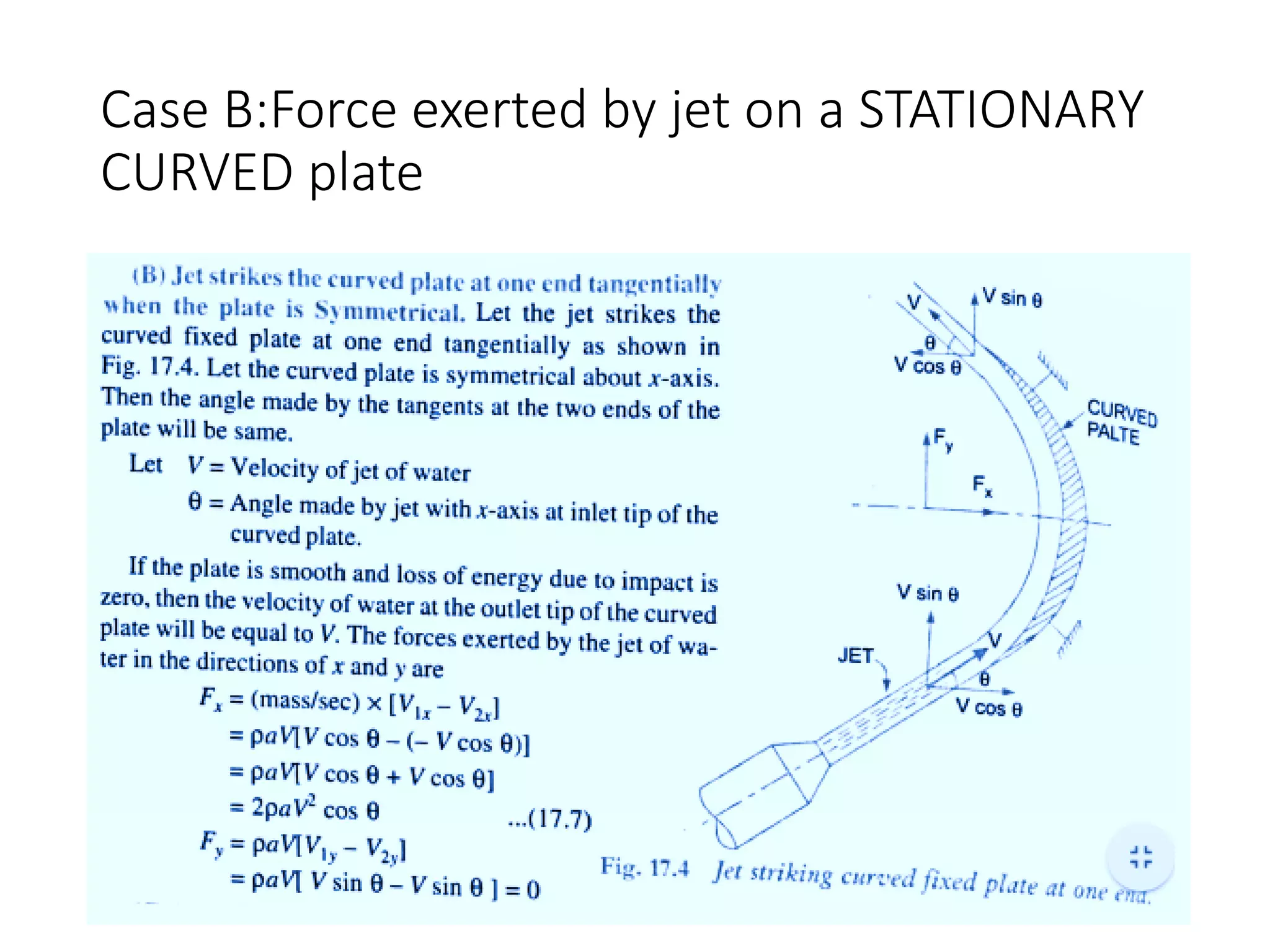
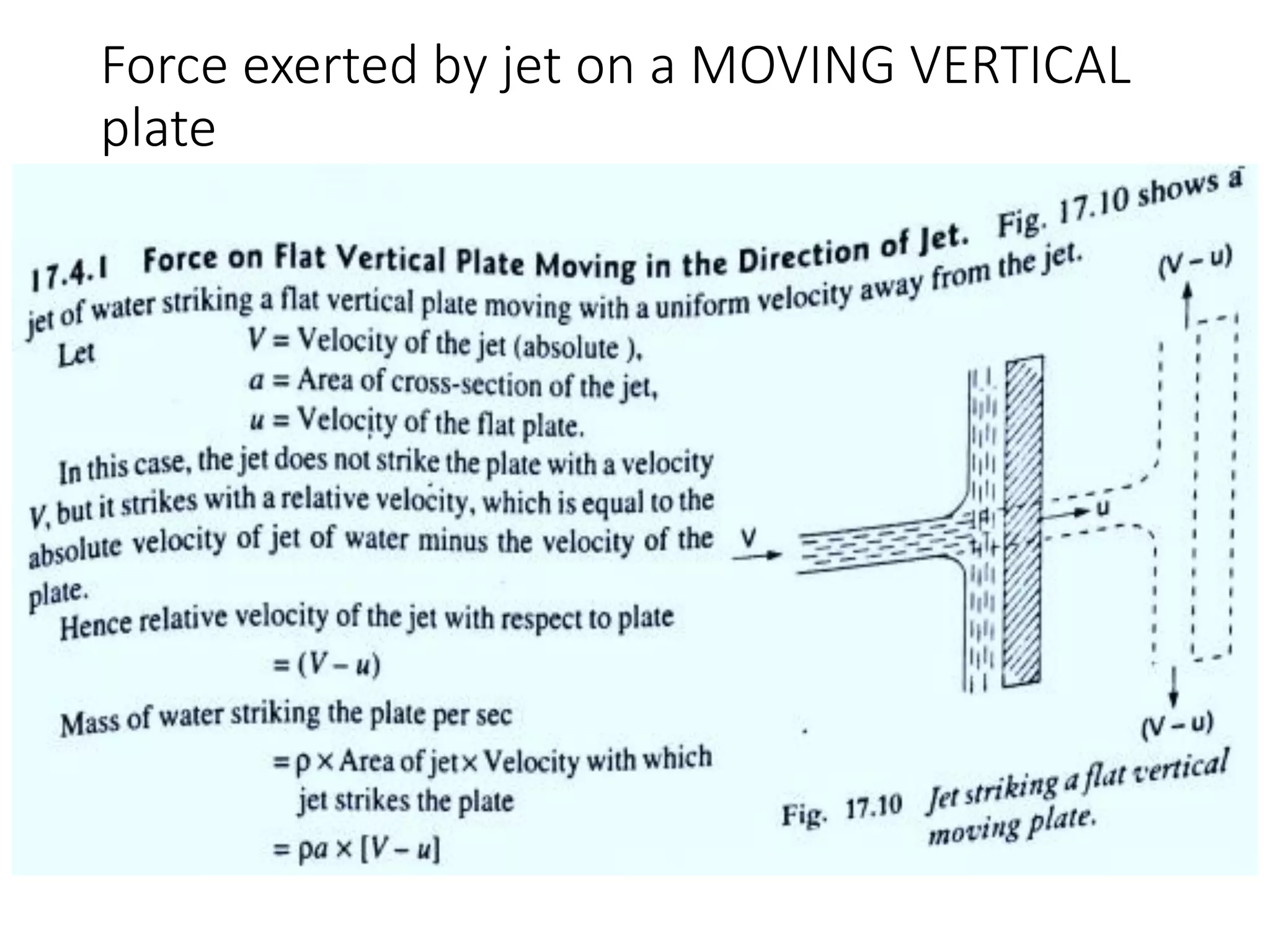
The document discusses momentum analysis of fluid flow. It contains the following key points:
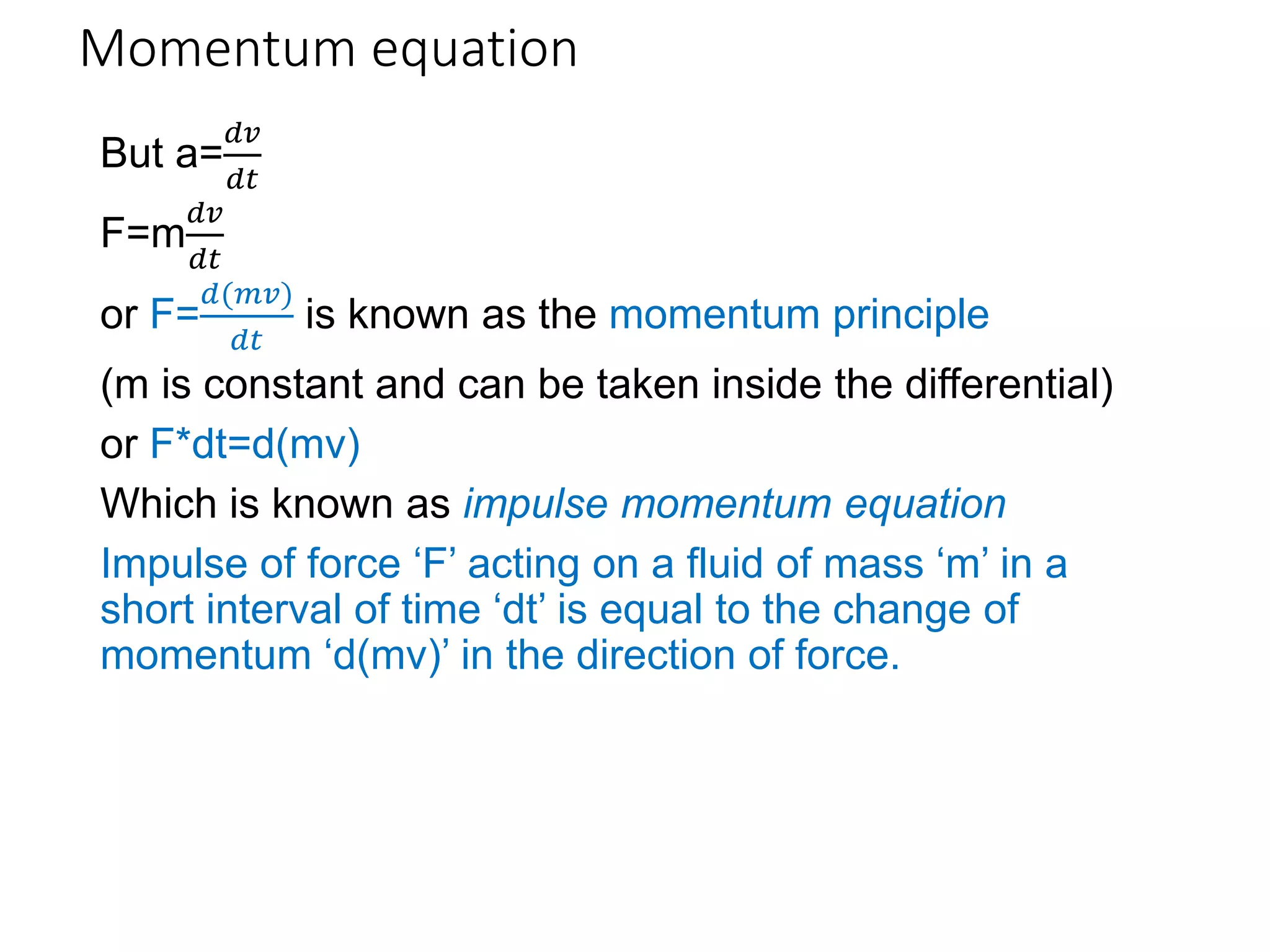
1) The momentum equation is based on the law of conservation of momentum, which states that the net force acting on a fluid mass is equal to the rate of change of momentum of the fluid.
2) The momentum principle can be written as an impulse-momentum equation: the impulse of a force acting on a fluid mass over a short time interval is equal to the change in momentum of the fluid.
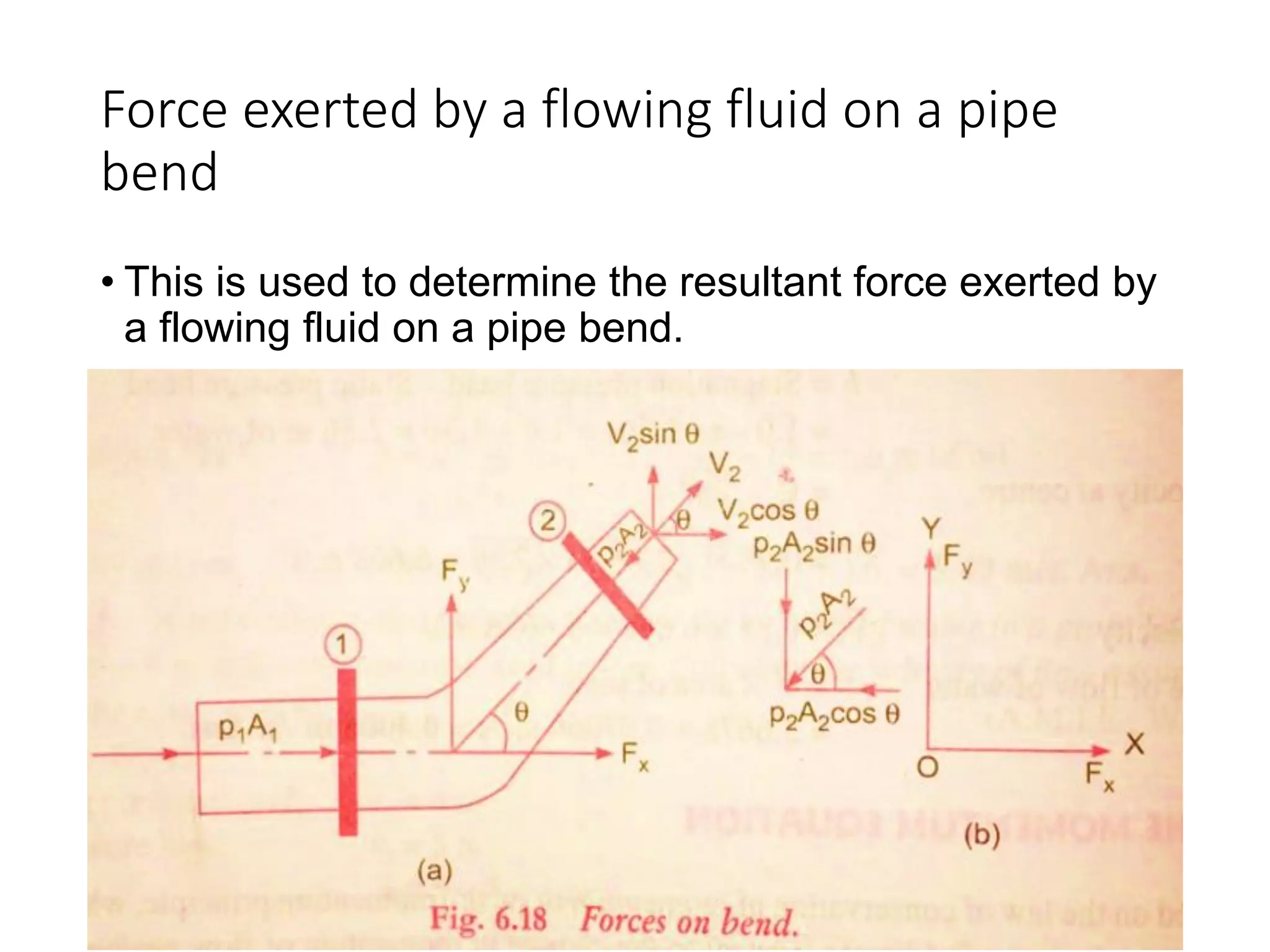
3) The momentum equation is used to determine the resultant force exerted by a flowing fluid on a pipe bend based on the fluid's velocity, pressure, area, and external forces at two sections of the pipe.