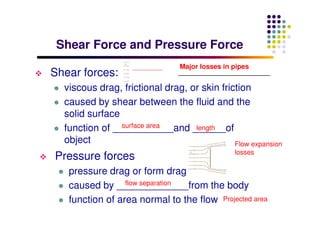
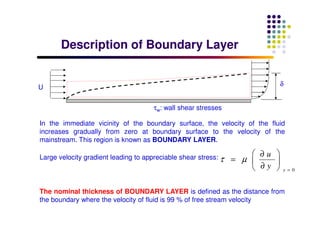
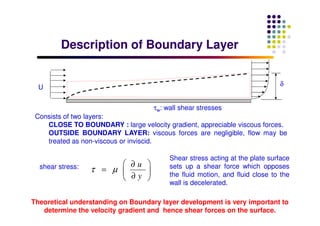
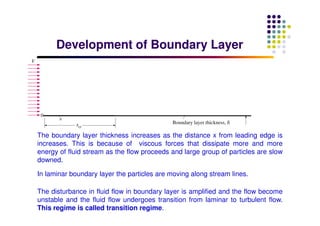
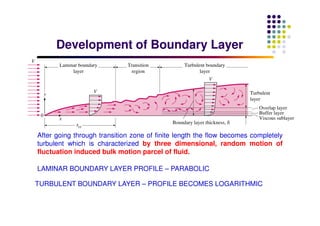
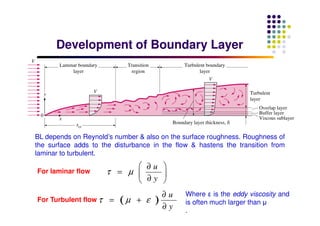
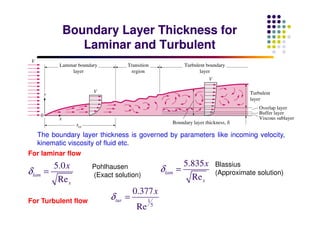
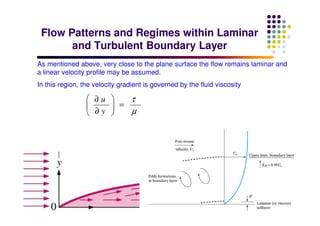
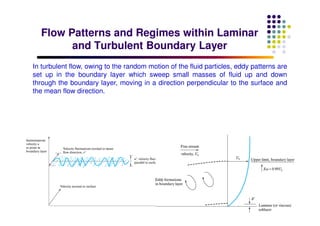
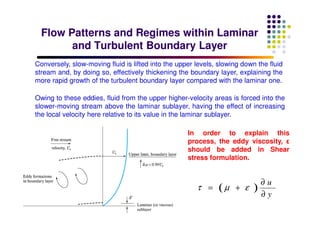
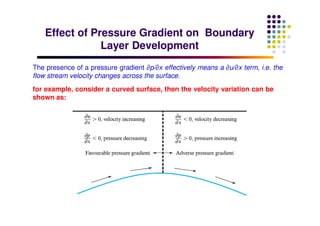
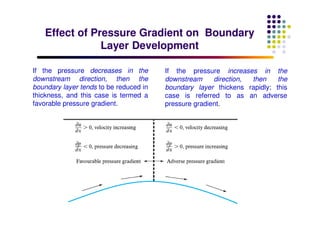
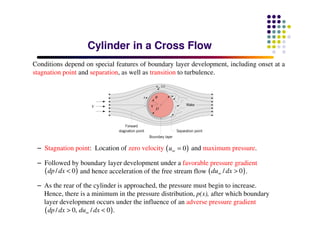
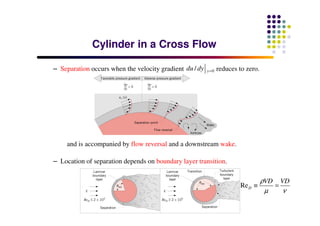
This document discusses boundary layer development. It begins by defining boundary layers and describing the velocity profile near a surface. As distance from the leading edge increases, the boundary layer thickness grows due to viscous forces slowing fluid particles. The boundary layer then transitions from laminar to turbulent. Turbulent boundary layers have a logarithmic velocity profile and thicker boundary layer compared to laminar. Pressure gradients and surface roughness also impact boundary layer development and transition.