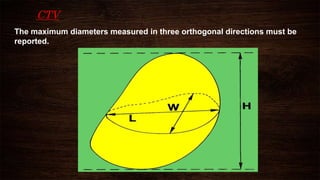
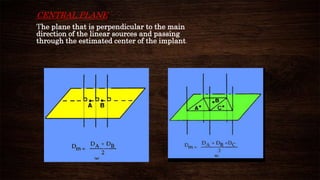
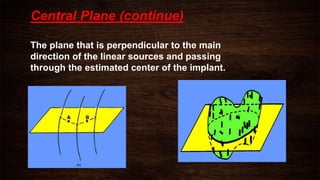
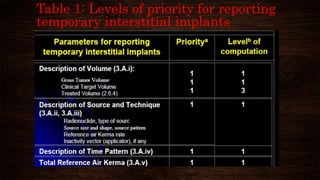
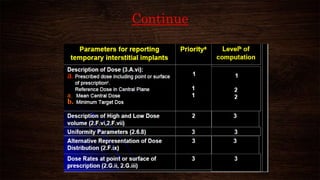
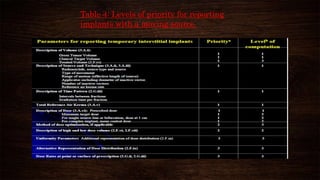
The document discusses advancements in brachytherapy, including the development of a common language for dose specification and reporting, as outlined in ICRU reports 38 and 58. It differentiates between temporary and permanent implants, describes dose distribution patterns, and emphasizes the importance of consistent reporting for treatment outcomes. Key parameters for dose specification and prescribing methods are also provided to ensure optimal treatment in interstitial brachytherapy.