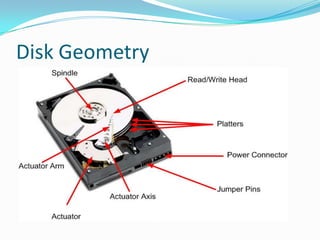
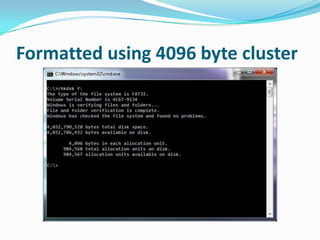
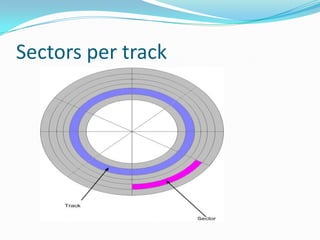
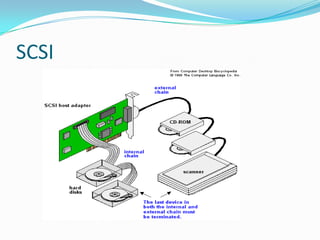
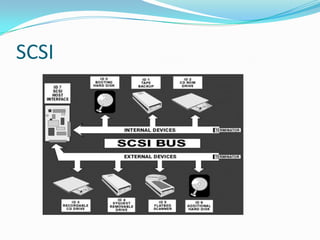
This document provides an overview of different storage devices and their key components. It discusses floppy disk drives, hard disk drives, solid state drives, optical drives like CDs, DVDs, and Blu-Ray. For hard disk drives, it describes the platters, read/write heads, actuator assembly, spindle motor, connectors, jumpers, logic board, integrated cache, and disk geometry including heads, cylinders, sectors per track, and write precompensation. It also discusses different hard disk interface types like PATA, SATA, SCSI, and identifies their data buses.