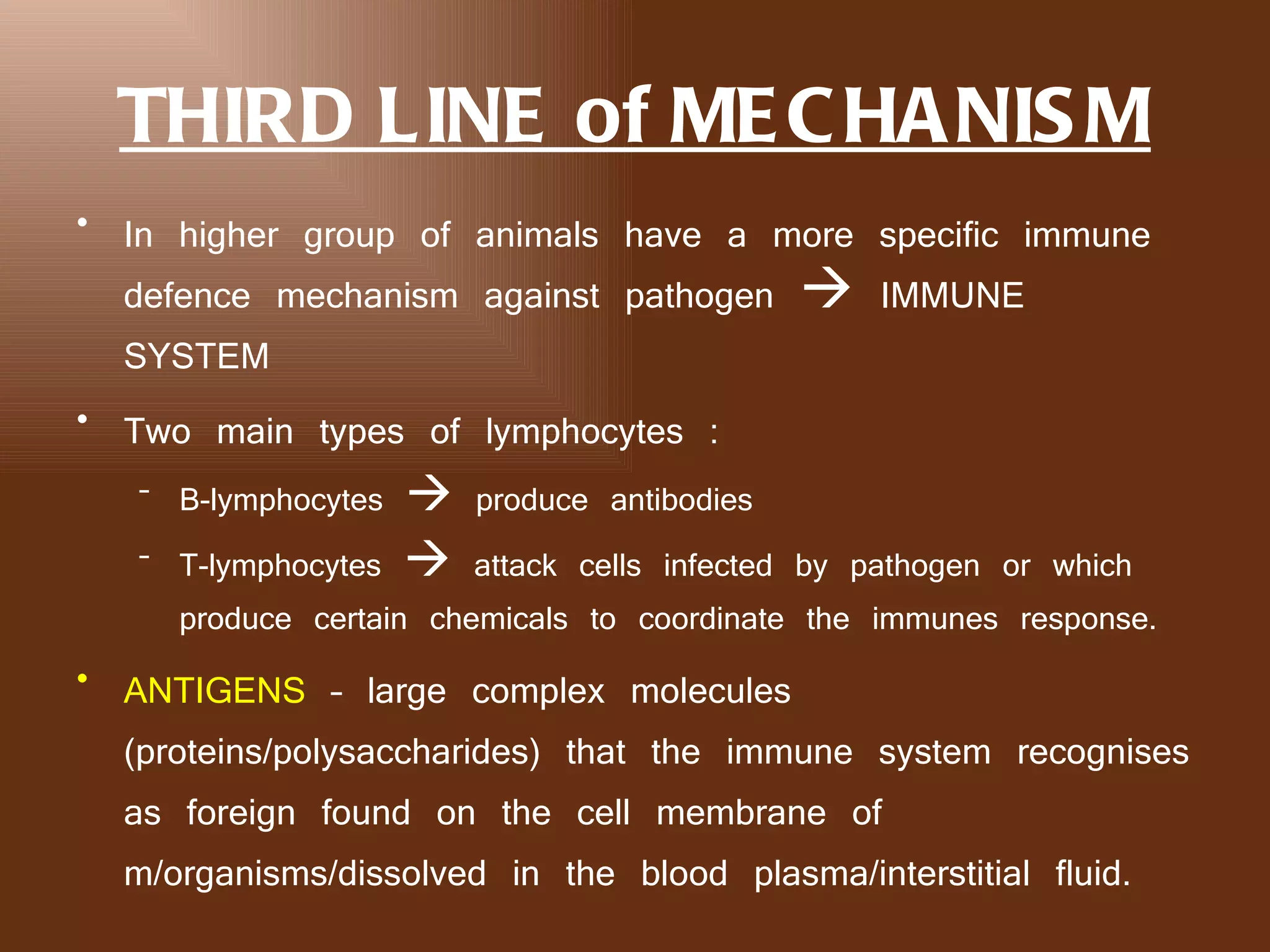
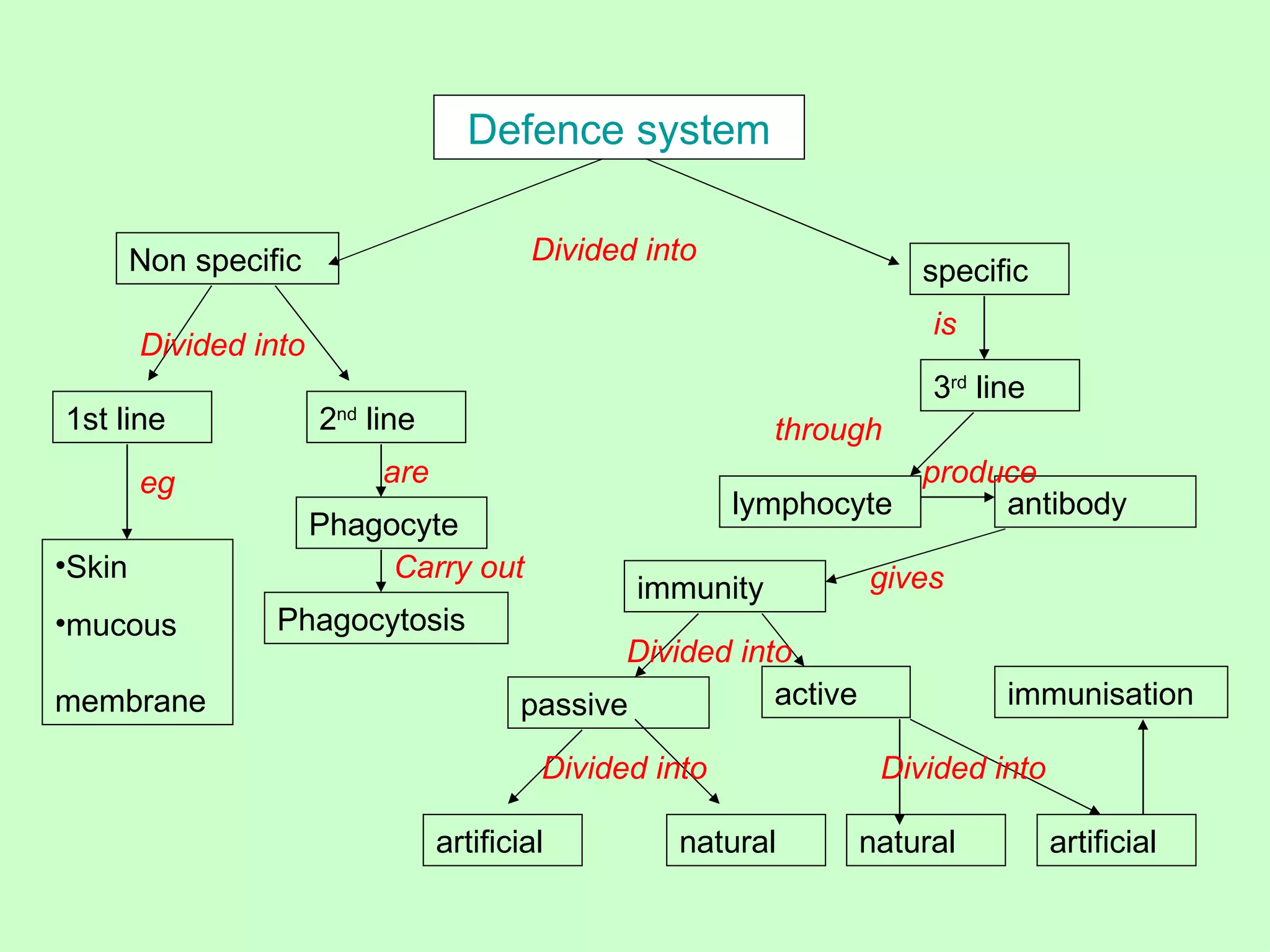
The document discusses the body's defense mechanisms against pathogens. It describes three lines of defense: non-specific defenses as the first line (skin, mucous membranes); phagocytosis by white blood cells as the second line; and the specific immune response involving antibodies produced by lymphocytes as the third line. It defines key terms like antigens, antibodies, immunity, and different types of immunity including active and passive immunity acquired naturally or through vaccination and immunization.