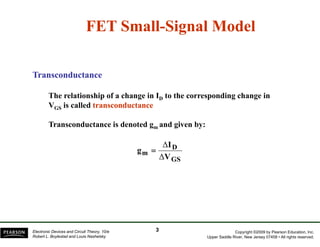
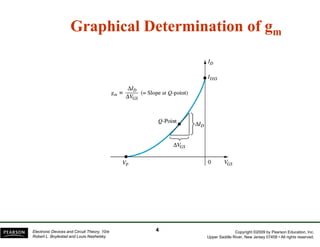
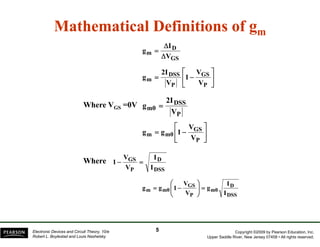
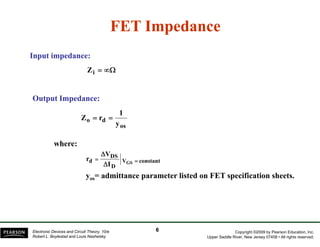
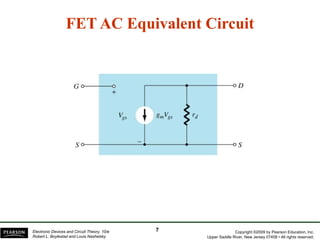
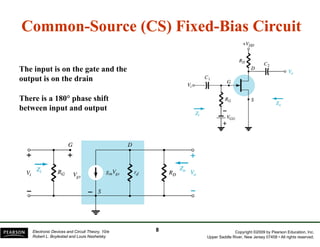
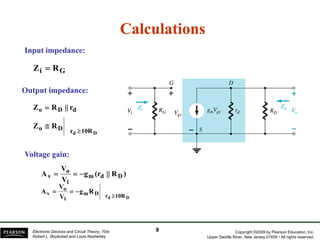
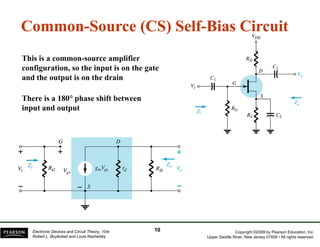
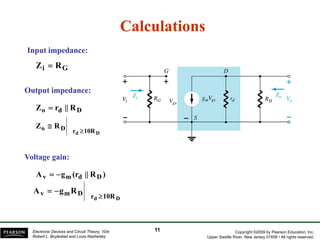
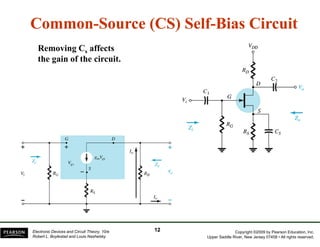
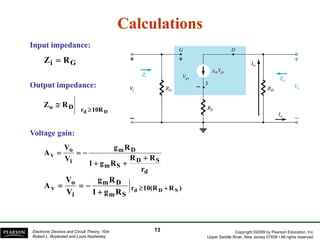
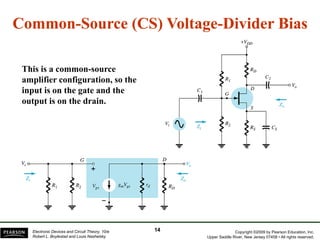
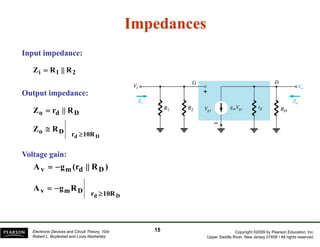
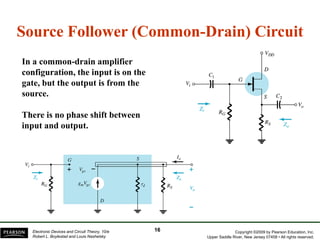
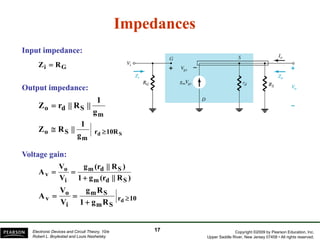
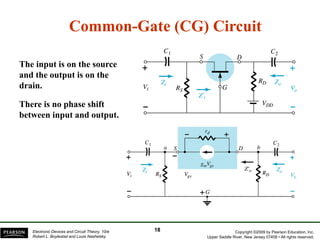
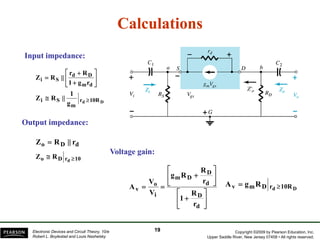
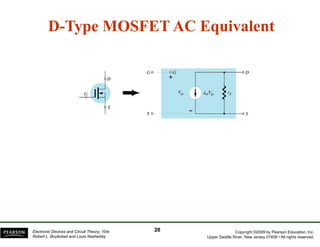
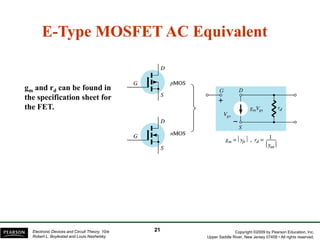
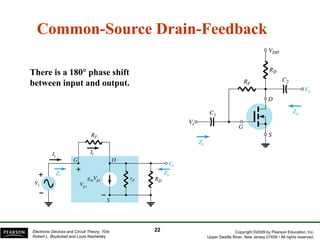
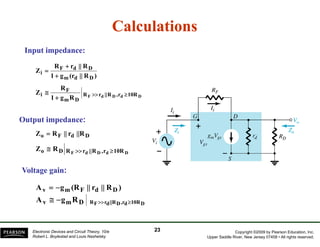
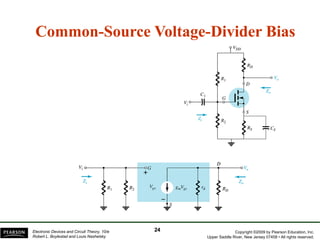
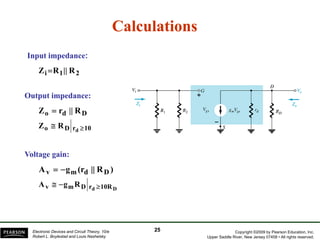
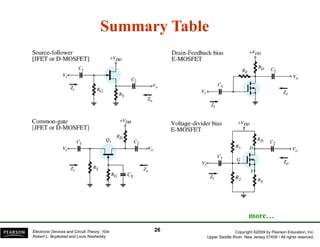
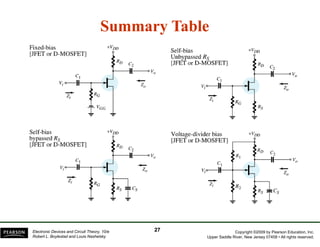
The document discusses field-effect transistors (FETs) and FET amplifiers. It describes the basic FET configurations including common-source, common-gate, and common-drain. It provides the small-signal models and calculations for voltage gain, input and output impedances for each configuration. Additional topics covered include biasing techniques, MOSFET models, and troubleshooting FET amplifiers.