1) The document discusses computer storage and data types. It explains how computers store programs and data in memory, including primary storage (RAM) and secondary storage (hard drives).
2) Variables are stored in either the stack or heap based on their type. Value types like integers are stored on the stack while reference types like objects are stored on the heap.
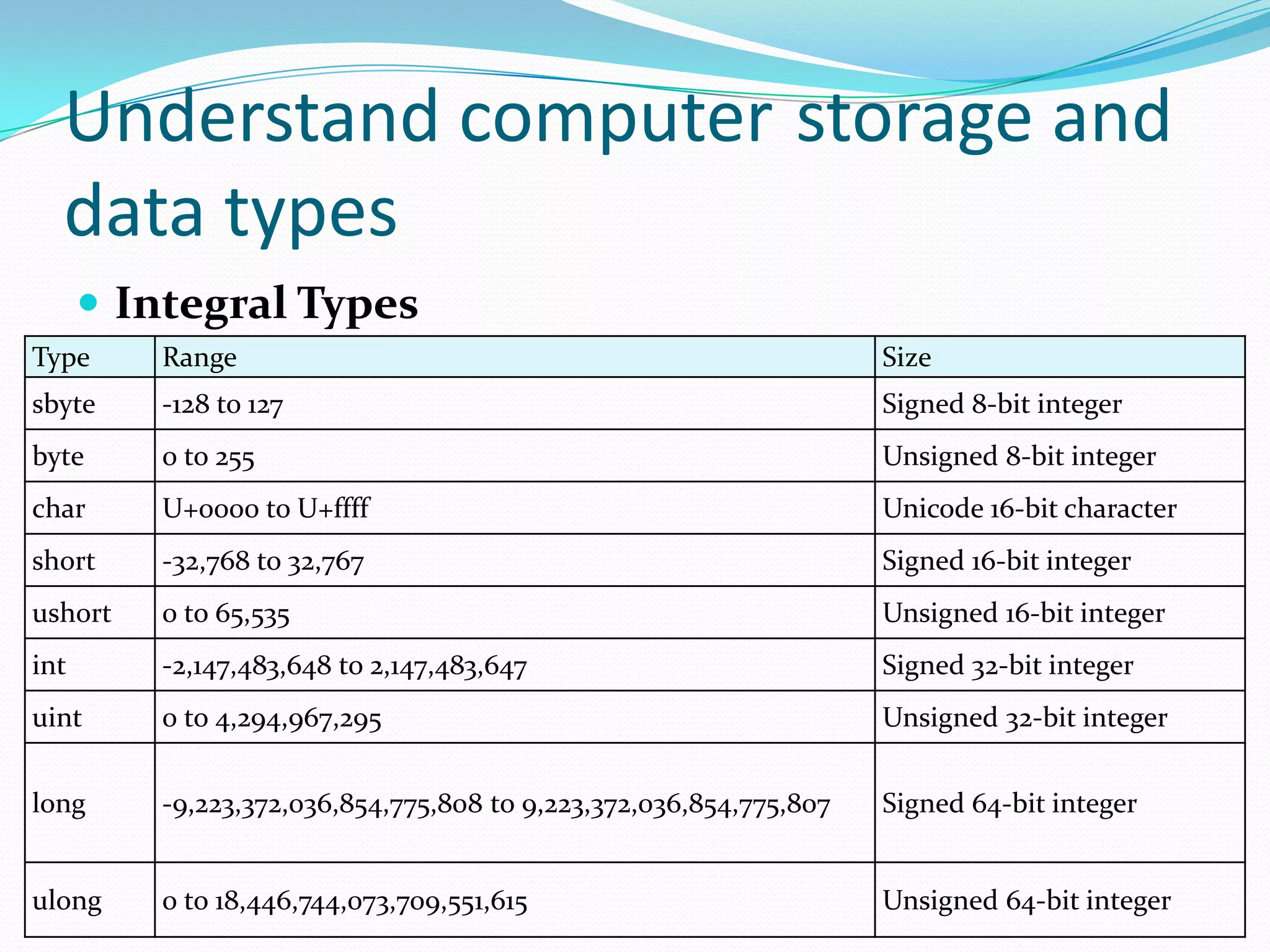
3) The document reviews different data types including numeric (integral, floating-point, decimal), textual, and boolean types. It provides examples of declaring variables of each type.