The document explains the process of fertilization in plants, which involves the union of male and female gametes, leading to the formation of a zygote and endosperm through double fertilization. It details the stages of pollination, pollen tube development, and the eventual formation of seeds and fruits, highlighting the significance of these processes in plant reproduction. Additionally, it outlines the structure of ovules and pollen grains, emphasizing their roles in successful fertilization and the development of new generations.
![FERTILIZATION IN PLANTS: HOW TO
EXPLAIN PLANT FERTILIZATION
Spread the love
FERTILIZATION IN PLANTS
Definition
Fusion between male gamete and female gamete of plant is called fertilization.
Events of fertilization
A] Pollination brings female and male gametophyte together- The male and female gametophytes must meet
and unite their gametes to fertilize egg. This is done by pollination, in which pollen is placed on the stigma of
the carpel.
B] Germination of pollen grain under suitable condition– The cytoplasm of the pollen grain absorbs sugar
and water from the stigma and bulges out to produce a tube known as pollen tube by braking down exine of
pollen grains. This germinating pollen tube grows down through the stigma and style of flower towards the
micropyle of the ovary. This tube produces chemical, calcium such as that dissolves the tissues of the style
and the tip of the pollen tube enters the ovary through the micropylar end occurring double fertilization.
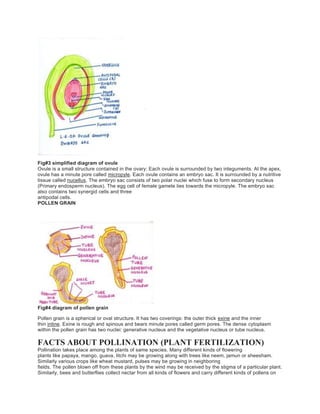
Fig#1 simplified diagram of double fertilization of the flower
C] Division of Nucleus– The generative nucleus of the pollen grain divides by mitosis and forms two male
gamete nuclei or sperm nuclei. The pollen grain, with tube containing two male gamates constitutes the
mature male gametophyte. The ovule contains the egg cell inside the embryosac.
D] Entry of pollen tube– The tip of pollen tube after entering the ovary through the micropyle, ruptures and
discharges two male gametes into the embryosac.
E] Double Fertilization- One of the male gametes fuses with the egg to form the zygote. This fusion is called
fertilization. Another Male gametes fuses with the deploid secondary nucleus. This nucleus is formed by the
fusion of two polar nuclei. Later forms the endosperm which is a food storing tissue. In this way double
fertilization occurs
Diagrammatic representation of steps of fertilization
Anther
↓
Pollengrain
↓
Stigma
↓
Pollen tube
↓
Micropyle](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/fertilizationinplants-230630104013-34fc771d/85/FERTILIZATION-IN-PLANTS-docx-1-320.jpg)