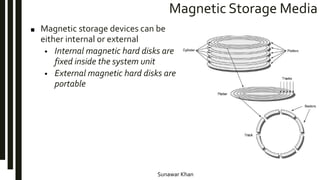
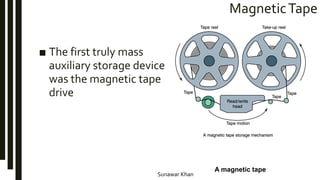
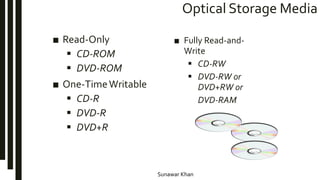
Storage devices store information to be recalled later and come in three main types: magnetic, optical, and flash memory. Magnetic storage uses disks or tapes and can be internal or external hard drives. Optical storage includes CDs, DVDs, and uses lasers to read and write data on disks. Flash memory cards have no moving parts and provide portable storage. Larger storage capacities are available but come at increased cost versus performance.