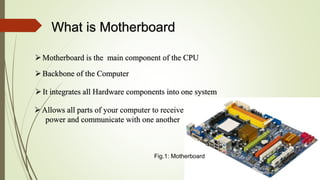
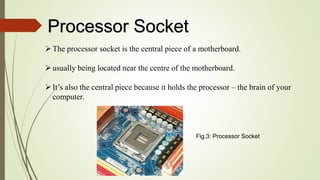
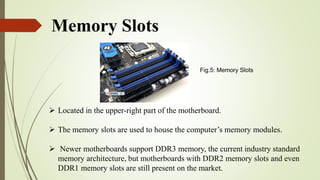
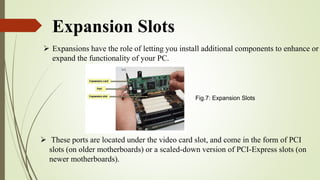
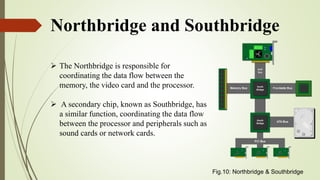
The document discusses the key components of a motherboard and their functions. It describes the central processing unit socket, power connectors, memory slots, video card slot, expansion slots, BIOS chip, CMOS battery, keyboard and mouse connectors, hard disk and floppy disk connectors, jumpers, northbridge and southbridge chips, front and rear panel connectors, and random access memory. The motherboard integrates all hardware components, allows communication between parts, and provides power distribution.