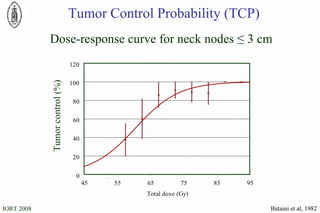
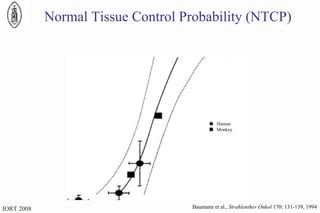
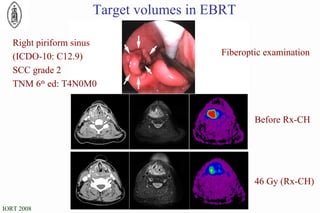
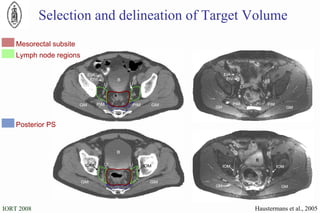
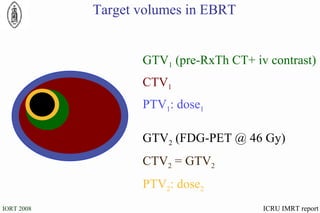
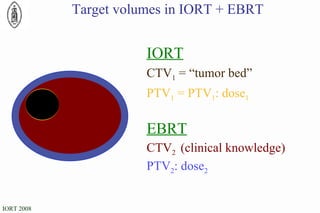
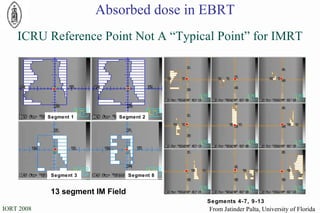
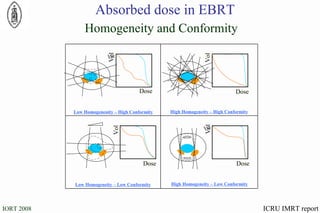
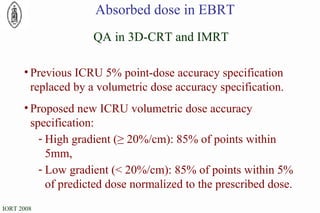
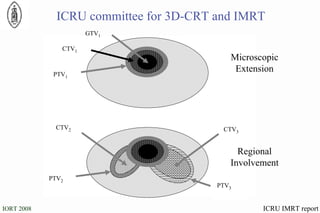
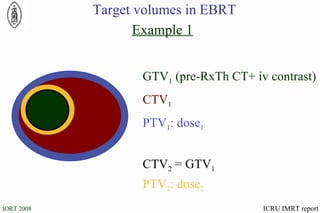
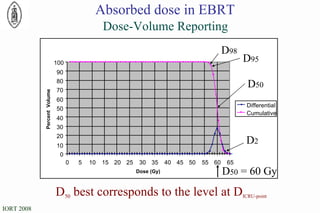
The document discusses standards for precision in radiation oncology, including definitions of target volumes and dose reporting levels according to International Commission on Radiation Units and Measurements (ICRU) reports. It notes unresolved issues for 3D conformal radiation therapy and intensity-modulated radiation therapy, such as margins between gross tumor and clinical target volumes. The document recommends that a new ICRU report is needed to address these modern radiotherapy techniques and provide common guidelines.