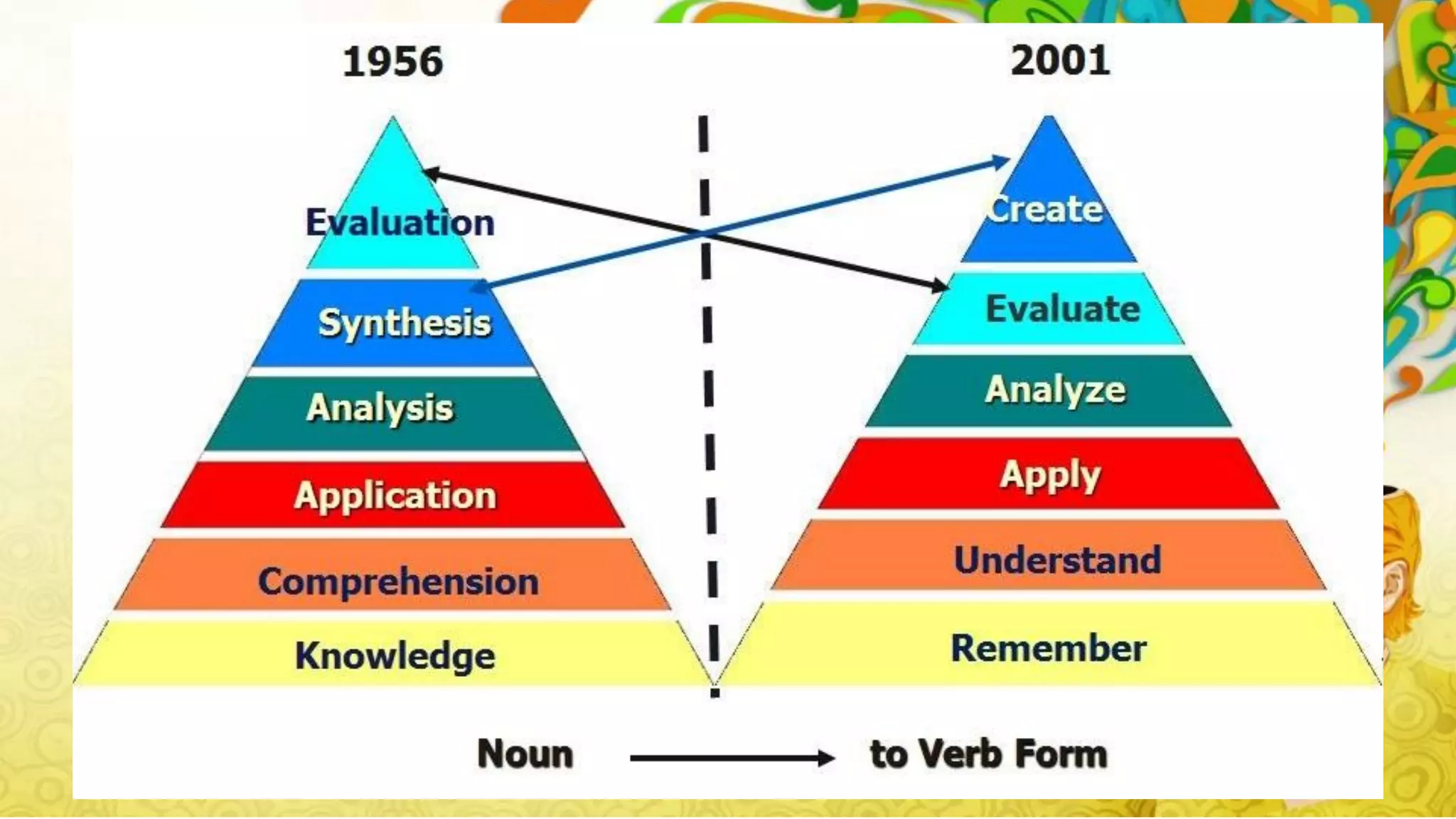
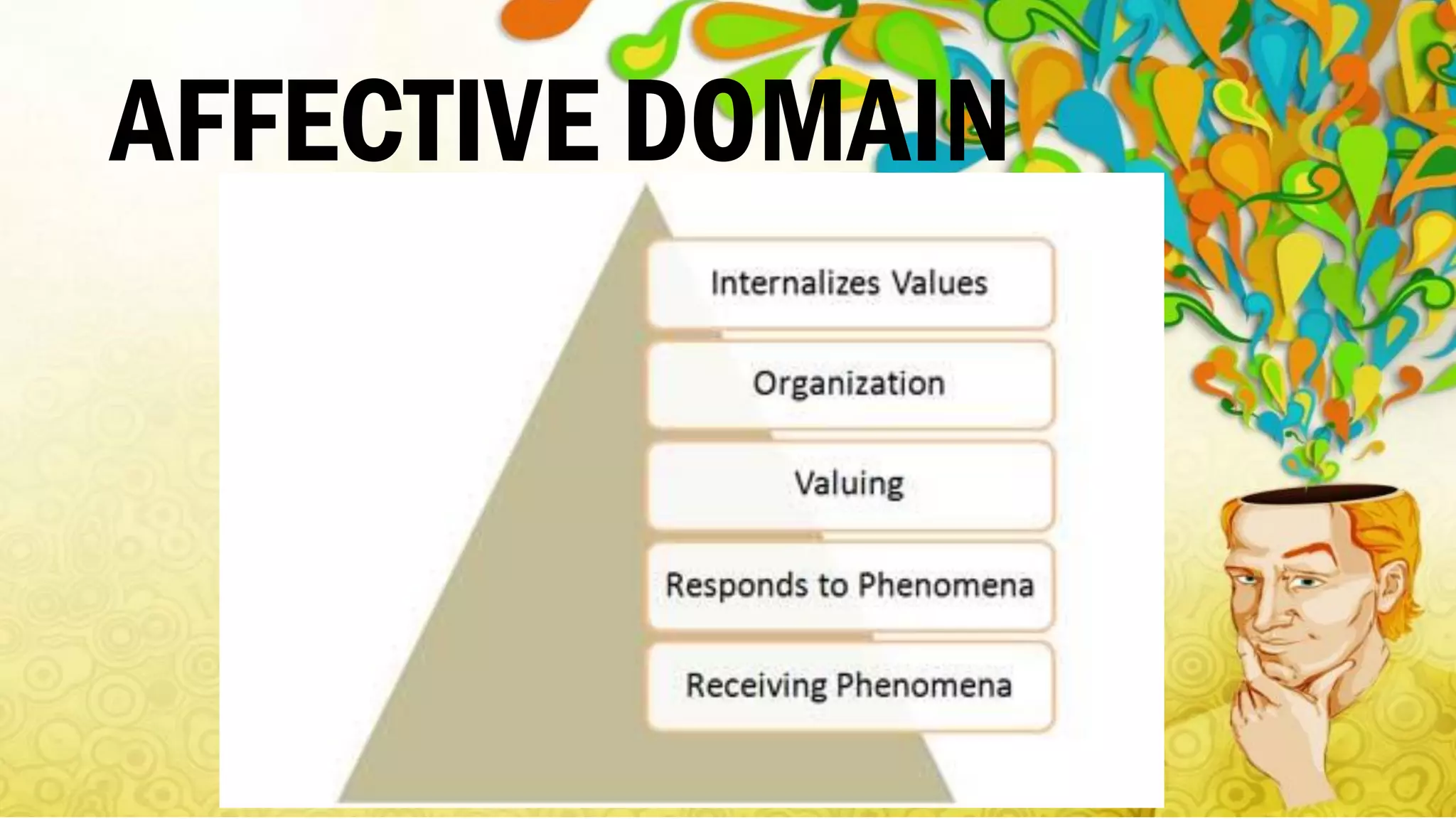
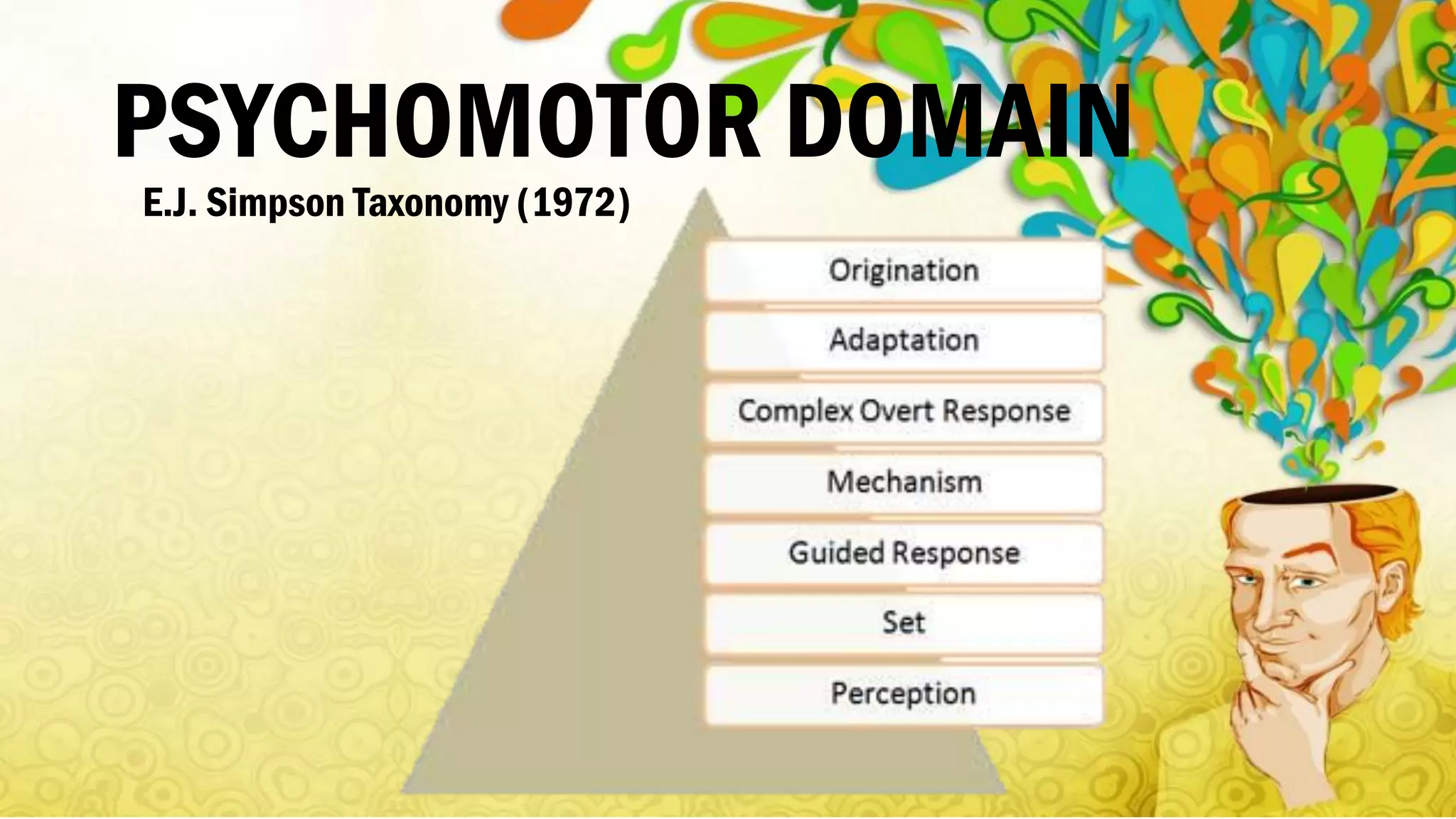
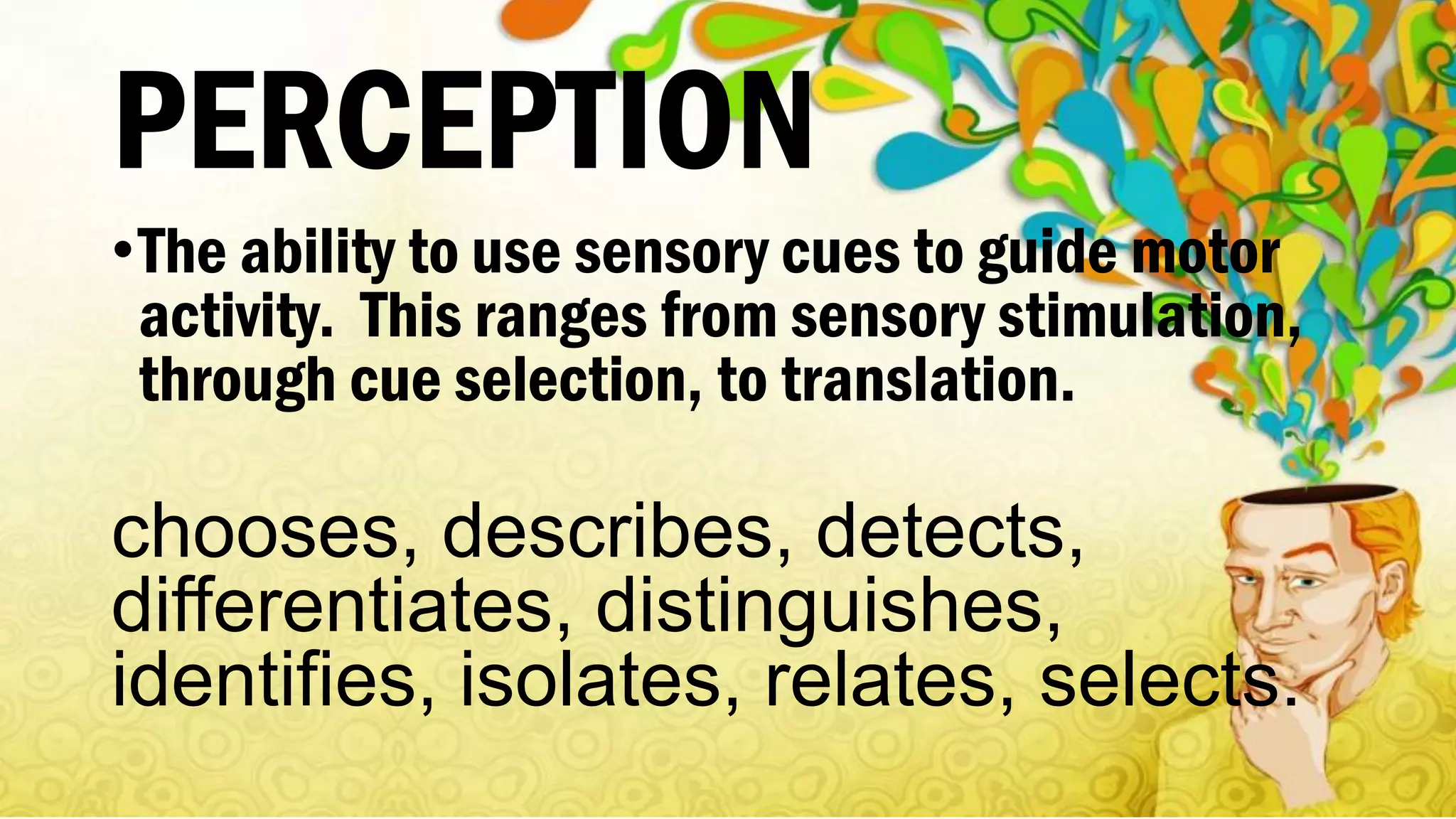
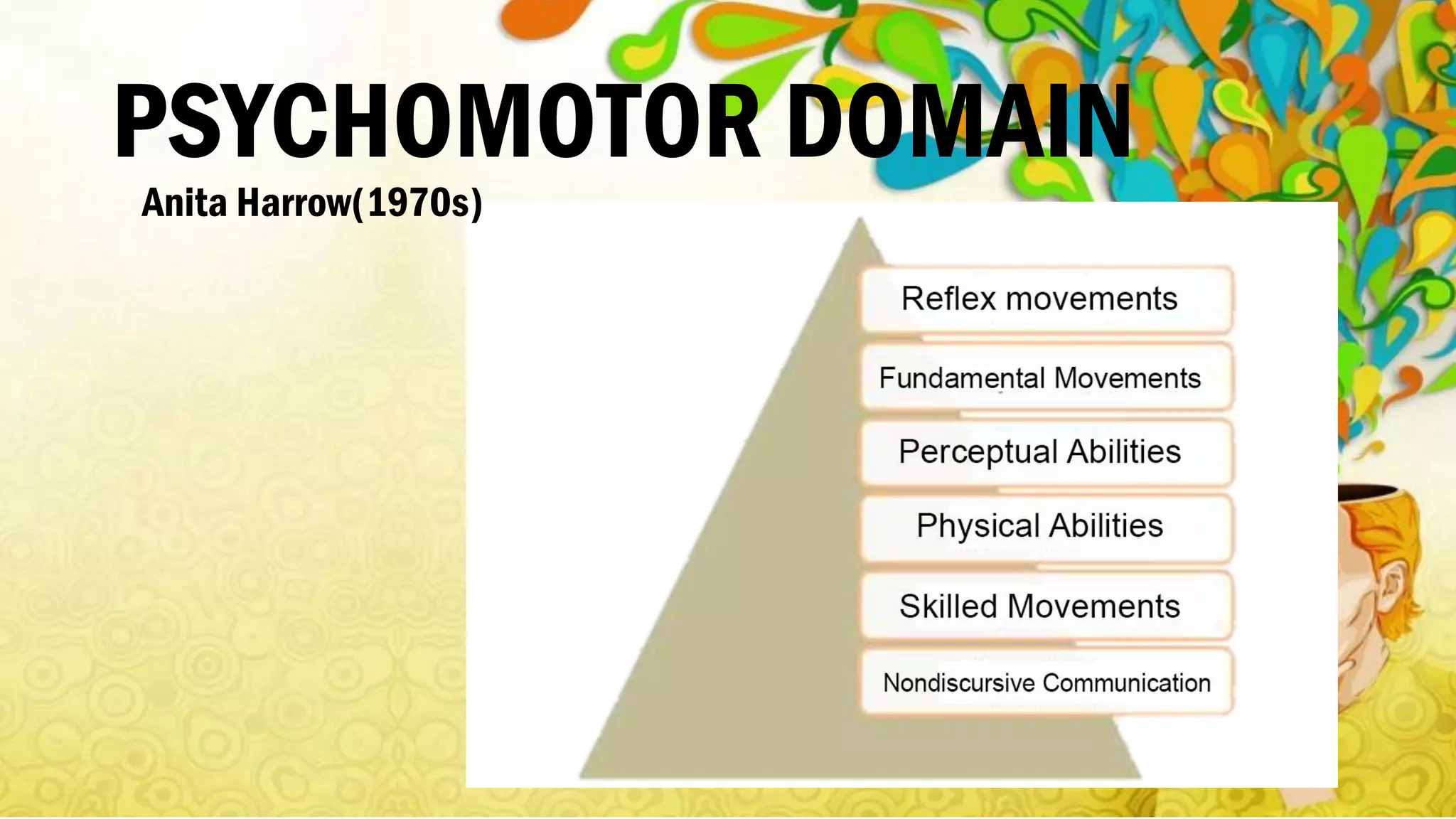
Bloom's Taxonomy, developed in 1956, categorizes educational objectives into three domains: cognitive, affective, and psychomotor. The cognitive domain focuses on thinking skills from basic recall to higher-level analysis and evaluation, while the affective domain addresses emotional responses and values, and the psychomotor domain pertains to physical skills and movement proficiency. Updates to the taxonomy reflect ongoing developments in educational psychology, emphasizing a structured approach to enhance learning outcomes.