06. System unit of computer
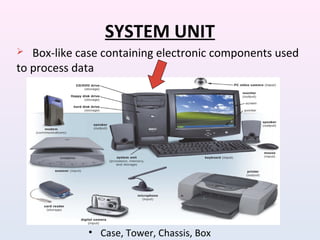
- 1. SYSTEM UNIT • Case, Tower, Chassis, Box Box-like case containing electronic components used to process data
- 3. What are all those parts inside my computer and what do they do???
- 4. The magical components inside the box.. CPU Memory card Sound Card Video Card Storage Units Power Supply
- 5. SYSTEM COMPONENTS Mother Board • This is where most of the electronics is located. • It is the main circuit board inside the CPU case. It holds the microprocessor, memory and other crucial circuits and components that control the operation of the Personal Computer. • Every device inside or connected to a Personal Computer finds it's way to this board. Motherboard
- 6. Major Components of a Motherboard SIMM RAM Bank Single Inline Memory Module stores data to be used by the microprocessor. ROM BIOS Basic Input/Output System stores permanent instructions that start the computer. Power Connector Supplies power to the motherboard. 16 Bit ISA Slots Allows expansion of computer through modem, sound and video cards. 32 Bit PCI Slots Allows expansion cards that can transfer data faster than ISA slots. Battery Provides power for the system clock. Cache RAM Stores and retrieves information for the microprocessor at a faster rate than SIMM RAM so instructions can be executed faster. Microprocessor / CPU Single integrated circuit that executes the majority of the instructions to process data.
- 7. Your computer couldn’t work without the motherboard. It ties everything together! It allows every part of your computer to receive power and communicate with each other. Everything that runs the computer or enhances it’s performance is either part of the motherboard or plugs into one of it’s expansion slots or ports.
- 8. 8 The Components of a Computer • Two main components on the motherboard – Central Processing Unit (CPU) •Also called a processor •Carries out instructions that tell computer what to do – Memory •Temporary holding place for data and instructions
- 9. SYSTEM COMPONENT CPU/PROCESSOR • The CPU refers to the microprocessor chip. • It’s speed is measured in Megahertz (MHZ) (Millions of cycles per second) or Gigahertz (GHZ) Billions of cycles per second. • A cycle is the time required for the CPU to execute an instruction step • Once information has been sent to a computer by one of the input devices it’s processed. The computer uses it’s brain to process the information. The computer’s brain is called the CPU, or Central Processing Unit. CPU (Central Processing Unit)
- 10. The CPU is also called the microprocessor. The word “micro” means small. Since the CPU is located on a small computer chip about 1 inch square, that makes sense!
- 11. CPU/PROCESSOR CPU controls all the parts of Computer. The CPU consists of THREE Components: 1. ALU (Arithmetic and Logic Unit): ALU is a digital electronic circuit that performs arithmetic and bitwise logical operations. It is a fundamental building block of many types of computing circuits. It has 2 sections – Arithmetic & Logic Section.
- 12. CPU/PROCESSOR 2. Control Unit: It directs operation of the processor. It tells the computer's memory, arithmetic/logic unit and input and output devices how to respond to a program's instructions 3. Memory: It holds the received data from input devices permanently / temporarily.
- 13. Types of Memory: Ram – Random Access Memory • Ram is a temporary memory used by the computer to run Active Programs and store current Data to make it readily available. • When a computer processes information, it uses software programs. Each program requires a certain amount of electronic memory, or RAM (Random Access Memory) to run correctly. • The amount of Ram available will determine how fast a program will run and how many windows can be open at one time. • Ram memory is considered Volatile / temporary because it disappears when the power is turned off. More RAM, faster the work!
- 14. Ram – Random Access Memory • Dynamic RAM (DRAM) DRAM is a classic form of RAM and has since been replaced by the faster and less expensive SDRAM. DRAM stores data electrically in a storage cell and refreshes the storage cell every few milliseconds. • Extended Data-Out RAM (EDO RAM) EDO RAM is faster than DRAM. EDO RAM has also been replaced by SDRAM. EDO RAM is an improvement on DRAM because it has advanced timing features. EDO extends the amount of time data is stored and has a reduced refresh rate. This alleviates the CPU and RAM from timing constraints and improves performance. • Synchronous DRAM (SDRAM) SDRAM replaced DRAM, FPM, and EDO. SDRAM is an improvement because it synchronizes data transfer between the CPU and memory. SDRAM allows the CPU to process data while another process is being queued.
- 15. Read-Only Memory • A second kind of computer memory is ROM, which stands for Read-Only Memory. • This memory is permanent. The information there was put there when the computer was made, this cannot be changed. • The computer needs the information in it’s ROM memory in order to function. • It keeps its contents even in absence of power. • ROM chips contain programs that start the computer and perform system diagnostics.
- 16. Read-Only Memory • PROM - (programmable read-only memory) is a memory chip on which data can be written only once. Once a program has been written onto a PROM, it remains there forever. Unlike main memory, PROMs retain their contents when the computer is turned off. • EPROM - (erasable programmable read-only memory) is a special type of PROM that can be erased by exposing it to ultraviolet light. Once it is erased, it can be reprogrammed. An EEPROM is similar to a PROM, but requires only electricity to be erased. • EEPROM - (electrically erasable programmable read-only memory). Pronounced e-e-prom, an EEPROM is a special type of PROM that can be erased by exposing it to an electrical charge. Like other types of PROM, EEPROM retains its contents even when the power is turned off. Also like other types of ROM, EEPROM is not as fast as RAM. A special type of EEPROM, referred to as flash memory or flash EEPROM, can be rewritten while it is in the computer rather than requiring a special device called a PROM reader. This is what most of you will have.
- 17. RAM & ROM RAM cards will remember what you tell them and can even change to remember new information. But, when the computer is turned off, it forgets everything you did! That’s why you always save your work! ROM is good at remembering, but cannot change it’s mind. It holds the information that was built into it! Remember RAM (Random Access Memory) and ROM (Read-Only Memory)?
- 18. Cache Memory Cache memory, also called CPU memory, is random access memory (RAM) that a computer microprocessor can access more quickly than it can access regular RAM. This memory is typically integrated directly with the CPU chip or placed on a separate chip that has a separate bus interconnect with the CPU.
- 19. SYSTEM COMPONENTS Hard Drive • The Hard Drive is the magnetic storage device - the computers main, long term storage. • All the computer programs and files you create and save are located here • It is referred to as non-volatile storage, because it does not disappear when the power is turned off. • The size of the Hard Drive is measured in Gigabytes. (Billions of Bytes). HDD (Hard Disk Drive)
- 20. Inside the Hard Disk Drive case you’ll find circular disks that are made of steel. On the disks, there are many tracks, or cylinders. An electronic reading device called the head passes back and forth over the cylinders, reading information from the disk or writing to it. Hard Disk Drives use Magnetic Recording Techniques. The magnetic medium can be easily erased and rewritten and will “remember” the magnetic flux patterns stored on it for many years!
- 21. Hard Disk Drives can spin at the rate of 7200 or more rpm’s (Revolutions Per Minute). That means in one minute, the hard drive spins around more than 7200 times!
- 22. RAM VERSUS HARD DRIVE • If we use the analogy of a desk: Then the work we are doing on the desk top would be using the RAM and the work we store in the file drawers would be on the HARD DRIVE.
- 23. BIOS CHIP A BIOS chip (Basic Input Output System) is a very important computer component. In simple terms, the BIOS chip wakes up the computer when you turn it on and reminds it what parts it has and what they do!
- 24. Network Interface Card A NIC card (Network Interface Card) allows your computer to talk to other computers! A cable called Cat5 is plugged into the NIC card and your computer can then be attached to a network and be on the internet! Used to connect to high speed internet access e.g. Cable or DSL lines ((Digital Subscriber Line).
- 26. CD / DVD Drive Power Button Restart Button USB Port Audio Out – Speaker / Headphone Audio In - Mic
- 28. The Components of a Computer • Storage Storage mediaStorage media Physical material on which data, instructions, and information are stored Eg: CD Storage mediaStorage media Physical material on which data, instructions, and information are stored Eg: CD Storage deviceStorage device Reads, Records and Retrieves items to and from a storage medium Eg: CD R/RW Storage deviceStorage device Reads, Records and Retrieves items to and from a storage medium Eg: CD R/RW Holds data, instructions, and information for future use
- 29. Disk Capacity It’s important to know how large your files are because eventually you won’t have enough space on your disk to hold more files. Knowing the total capacity of your disk, how much space is left on your disk, and how large the file is, you can make accurate decisions as to whether to save the file to the current disk, or save the file to a different diskette with more disk capacity.
- 30. • Floppy disk Thin, circular, flexible disk enclosed in rigid plastic shell ~1.44 MB space The CPU has places to insert disks. A floppy disk drive reads information from floppy disk inside a hard plastic case.
- 31. CD-ROM Disc Drive CD-ROM stands for Compact Disk-Read Only Memory. They are flat, shiny metal discs that store information. CD-RW stands for Compact Disk- ReWrite. This type of disk allows you to write information to it, as well as read from it. Most can hold up to ~700 megabytes of information. DVD Drive / Burner The computers also come with the option of a DVD drive. A DVD (Digital Video Disc) looks just like a CD, but holds much more information! They can store 4.7 gigabytes of data! DVD – ROM & DVD - RW
- 32. Flash Drive / Pen Drive / USB Drive A Flash Drive is a relatively new storage device. It’s like a mini, portable hard drive! You plug it into the USB (Universal Serial Bus) port and you can save to it!
- 33. 33 •Memory Cards - Miniature storage media Digital cameras Digital cameras Handheld computers / Smartphones Handheld computers / Smartphones Portable, thin memory cards used in: Portable, thin memory cards used in:
- 34. • Portable Hard Disks
- 35. SYSTEM COMPONENTS • Power Supply • 250 – 500 Watts • DO NOT OPEN • (This is the power source that makes everything go). Power Supply You can see the power supply from the back of your computer because of the power cord and the cooling fan. Computers put out a LOT of heat and need the fan to keep them from overheating.
- 36. Power Supply If there is any one component that is absolutely vital to the operation of a computer, it is the power supply! Without it, a computer is just a box full of plastic and metal. The power supply converts the alternating current (AC) line from your home or school to the direct current (DC) needed by the computer.
- 37. POWER PROTECTION • Uninterruptible Power Supply • (UPS) 280 VA – 400 VA • Essentially a battery back-up in case of a power failure
- 38. Thank You