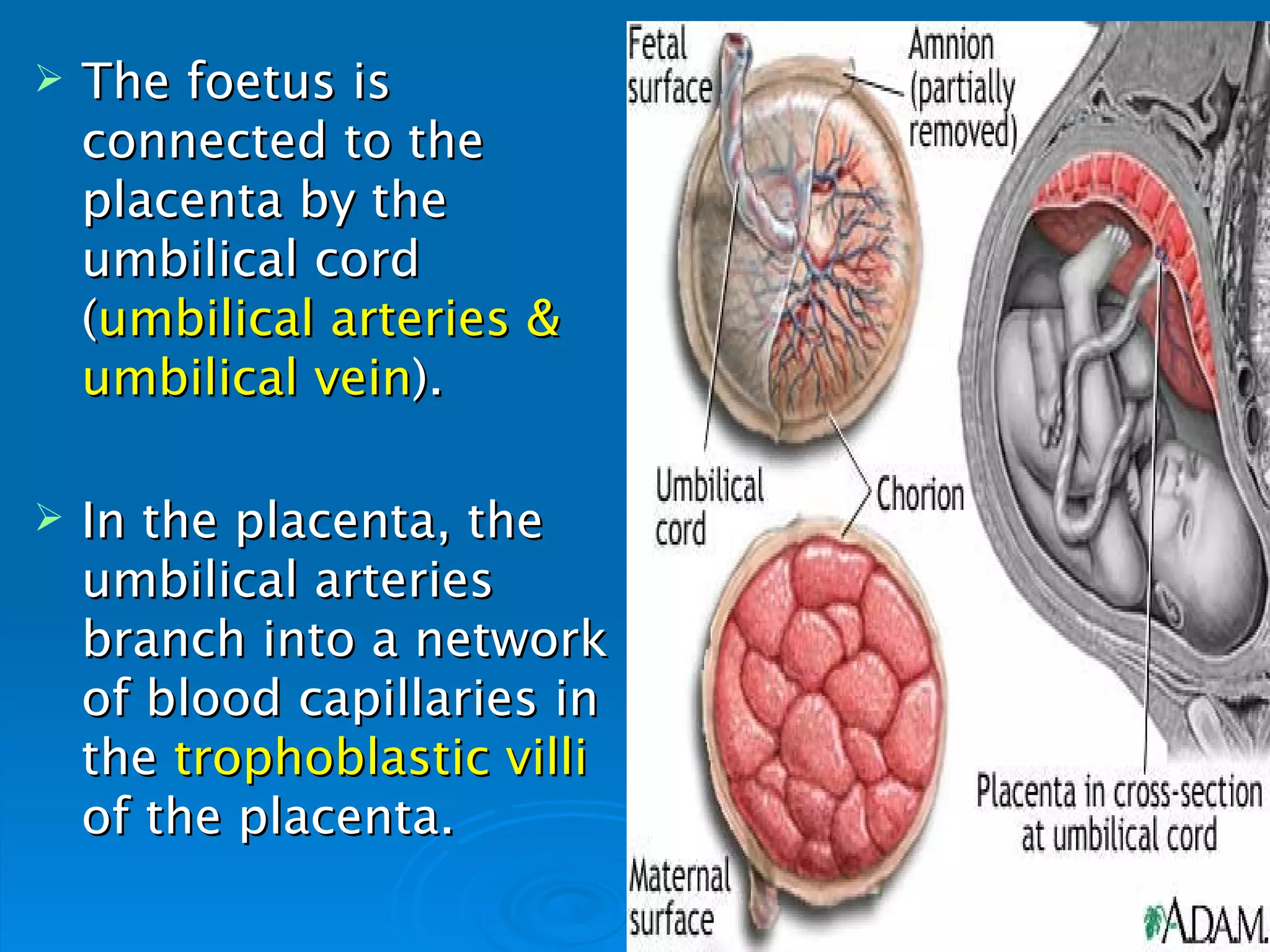
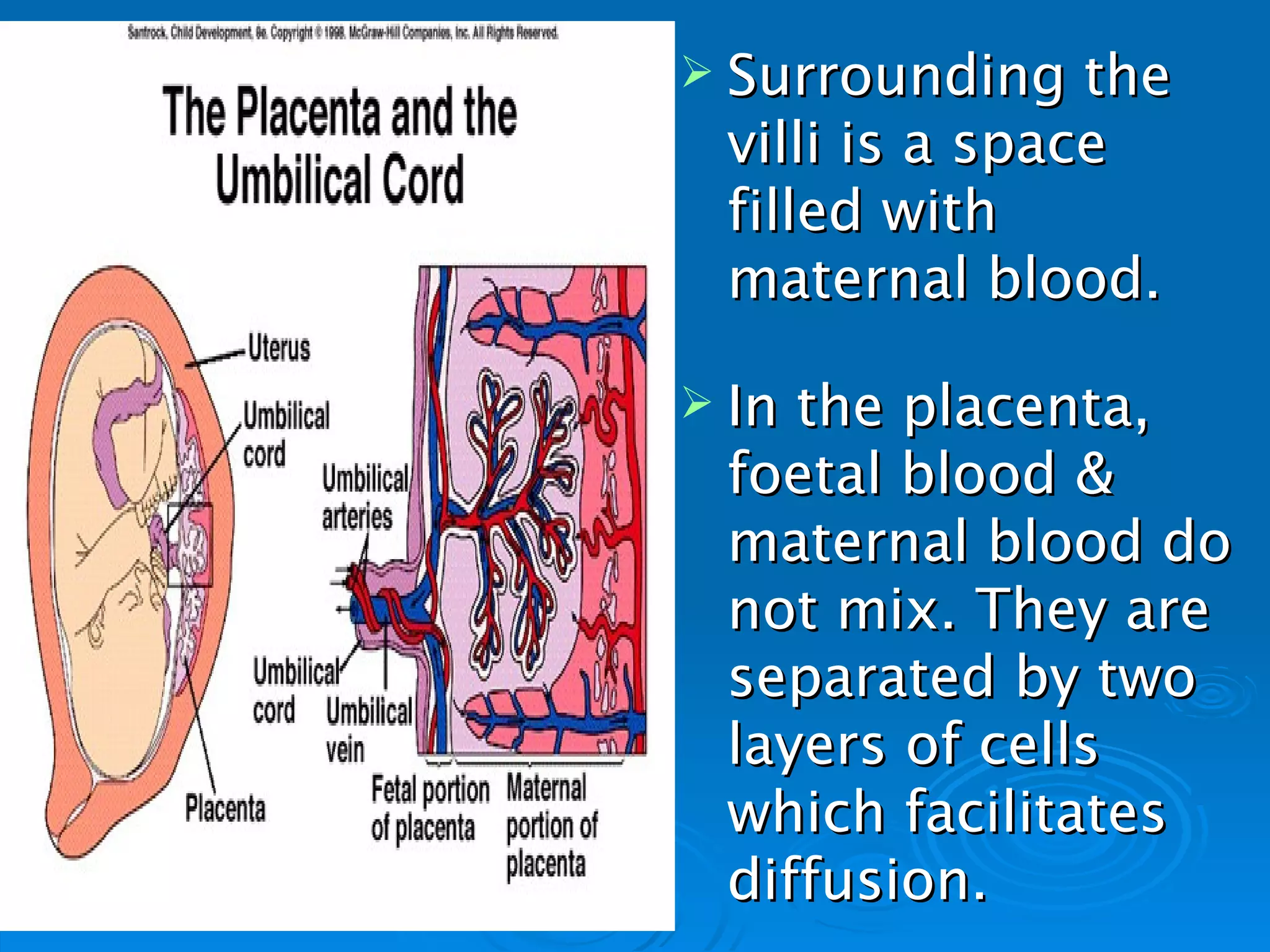
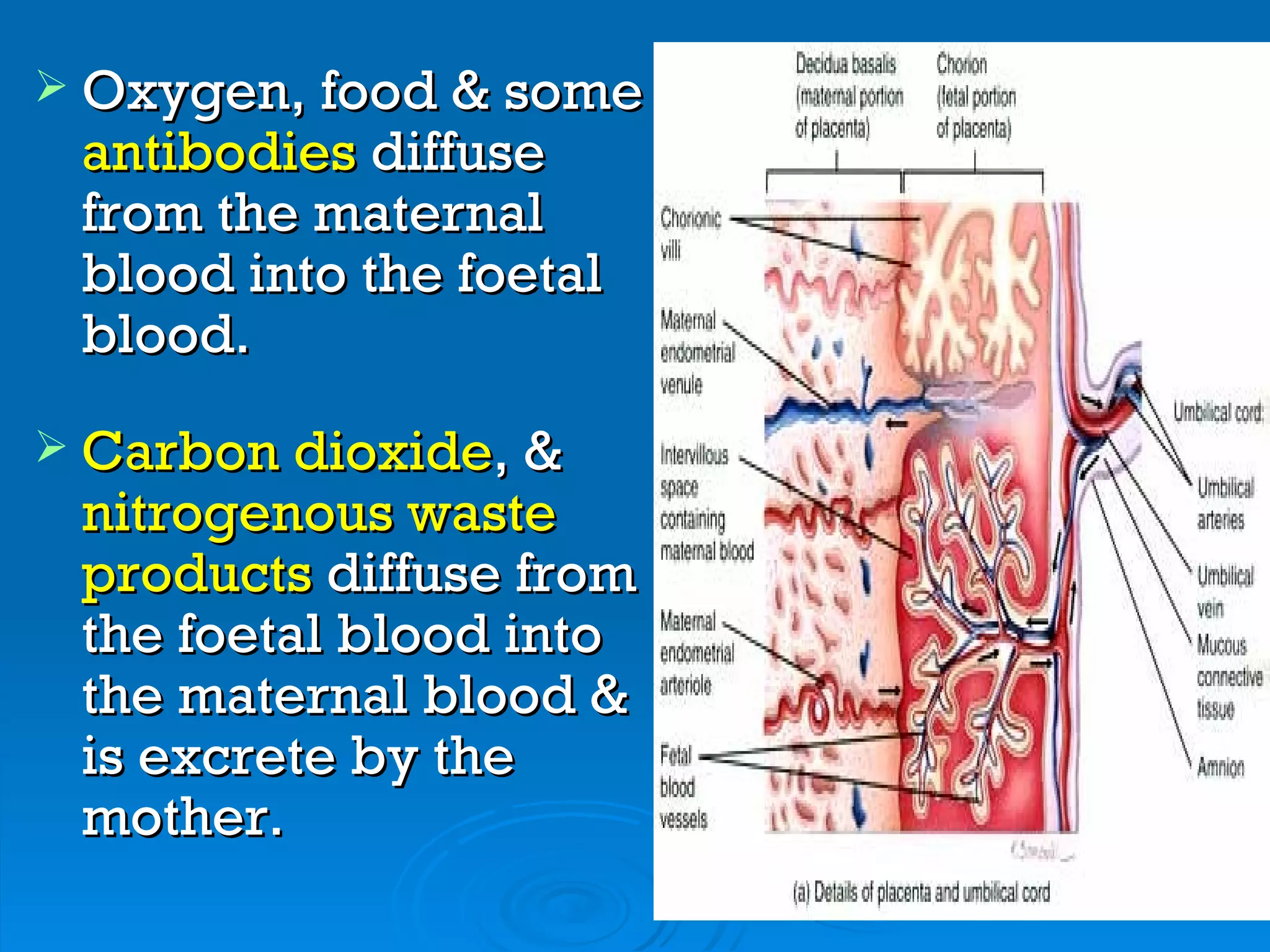
The placenta functions to exchange oxygen, food and waste between the fetus and mother via trophoblastic villi. The umbilical cord connects the fetus to the placenta, carrying oxygenated blood to the fetus and deoxygenated blood away. This separate circulatory system is essential to prevent issues from incompatible blood groups or high maternal blood pressure from damaging the delicate fetus.









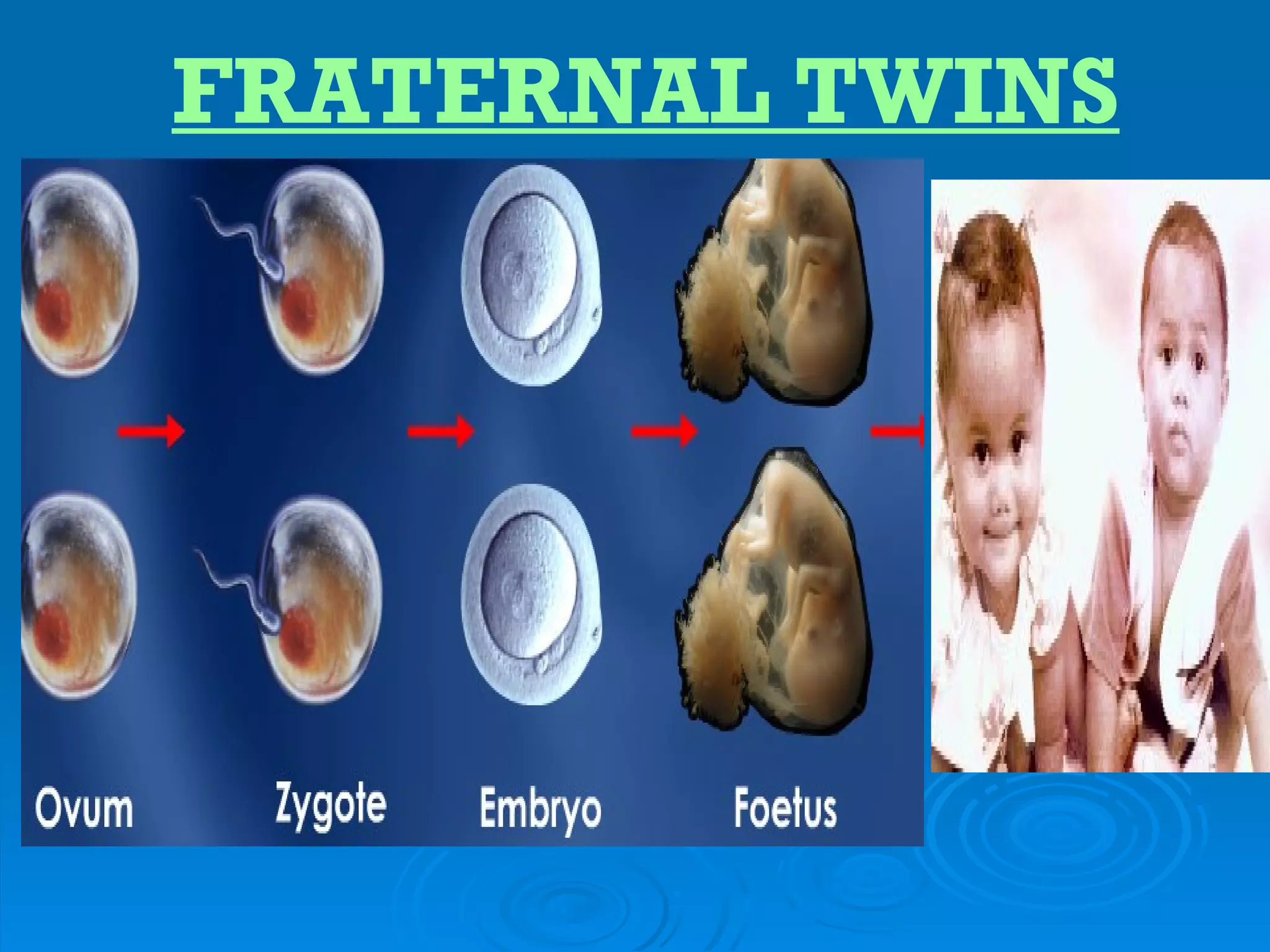


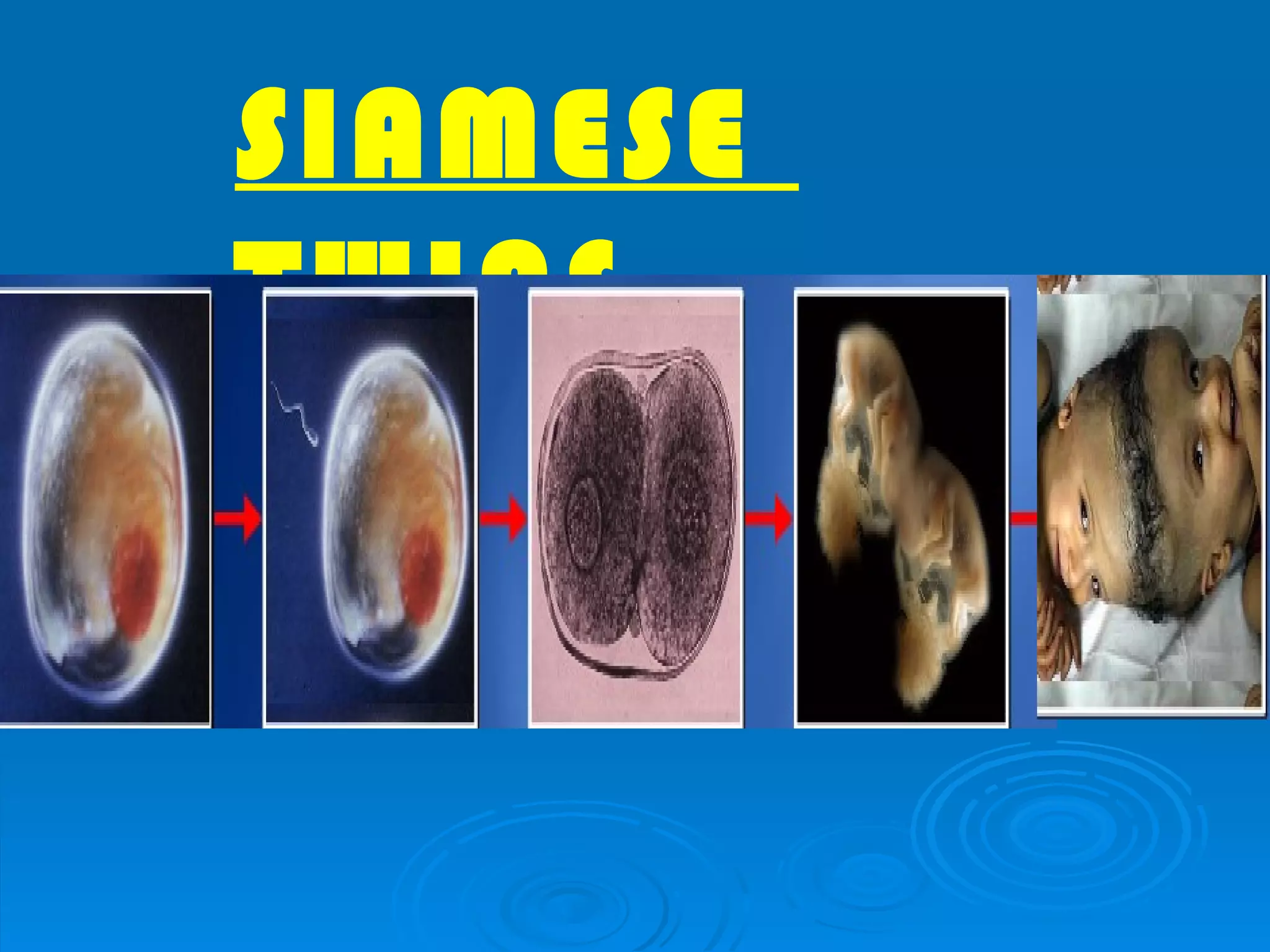




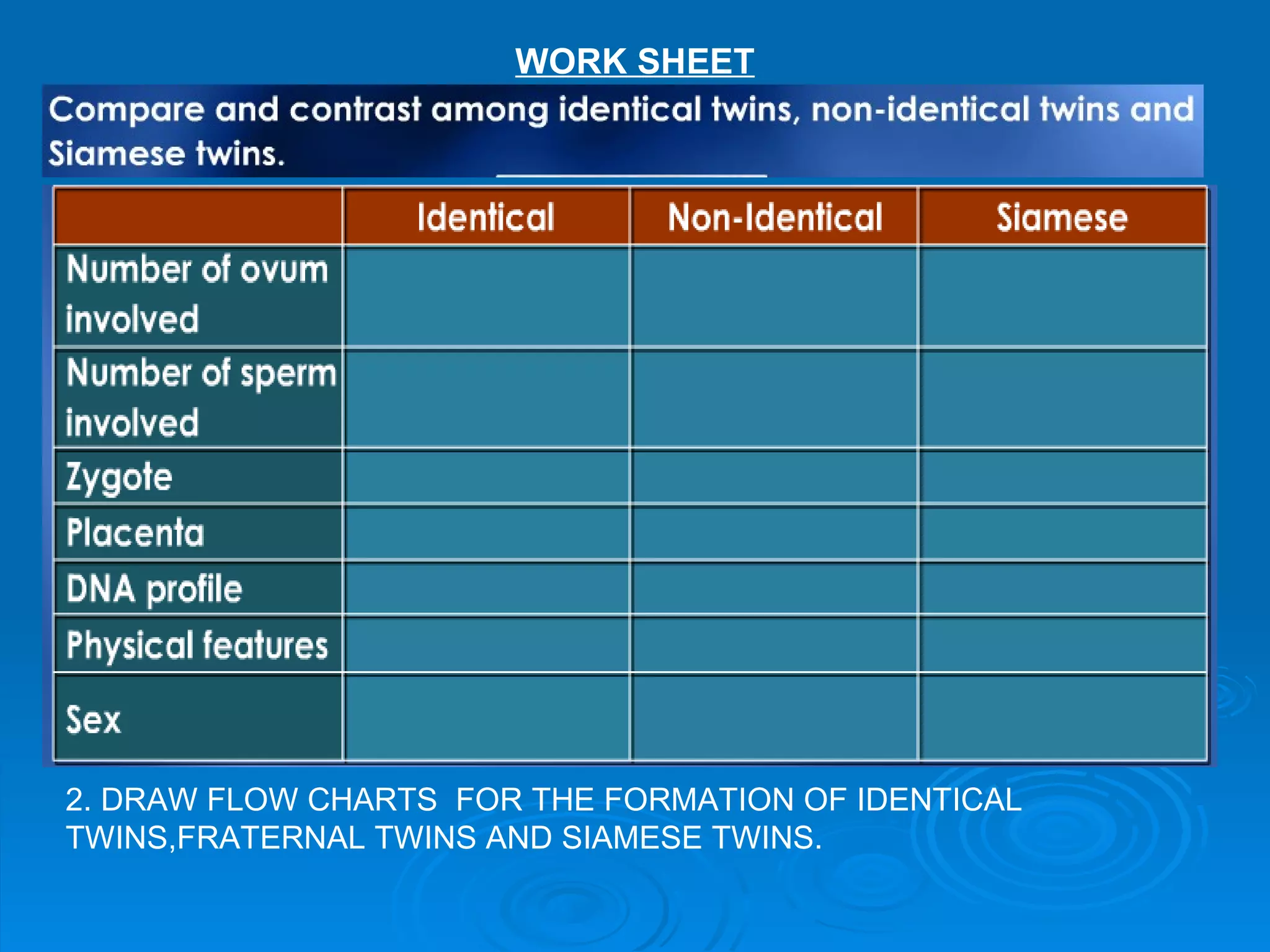








![4[1].3 FORM 5](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/41-3earlydevelopmentofzygote-120603003204-phpapp02/75/4-1-3-FORM-5-34-2048.jpg)