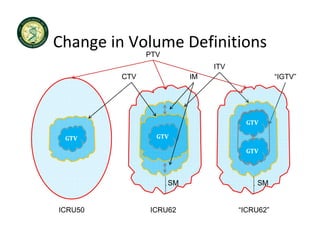
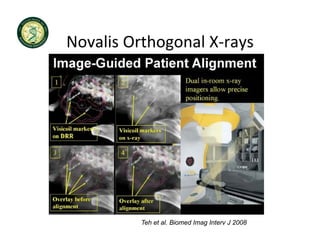
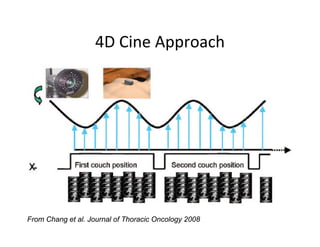
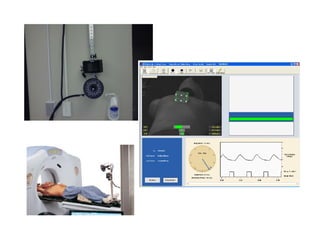
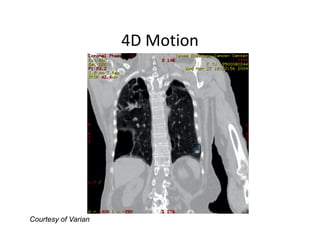
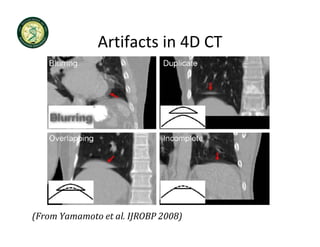
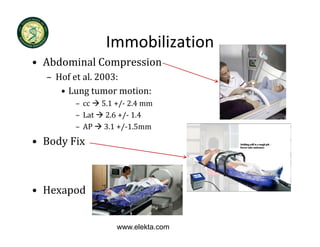
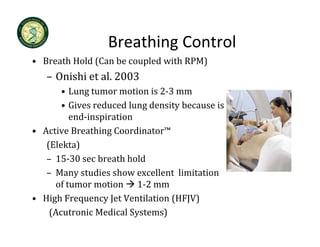
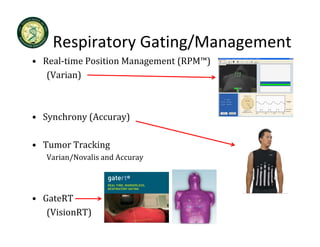
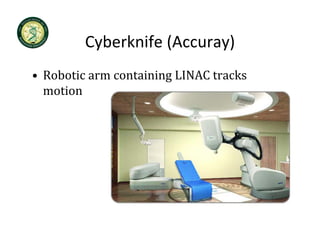
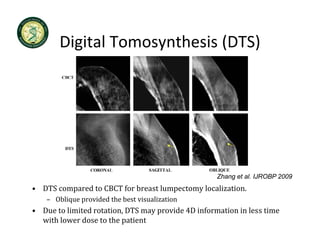
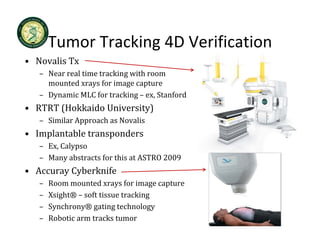
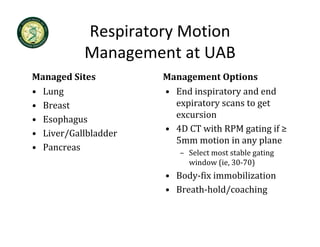
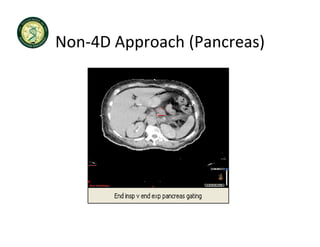
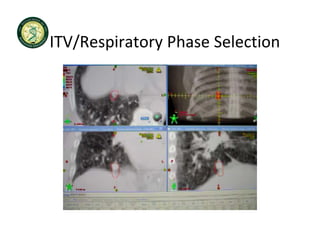
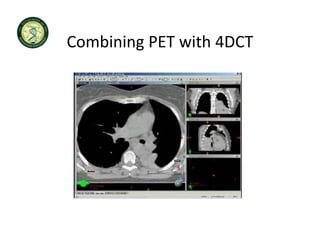
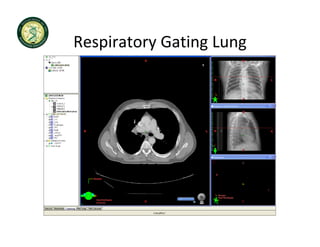
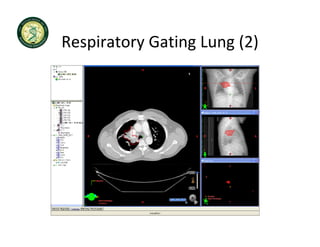
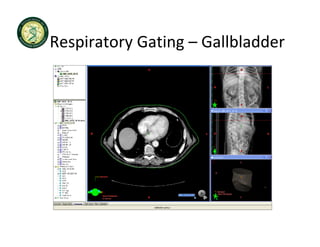
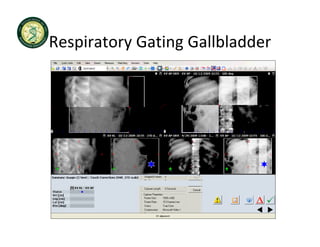
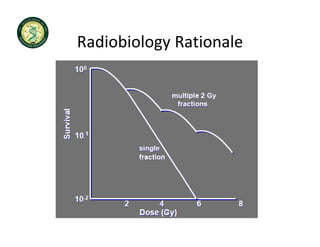
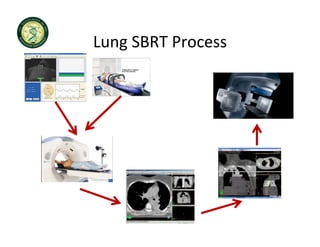
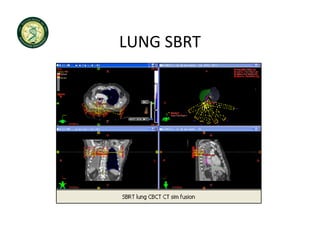
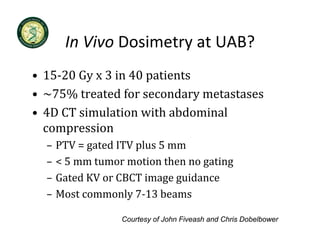
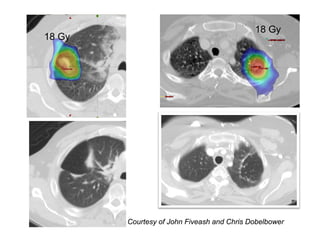
4D-IGRT involves accounting for tumor motion during radiation therapy delivery. It uses 4D computed tomography (4D CT) imaging, which captures tumor position at different respiratory phases. This allows delineation of an internal target volume (ITV) that encompasses the full range of tumor motion. Treatment can then be delivered over the entire respiratory cycle or gated to a specific phase such as end-exhalation using respiratory tracking systems. The goal is to ensure accurate radiation delivery while minimizing doses to surrounding healthy tissues.