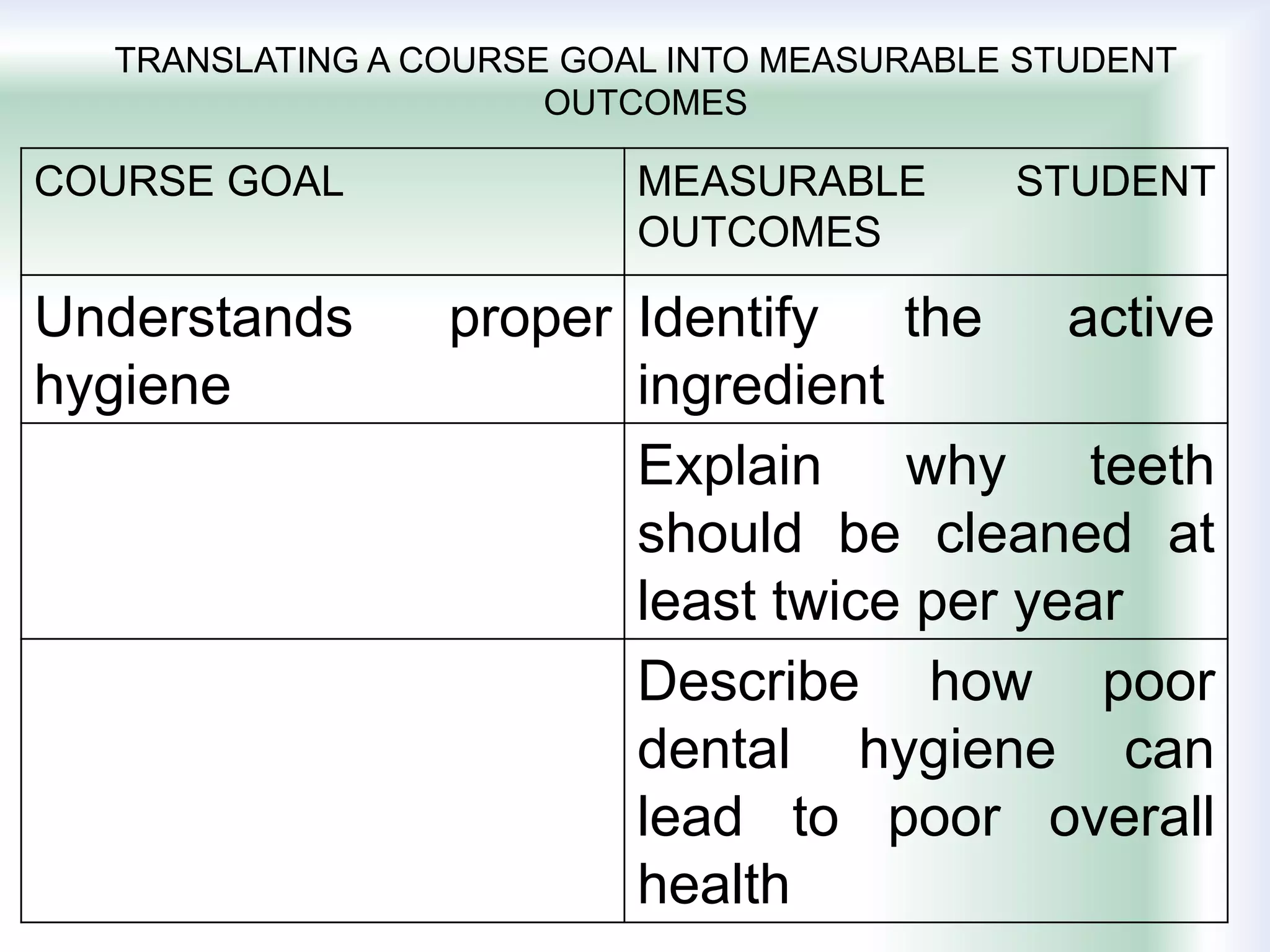
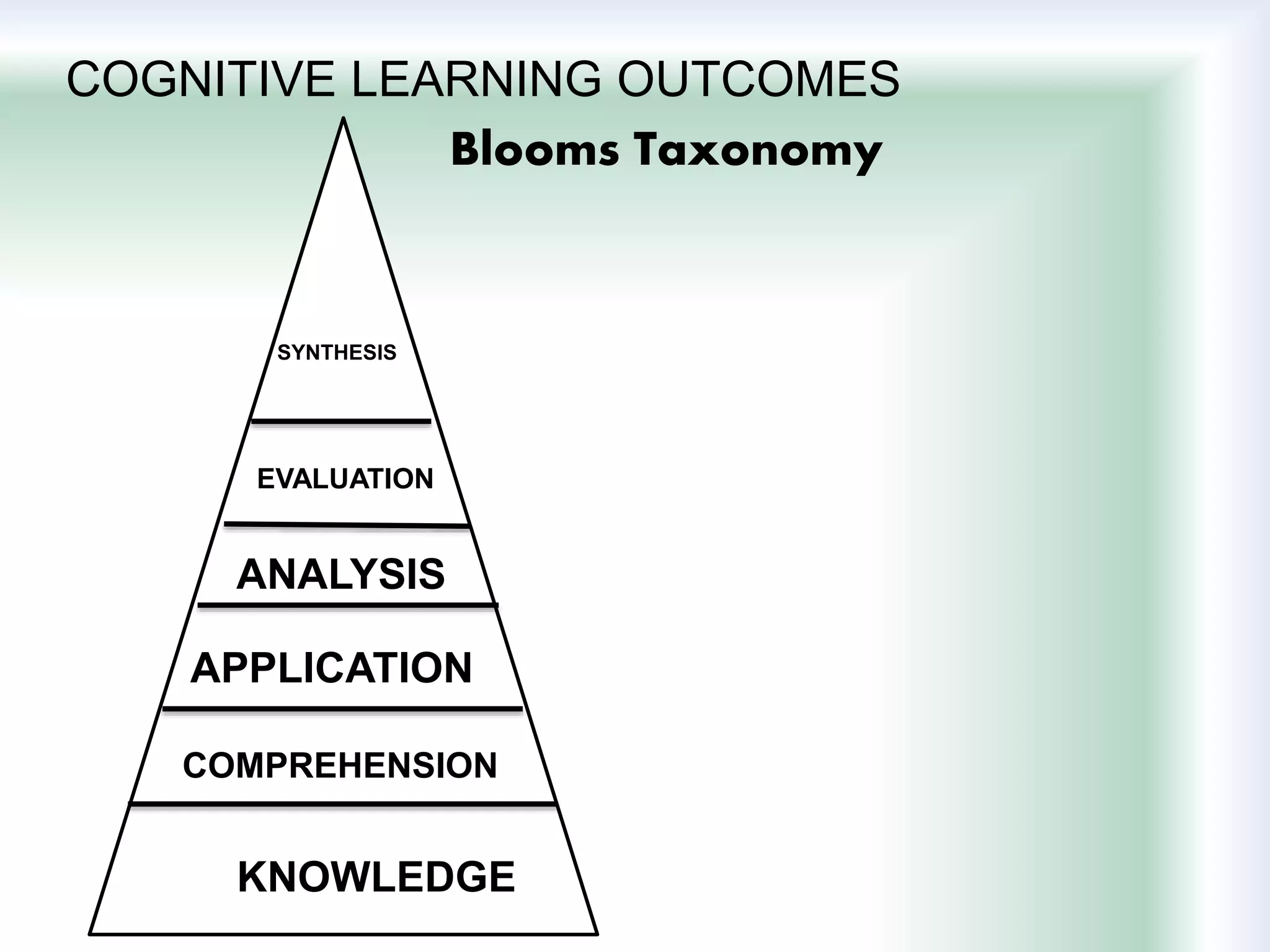
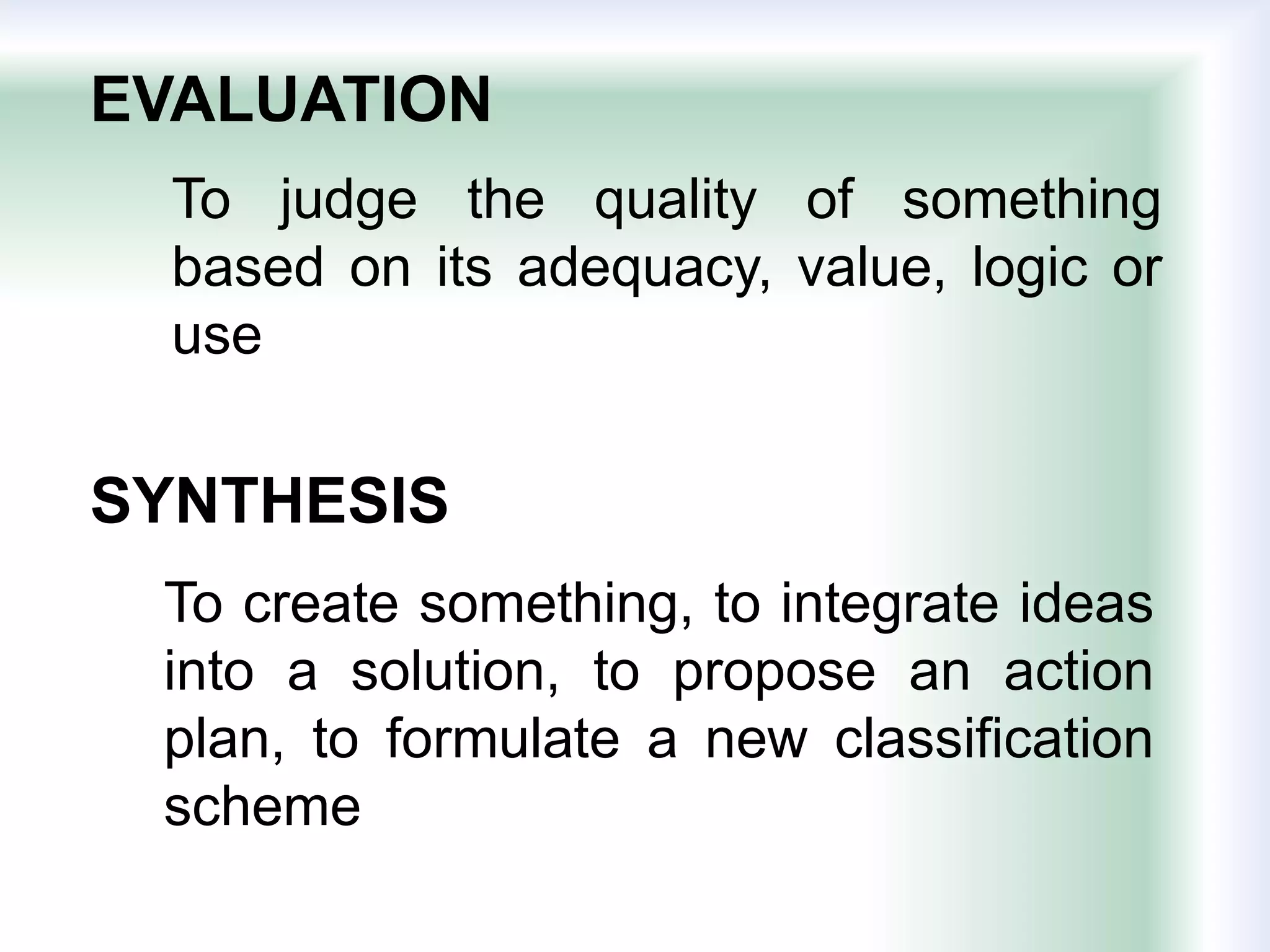
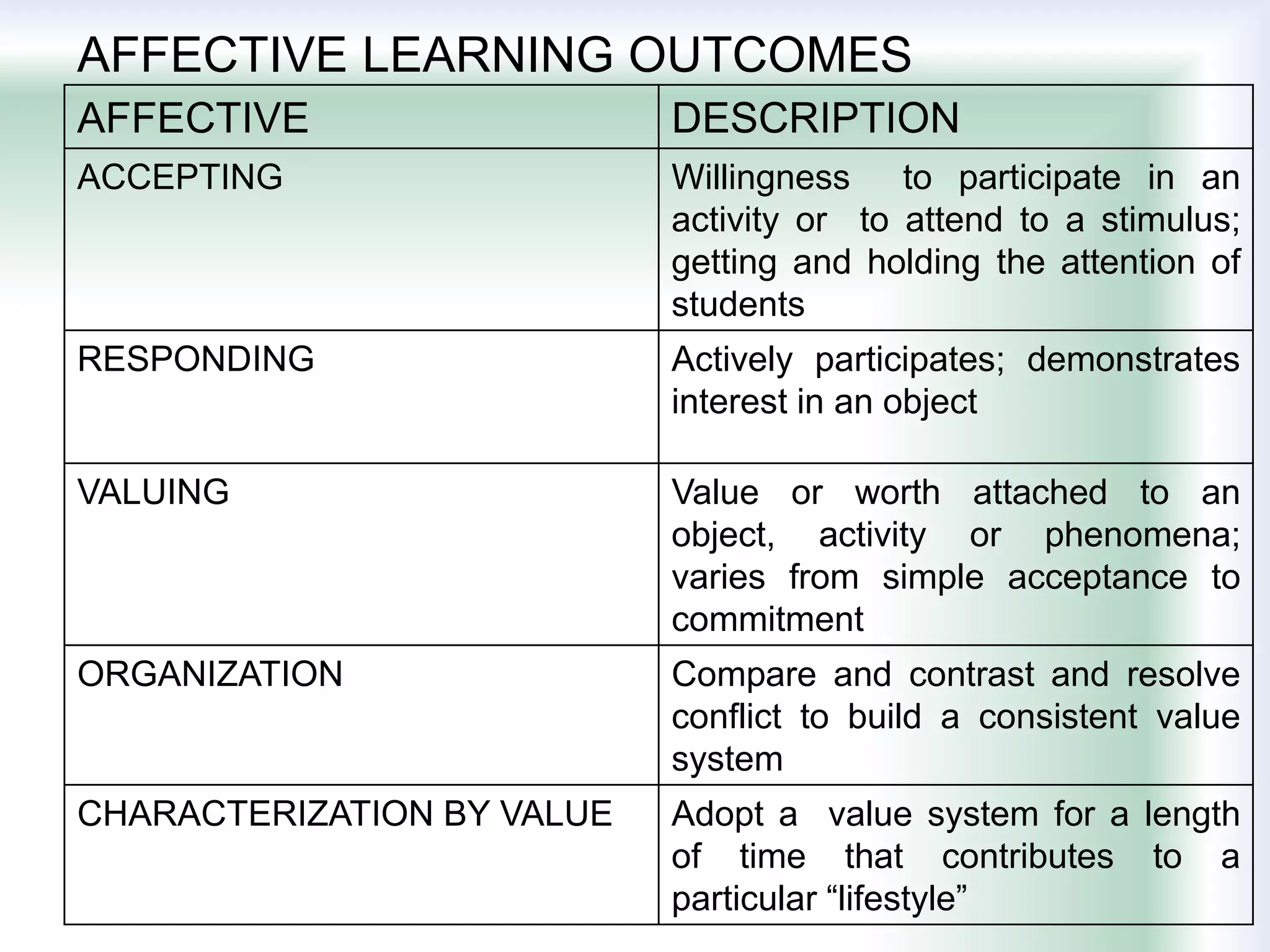
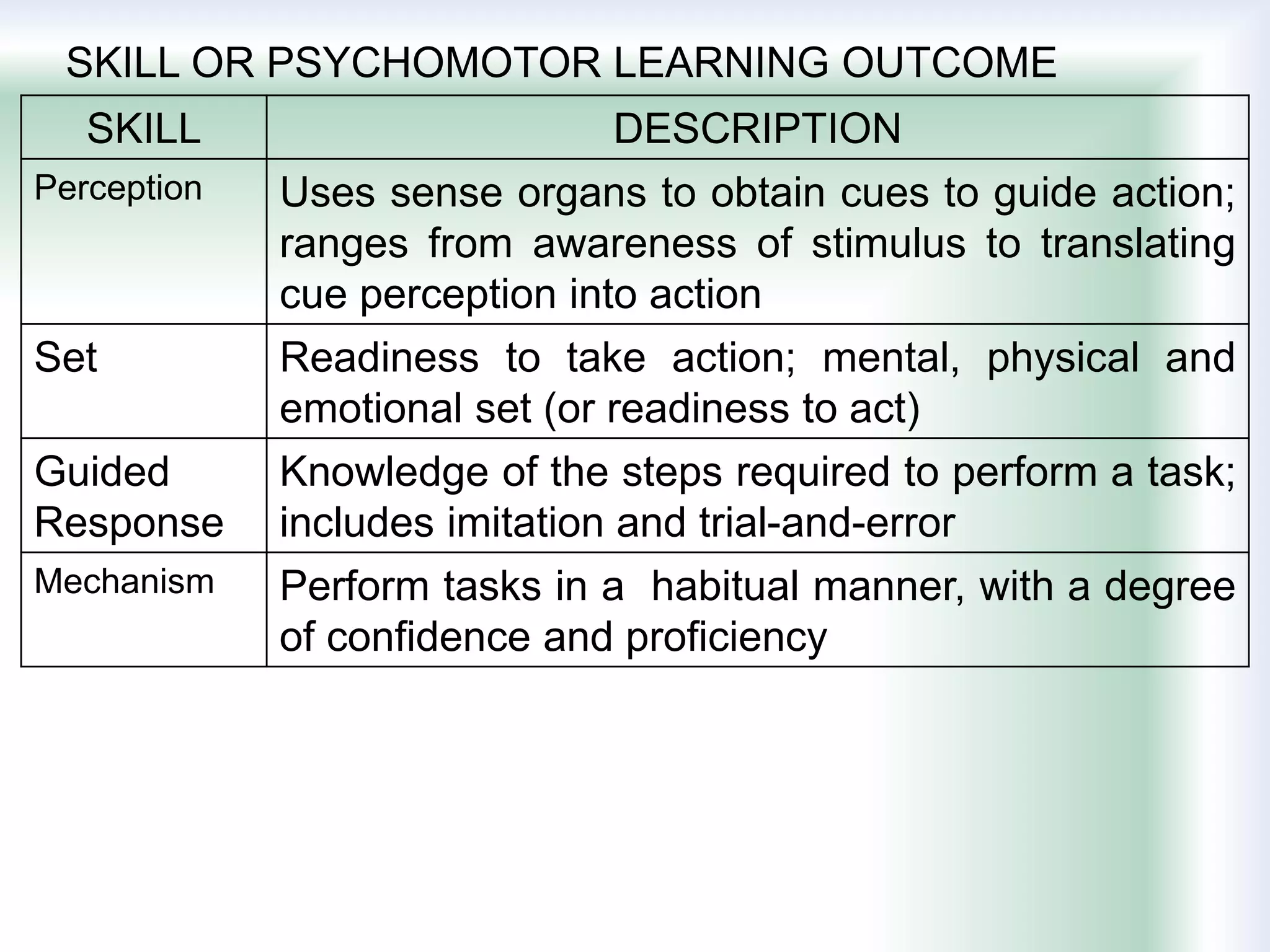
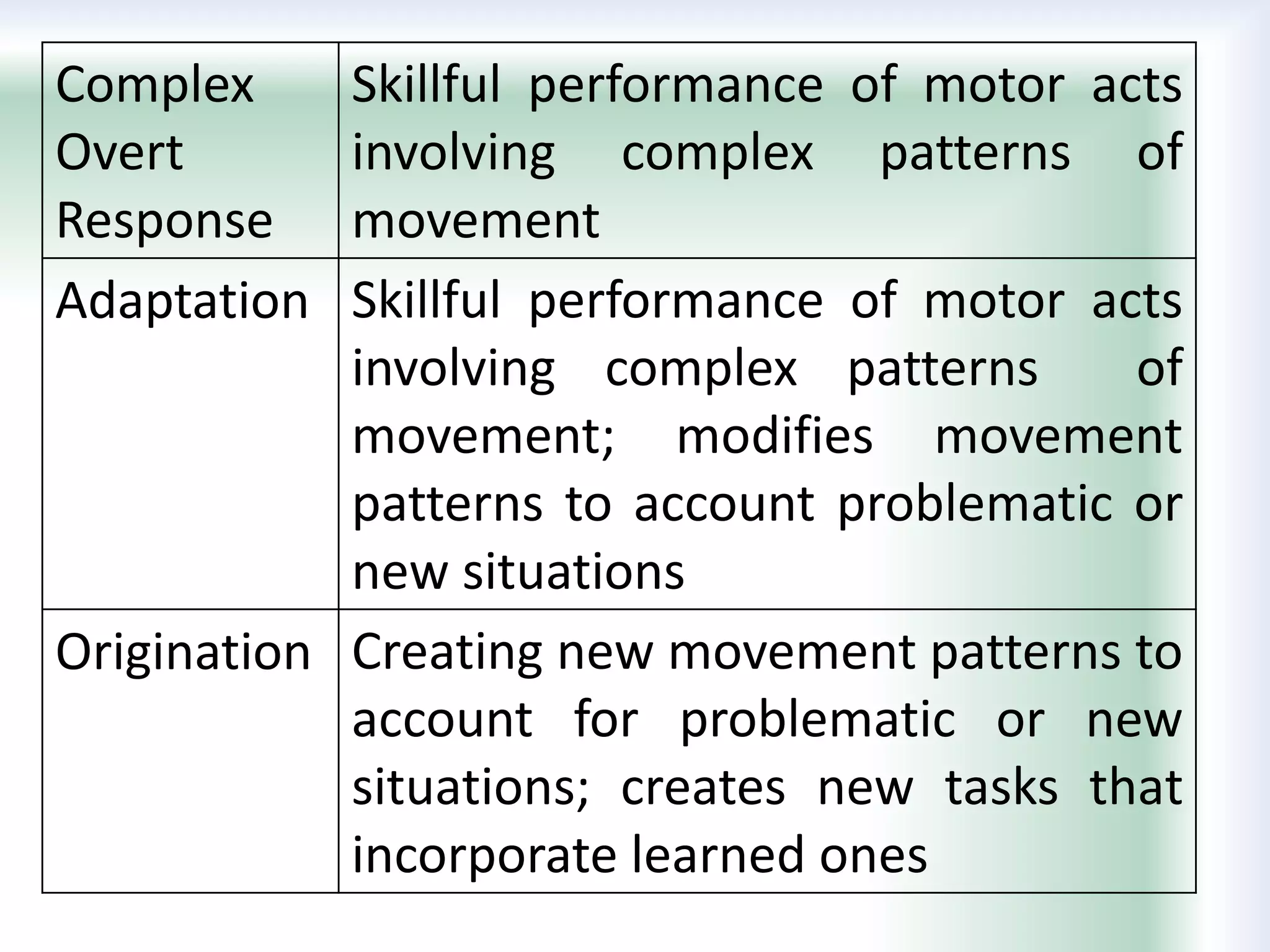
The document discusses learning goals, objectives, and outcomes. It defines learning goals as broad statements about the curriculum, objectives as more specific statements about instruction, and outcomes as what students will know and be able to do by the end of a course. Learning outcomes have three components: an action verb describing the performance, a learning statement specifying what will be demonstrated, and a criterion for acceptable performance. Different types of learning outcomes are also described, including cognitive, affective, and psychomotor outcomes. The importance of writing clear, measurable learning objectives and using assessment results to improve goals, teaching, and curriculum is emphasized.