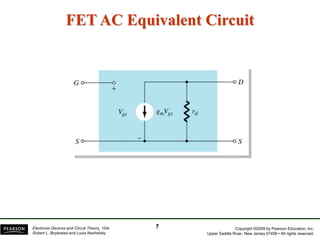
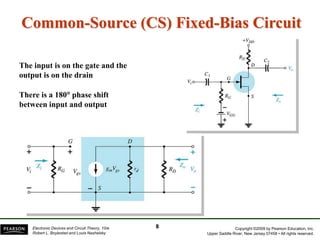
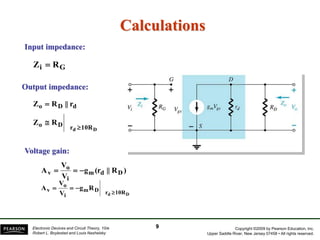
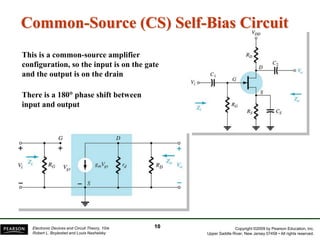
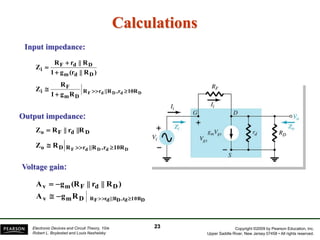
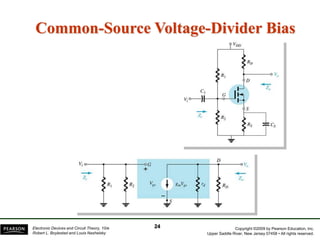
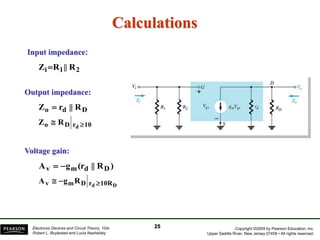
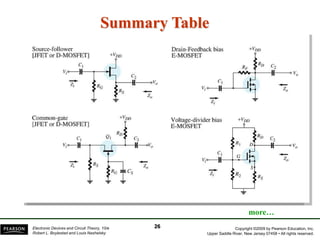
The document discusses FET amplifiers, including:
- FETs provide excellent voltage gain, high input impedance, low power consumption, and a good frequency range.
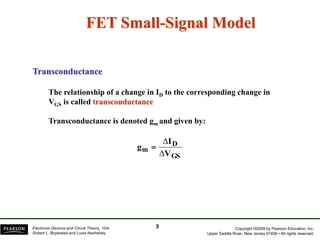
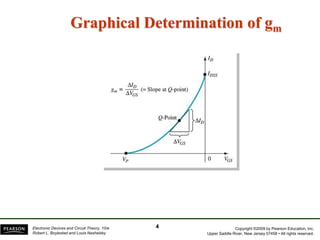
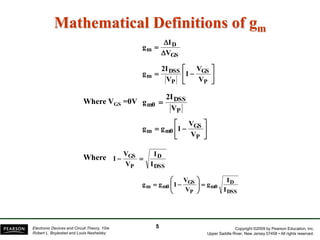
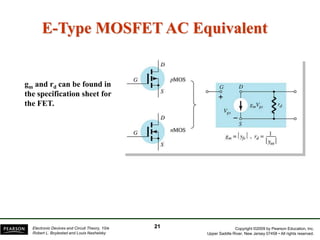
- Transconductance (gm) is the relationship between a change in drain current (ID) to the corresponding change in gate-source voltage (VGS).
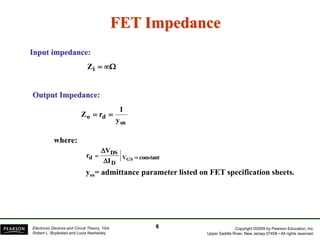
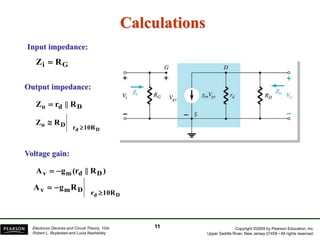
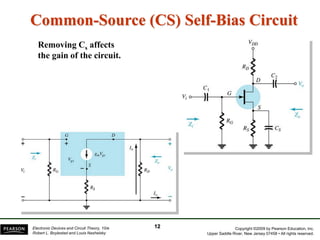
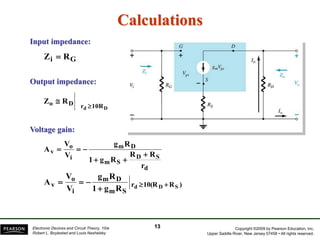
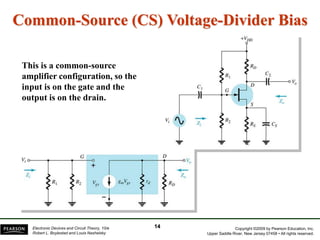
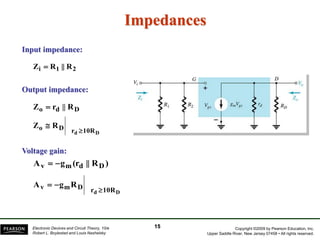
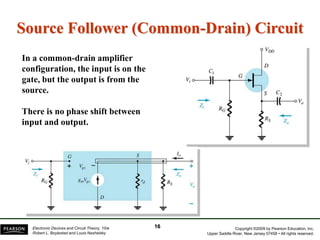
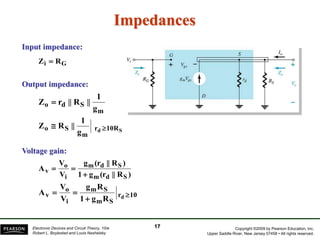
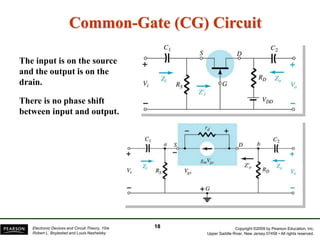
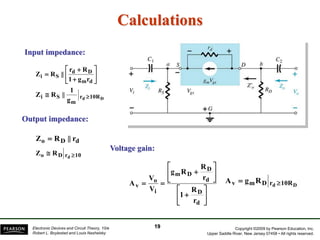
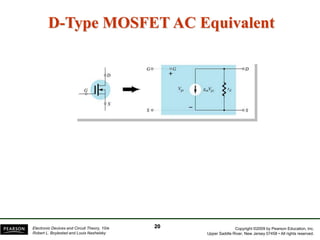
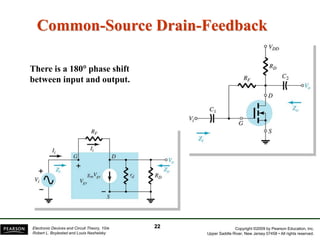
- There are several common FET amplifier configurations - common-source, common-gate, common-drain, and their input/output relationships and calculations for voltage gain, input and output impedances.