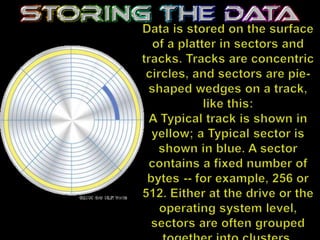
The hard drive is the computer's main storage device that permanently stores all data. It uses rapidly rotating disks coated with magnetic material to store and retrieve digital information electromagnetically. A hard drive consists of stacked disks with data recorded in concentric circles, read and written by heads on each side of the disks as they spin. Hard drive performance is measured by data rate and seek time. Common interfaces include ATA, SATA, and SCSI.















![1.) Original term for Hard Disk Drive.
2.) The Hard Drive was First
Introduced on _____ .
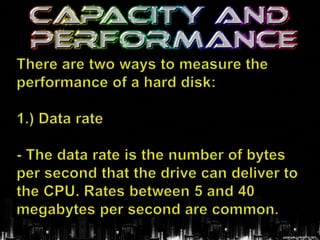
Nos. (3-4) Two ways to Measure the
Performance of a Hard Disk .
5.) Standard Term for [SCSI]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/harddiskdriverevised-140730081135-phpapp01/85/Hard-Disk-Drive-18-320.jpg)
![6.) Platters is Coated with __________
which is used to Store and Retrieve
Digital Information.
7.) A Hard Drive Disk Unit has a Rotation
Speed Varying from ________ RPM.
8.) Standard Term for [LBA].
9.) The Number of Bytes per Second that
the Drive can Deliver to the CPU.
10.) Amount of Time Between when the
CPU Requests a File.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/harddiskdriverevised-140730081135-phpapp01/85/Hard-Disk-Drive-19-320.jpg)
