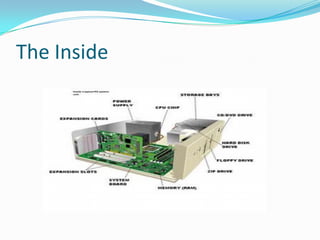
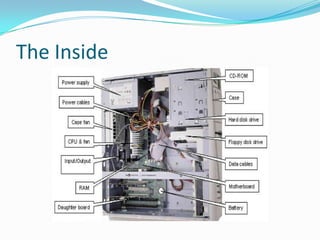
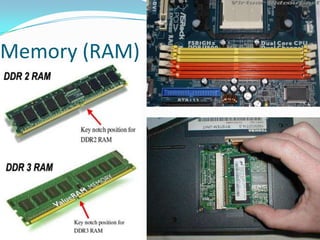
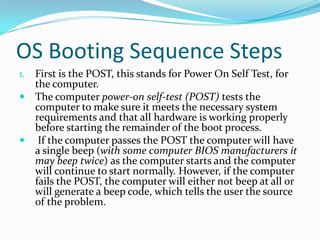
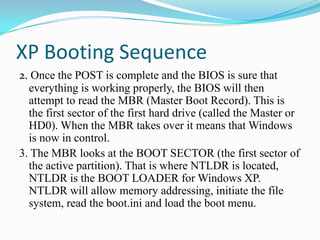
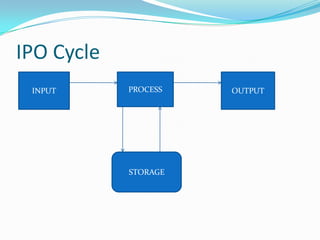
The document provides an overview of the components and boot up process of a personal computer. It discusses the external components like the monitor, keyboard and case. Internally it covers the motherboard, CPU, memory, fans, hard drives and BIOS. It explains motherboard components like sockets and slots. It then details the boot up sequence from POST to loading the operating system, including the role of the BIOS, MBR and bootloader.