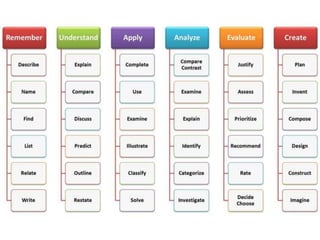
This document discusses instructional objectives and learning outcomes. It defines objectives as specific, measurable behaviors that students will exhibit after instruction. Objectives provide direction for instruction and assessment. Learning outcomes describe the knowledge, skills, and expertise learners will gain. The document outlines different types of objectives and outcomes and provides tips for writing objectives and outcomes, including using action verbs and focusing on observable behaviors.