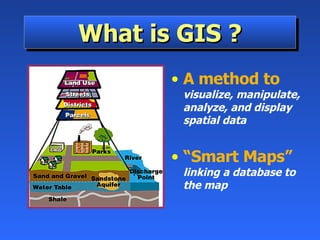
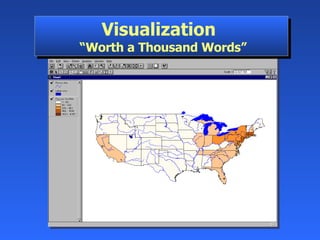
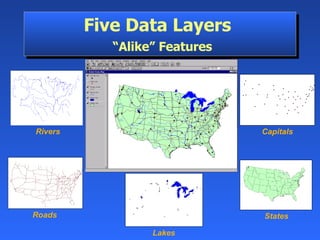
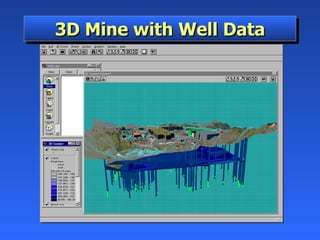
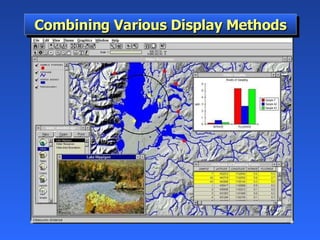
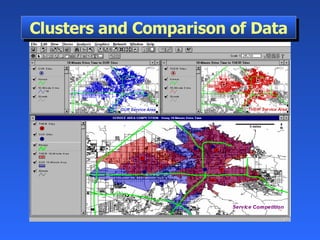
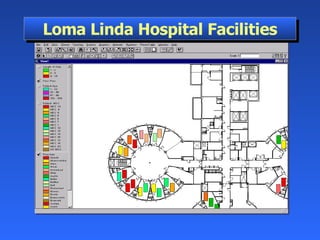
Geographic Information Systems (GIS) is a system of computer software, hardware, and data that helps users manipulate, analyze, and present spatial information. GIS turns data into information by allowing users to visualize, analyze, and interact with spatial data linked to locations. Common uses of GIS include emergency services, environmental monitoring, business site selection, transportation planning, and more. GIS combines data from various sources and allows users to ask questions of and get insights from the interactive maps and databases.