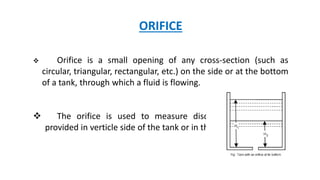
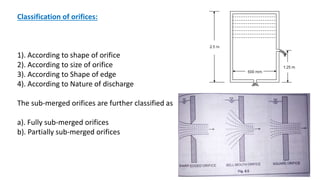
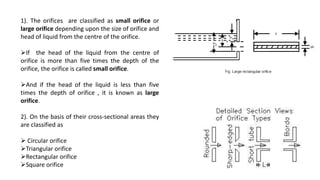
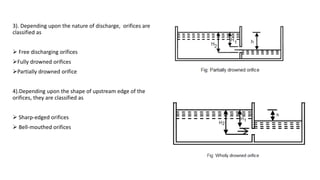
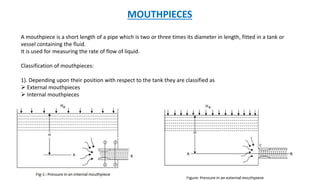
This document discusses types of orifices used for fluid flow measurement. Orifices can be classified based on their shape (circular, triangular, etc.), size (small or large), edge shape (sharp or bell-mouthed), and whether the flow is submerged or free-flowing. Orifice meters consist of a flat plate with a circular hole and are used to measure flow rates in pipes. They offer little pressure drop but require straight pipe runs and full pipeline filling to maintain accuracy. Mouthpieces are also used for flow measurement and can be internal or external, and classified based on their shape (cylindrical, convergent, convergent-divergent) and whether the flow exits fully or