The document discusses recent advancements in linear accelerator technology for cancer treatment, highlighting developments such as the use of heavy particles, image guidance, and online adaptive radiotherapy. It details the evolution of treatment planning, inclusion of artificial intelligence in decision-making, and the emergence of MR-LINAC systems for enhanced precision in radiotherapy. Additionally, it reviews safety concerns, cost implications, and training requirements associated with these technologies, underscoring their potential to improve patient outcomes and treatment efficacy.
![RECENT ADVANCES IN LINEAR
ACCELERATORS
DR. UPASNA SAXENA
HCG CANCER CENTRE, BORIVALI[MUMBAI]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/icroproadvance2021-recentadvancesinlinearaccelerators-211201040416/75/Rrecent-advances-in-linear-accelerators-MR-linac-1-2048.jpg)


![TREATMENT PLANNING
• Evolved from 3DCRT to IMRT/IGRT/VMAT/SBRT
• Multileaf collimators
• Leaf width – 1 cm to
1mm
• Single stack or double
stack
• Revolutionary discovery of
FFF [Flattening free filters]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/icroproadvance2021-recentadvancesinlinearaccelerators-211201040416/75/Rrecent-advances-in-linear-accelerators-MR-linac-4-2048.jpg)





![MOTION MANAGEMENT
• It is the management of motion due to bodily
functions like breathing, swallowing etc.
• Respiration is managed by [- Edward Brandner et al, Medical Physics
2017]
– Margins to account for the motion - ITV
– Motion mitigation – abdominal compression
– Gating of beams
– Breath hold using ABC [active breath coordinator]
– Real time tracking
– Surface guided radiotherapy [SGRT]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/icroproadvance2021-recentadvancesinlinearaccelerators-211201040416/75/Rrecent-advances-in-linear-accelerators-MR-linac-10-2048.jpg)






![• Deep learning convolutional neural network [CNN]
and hyperparameters in these models are used
• Uses the acquired 3D iCBCT as input to the neural
network and gives a similar output that the
clinician can assess and accept](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/icroproadvance2021-recentadvancesinlinearaccelerators-211201040416/75/Rrecent-advances-in-linear-accelerators-MR-linac-17-2048.jpg)
![• Once image is approved, deformable registration is used by the system to
make an image S-CBCT that conforms with the CBCT
• Then the IOE (Intelligent optimization engine) generates IMRT/VMAT plans
with
high degree of dose conformity
Due significance to OAR doses
intelligent trade off clinically
• The IOE works by having Q-functions [quality functions] laid down before
hand for the planning purpose
Target upper dose [TUD] goal
Target lower dose [TUD] goal
Organ upper dose [OUD] goal
• Artificial intelligence makes multiple plans to choose from, approval of
clinician to move ahead and a very fast process](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/icroproadvance2021-recentadvancesinlinearaccelerators-211201040416/75/Rrecent-advances-in-linear-accelerators-MR-linac-18-2048.jpg)


![• Assessed ART in 39 pelvic patients on Ethos [varian] in the preclinical phase
• 75% patients needed either minimal editing or no editing
• Adaptive plans showed similar PTV coverage, 88% plans were actually better – IMRT being better than VMAT
• Other plan evaluation parameters were similar, MUs were occasionally higher. Infact CI, HI were superior for
adaptive plans
• They also met the QA satisfactorily
• Single dose plans needed one iteration while SIB plans needed 2-3 review plans
• Time from CBCT approval to starting treatment – 17.6 min
• Reduced V45 to bowel bag 24-30%
• Adaptive plan generation was found superior to plan library approach – possibly due to reduction of margins, the
high dose PTV volume was reduced even upto 42%](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/icroproadvance2021-recentadvancesinlinearaccelerators-211201040416/75/Rrecent-advances-in-linear-accelerators-MR-linac-21-2048.jpg)
![As compared to MRLinac
PROS
• Training requirements are lesser on CT based oART- workflow training is essential
• On couch time is similar to MRogRT
• logistically and financially the CT based systems for oART are superior in feasibility
CONS
• Delineation is superior for soft tissue in MR based systems
• Automated influencer contour generation might not be possible in certain clinical
situations [post prostatectomy, urinary catheter in situ etc]
• The intrafraction imaging is not yet incorporated in the CT based systems [like 3D cine
MRI in the MR based systems]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/icroproadvance2021-recentadvancesinlinearaccelerators-211201040416/75/Rrecent-advances-in-linear-accelerators-MR-linac-22-2048.jpg)




![MRSim & MRLinac
• MR-Sim is a diagnostic MRI like the CT sim that is a hybrid of MR and CT
• helps in contouring targets and OARs for radiotherapy planning.1 using electron density allocatoin
• MR Sim may or may not be used for planning purpose with a MR Linac
• MR CT coregistration for contouring can cause errors of 1-2mm17
• Combined use of MR Sim and MR Linac holds promise for better delineation and accturate delivery
• MR Sim has features like [J Applied Clin Med Physics. 2015;16(2):218-240., Phys Med Biol. 2015;60(22):R323-361.]
• coil bridges to prevent deformation of the patient’s body contour
• MRI compatible mobilization devices to minimize patient movement
• rigid flat table top
• laser positioning system
• wider bore
• patient imaged in treatment (as opposed to imaging) position
• dedicated scan protocols.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/icroproadvance2021-recentadvancesinlinearaccelerators-211201040416/75/Rrecent-advances-in-linear-accelerators-MR-linac-27-2048.jpg)
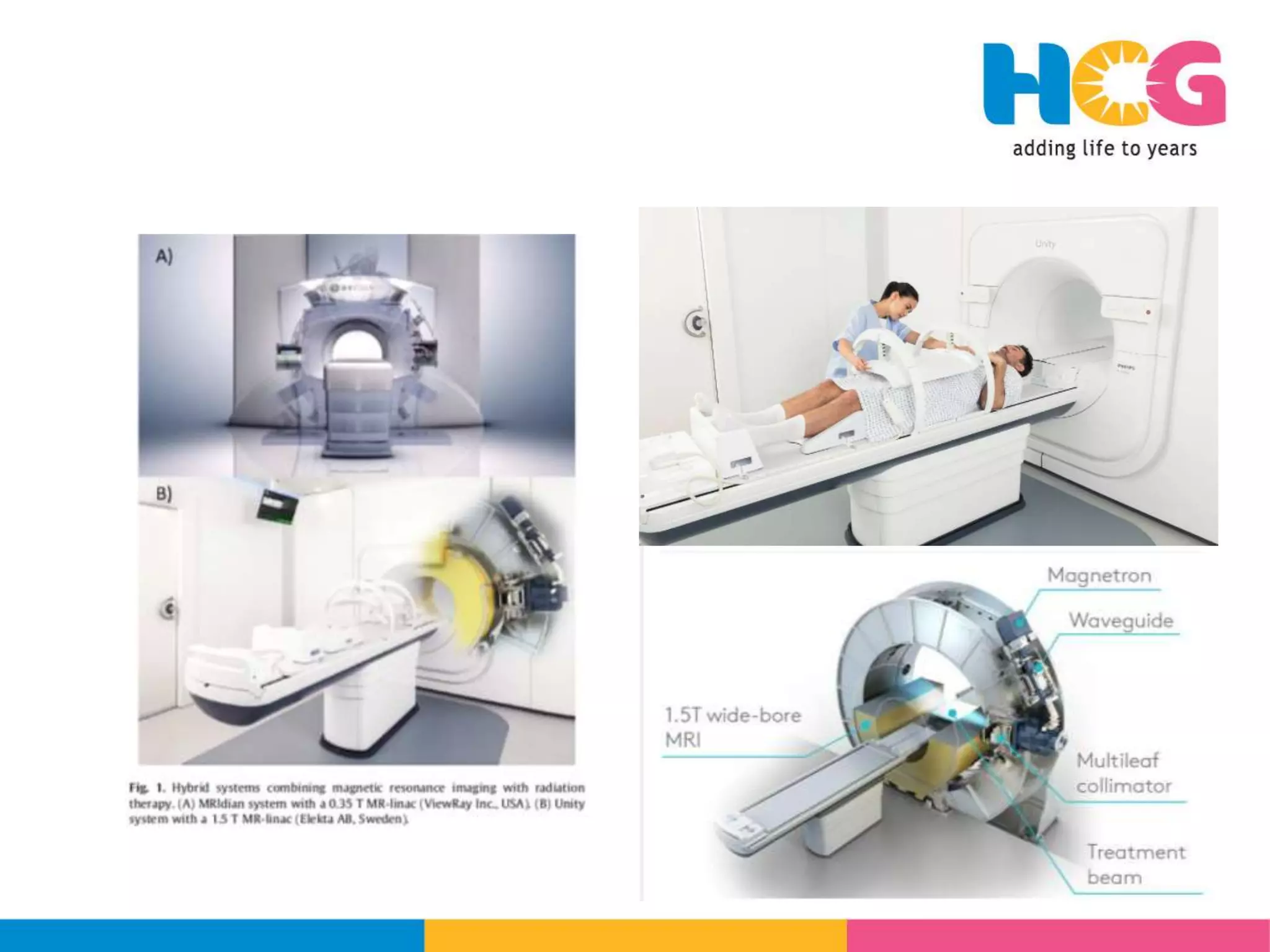
![MRLinac
• MR linac is a hybrid device with a linear accelerator to deliver radiotherapy and a MRI
scanner [somewhat like the CBCT acquisition in other linacs]
• It allow for online real time MR imaging for customization and high-precision adaptive
radiotherapy.Termed as MR guided radiotherapy [MRgRT]
• MR-linac systems offer real-time tumour tracking and beam gating.
• The first MR based treatment was done in 2014 in Siteman Cancer Centre, Cleaveland,
on the Co60 based MRIdian
• The first MRLinac based treatment was done in 2017 at the Henry Ford Cancer Institute,
Detroit on MRIdian MR Linac of Viewray
• Two main models are available for clinical practice, the Unity by Elekta and the MRIdian
MR Linac of Viewray
• (CADTH rapid response report: summary with critical
appraisal). Ottawa (ON): CADTH; 2019
• Radiol Oncol. 2019;132.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/icroproadvance2021-recentadvancesinlinearaccelerators-211201040416/75/Rrecent-advances-in-linear-accelerators-MR-linac-28-2048.jpg)

![MRIdian
• 0.35 Tesla MRI with split magnets and
field aligned along craniocaudal axis
of patient
• It has two models - Co60 [MRIdian]
and 6 MV linac [MRIdian Linac]
• The beam does not pass between
magnetic field
• By ViewRay](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/icroproadvance2021-recentadvancesinlinearaccelerators-211201040416/75/Rrecent-advances-in-linear-accelerators-MR-linac-30-2048.jpg)

![• Beam is collimated by a ‘double focused stacked multileaf
collimator’- so the length is 11 cm [5.5 cm for each MLC]
• The beam passes only through a 5 mm thick fibre glass
between the split magents, NOT through the magnetic field
due to split magnets
• Use reference plan dosimetry to assess the need to replan](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/icroproadvance2021-recentadvancesinlinearaccelerators-211201040416/75/Rrecent-advances-in-linear-accelerators-MR-linac-33-2048.jpg)
![BENEFITS FROM MR LINAC
• Superior in imaging soft tissue – target and OAR
• Precise contouring enables margin reduction and if needed dose
escalation- which could promise better control rates [Br J
Radiol. 2019;92(1094):20180505.]
• Multiple imaging is not associated with radiation dose escalation
• Regular imaging helps in response assessment, need of plan adaptation or
change of treatment objective [J Med Imag Radiation Sci. 2019;50(2):195-198].
• Differential response can be used to assess genomics related biological aspects
like hypoxia and resistance](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/icroproadvance2021-recentadvancesinlinearaccelerators-211201040416/75/Rrecent-advances-in-linear-accelerators-MR-linac-34-2048.jpg)





![TREATMENT IMPLEMENTATION
IMAGE ACCQUISITION AND APPROVAL
CONTOURING/PLAN ASSESSMENT AND DELIVERY
• A gold standard contouring with quality checks– using either rigid or deformable registration
– Partial recontouring of OARs [2-3 cm around target volume]
• Plan generation and approval – about 15 minutes
• Repeat MRI to check for changes
• Initiate treatment
• Cine MRI checks for any geographical miss, and manually stopping if present
– MRIdian - 8 frames of saggital images per second
– unity images in all three planes
• The complete process from beginning to end could extend to 15-30 mins or if complete replanning is needed, could take upto 60 minutes
• MRIdian permits gating and breath hold [duty cycle efficiency 67%-87%]
• Unity compiles daily data each day for composite treatment at end and offline analysis
• Phantom based QA in not possible since moving the patient invalidates adaptive workflow- hence Monte Carlo based tool in](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/icroproadvance2021-recentadvancesinlinearaccelerators-211201040416/75/Rrecent-advances-in-linear-accelerators-MR-linac-40-2048.jpg)
![PATIENT SELECTION
• Clinical parameters
– Physically unsuitable – implants/pacemakers
– Clinically unsuitable – severe psychological issues, severe claustrophobia, inability to
understand instructions
– Borderline unsuitable – mild claustrophobia- attempt anesthesia/counselling/
medicines/music/aromatherapy
– Suitable
• Oncology criteria – prostate, head and neck, pancreas/upper abdomen, pelvic
treatments, reirradiation, SRS/SBRT. Others cervix, breast, esophagus, brain,
rectum [international MR-linac Consortium ]
• Soft criteria
– Elderly / Frail patient
– Obese [BMI>40] – due to bore size, imaging artifacts
– Chachexic[WEIGHT<40Kg] – due to body heating
Unsuitable patients to be shifted without delay to other CT based linear accelerator](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/icroproadvance2021-recentadvancesinlinearaccelerators-211201040416/75/Rrecent-advances-in-linear-accelerators-MR-linac-41-2048.jpg)



![• MRIdian linac detailing
• The system [MR+CT] has a localization accuracy of 1+/-0.1 mm [Wen et al]
• Due to small bore of 70 cm,
– Lateral shift at high couch positon is +/-7cm.
– Lesser for lower couch position
• Beam is 6MV – FFF delivered at SAD 90 cm
• Two stacks of MLC [5.5 cm each so total 11 mm total height].
• Total 138 leaves
• Leaf width at isocentre 8.3 mm
• Field size – Bohoudi et al
– Smallest – 0.2x0.415 cm 2
– Largest – 27.4x24.2 cm2](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/icroproadvance2021-recentadvancesinlinearaccelerators-211201040416/75/Rrecent-advances-in-linear-accelerators-MR-linac-45-2048.jpg)
![• Six shielding compartments[known as buckets] are mounted on the gantry to
house the parts of linac – gun, magnetron, MLC as shown in image]
• The shielding has
– Ferromagnetic cylinders to block magnetic fields from reaching linac
– Radiofrequency shields [with copper reflectors and carbon absorption to prevent RF noise
from disturbing magnetic field]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/icroproadvance2021-recentadvancesinlinearaccelerators-211201040416/75/Rrecent-advances-in-linear-accelerators-MR-linac-46-2048.jpg)
![• Registration - rigid or deformable
• Contouring – with or without CT/MRI registration
• Plan options – 3DCRT & IMRT
• If MR is used to contour and plan, bulk electron density allocation is done
– using six pre-decided densities
– custom density allocation.
• Average time patient in to plan approval on cobalt MRIdian
– 12+/-4.5 mins by Bohoudi et al
– 24 mins by Lamb et al
• Cine MRI deformable registration with reference image
• allows for gating of the beam [in both free breathing and breath hold]
• Post treatment system generates a report of MU and MLC positions, recalculations and composite
of treatment delivered can also be generated and viewed.
• Cai et al and Lamb et al have also developed an in house automated system for plan evaluation and
quality checks
• Adaptive gated MRLinac based SBRT required slots upto 90-120 minutes [from
patient in to out]- Lamb et al 2017- MEDIAN TIME TO BEAM COMMENCEMENT WAS 55
MINS [34-99 MINS]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/icroproadvance2021-recentadvancesinlinearaccelerators-211201040416/75/Rrecent-advances-in-linear-accelerators-MR-linac-47-2048.jpg)



![• Zhang et al and Peronie et al described feasibility of MrgoART, however
the validation had not been done previously as has veen addressed here
by Mittauer et al
• Abdominal deformable phantoms [with material compatibility for CT and
MRI] and dose delivered with replanning was assessed using dosimeters
• The dose vector fields [DVF] were with in 5 mm which is in the acceptable
limits as per TG132
• Accumulated maximum dose variation was 0.21 Gy for arithmetic
calculation and 0.31 Gy for deformed calculation – for a plan of 25Gy/5#](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/icroproadvance2021-recentadvancesinlinearaccelerators-211201040416/75/Rrecent-advances-in-linear-accelerators-MR-linac-51-2048.jpg)



