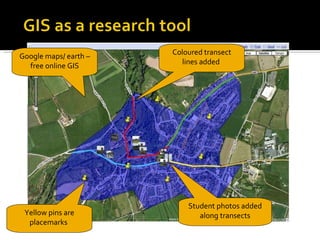
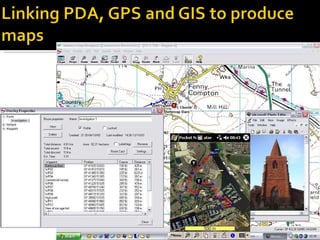
GIS allows users to store, manipulate, and analyze spatial data represented in layers. It underpins data with vector locations that can then be plotted to show information geographically. Users can ask questions of spatially-related data, search for patterns and distributions, and investigate relationships between different data sets. How data is displayed through options like color, size, and classification can influence the patterns seen. It is important to consider who created data sets and how current they are.