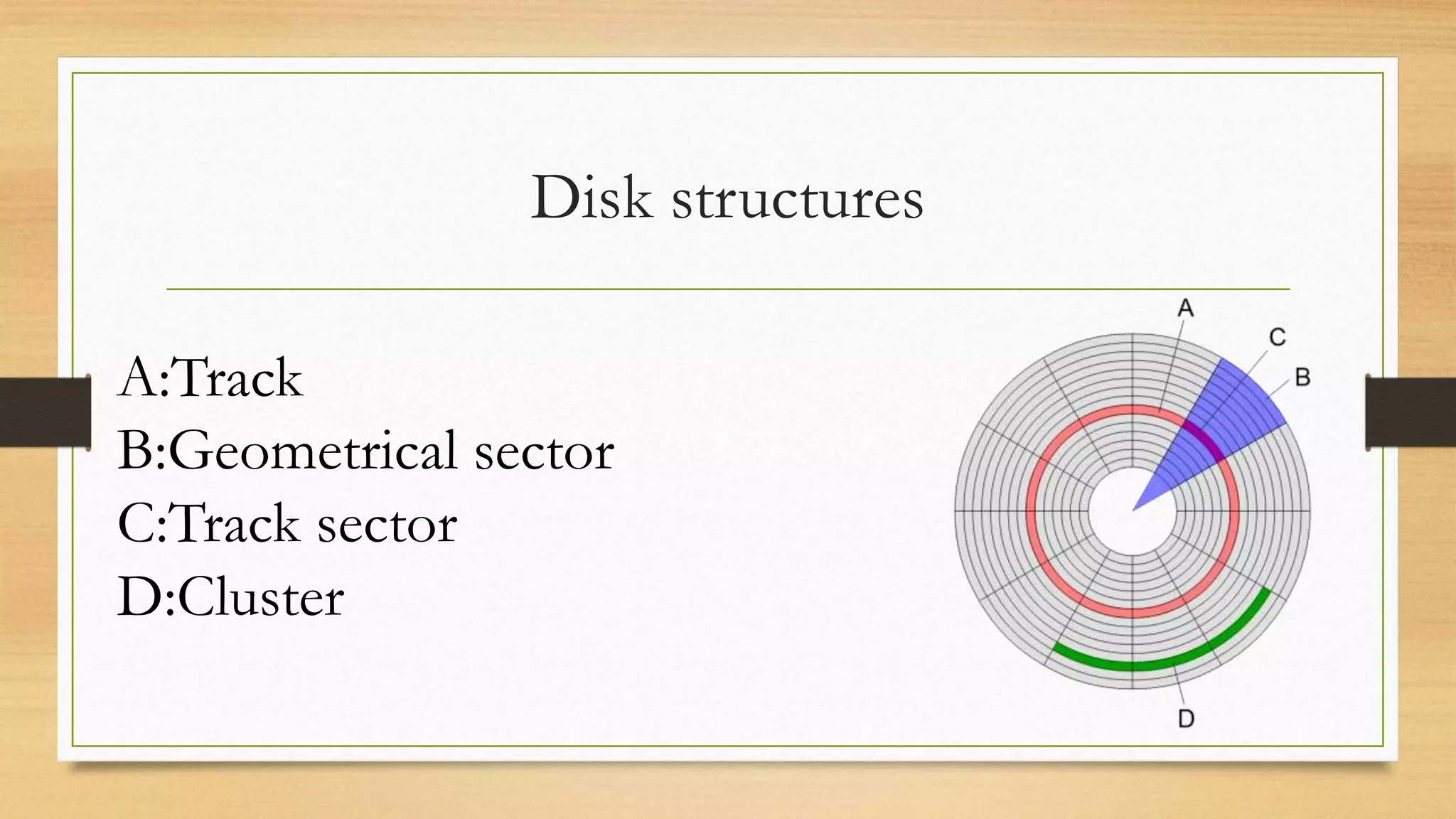
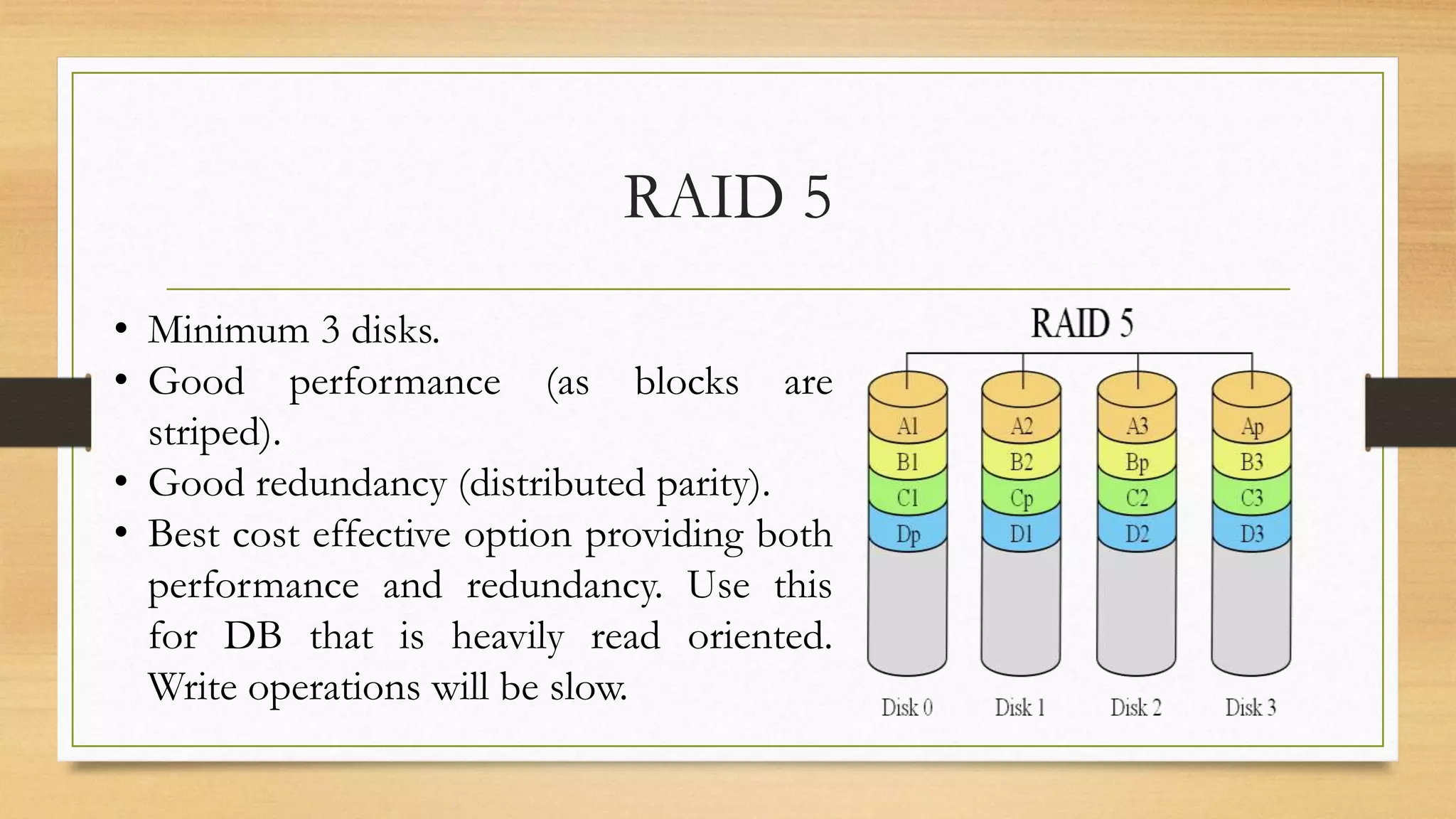
Storage holds data and information for future use. Common storage media include hard disks, SSDs, flash drives, and optical discs. Storage capacity is measured in bytes, kilobytes, megabytes, and larger units. A storage device contains hardware that writes data to storage media and reads data from storage media. Common interfaces that connect hard disks include PATA, SATA, SCSI, and SAS. Hard disks contain spinning platters, read/write heads, and motors, while SSDs use flash memory. RAID configurations like 0, 1, 5, and 1+0 provide different balances of performance and redundancy.