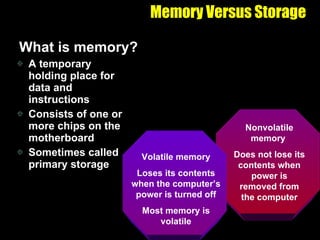
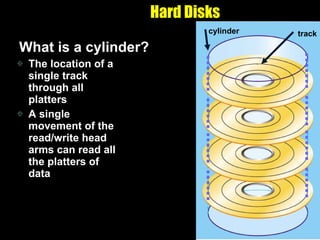
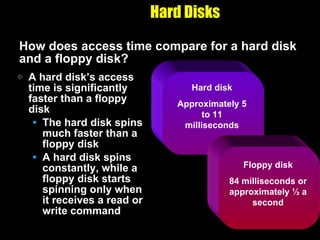
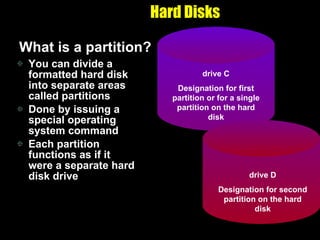
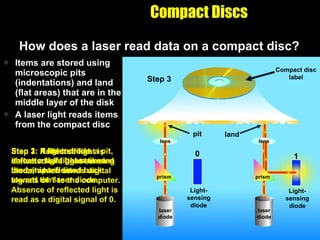
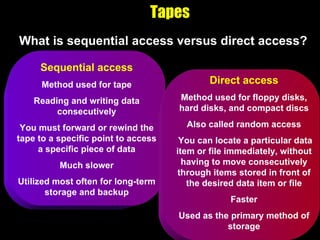
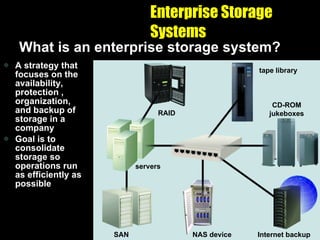
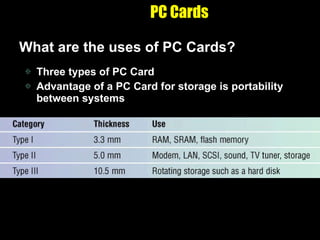
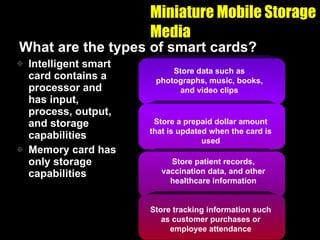
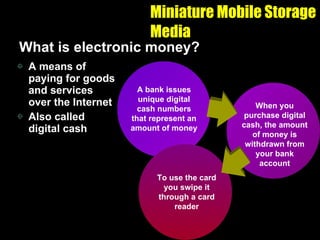
The document discusses various types of storage media including memory, floppy disks, hard disks, CDs, DVDs, tapes, smart cards, microfilm, and microfiche. It compares their storage capacities, how data is stored and accessed, common uses, and life expectancies.