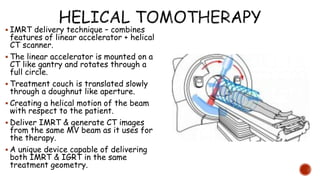
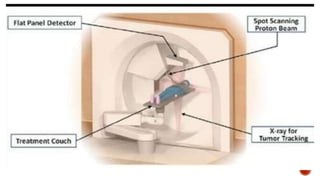
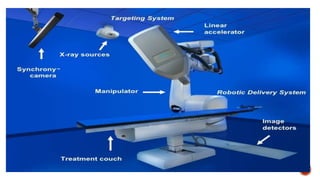
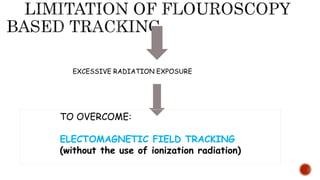
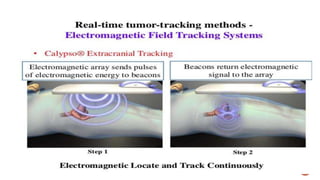
This document discusses image-guided radiation therapy (IGRT) and various IGRT techniques. It describes how IGRT aims to increase the accuracy and precision of radiotherapy delivery by applying image-based target relocalization. Common IGRT techniques mentioned include portal imaging, on-board cone-beam CT (CBCT), in-room CT, ultrasound and real-time tumor tracking. CBCT allows visualization of the tumor location using kilovoltage or megavoltage X-rays rotating around the patient. Real-time tumor tracking involves synchronizing radiation delivery with the respiratory cycle using implanted fiducial markers and fluoroscopy.