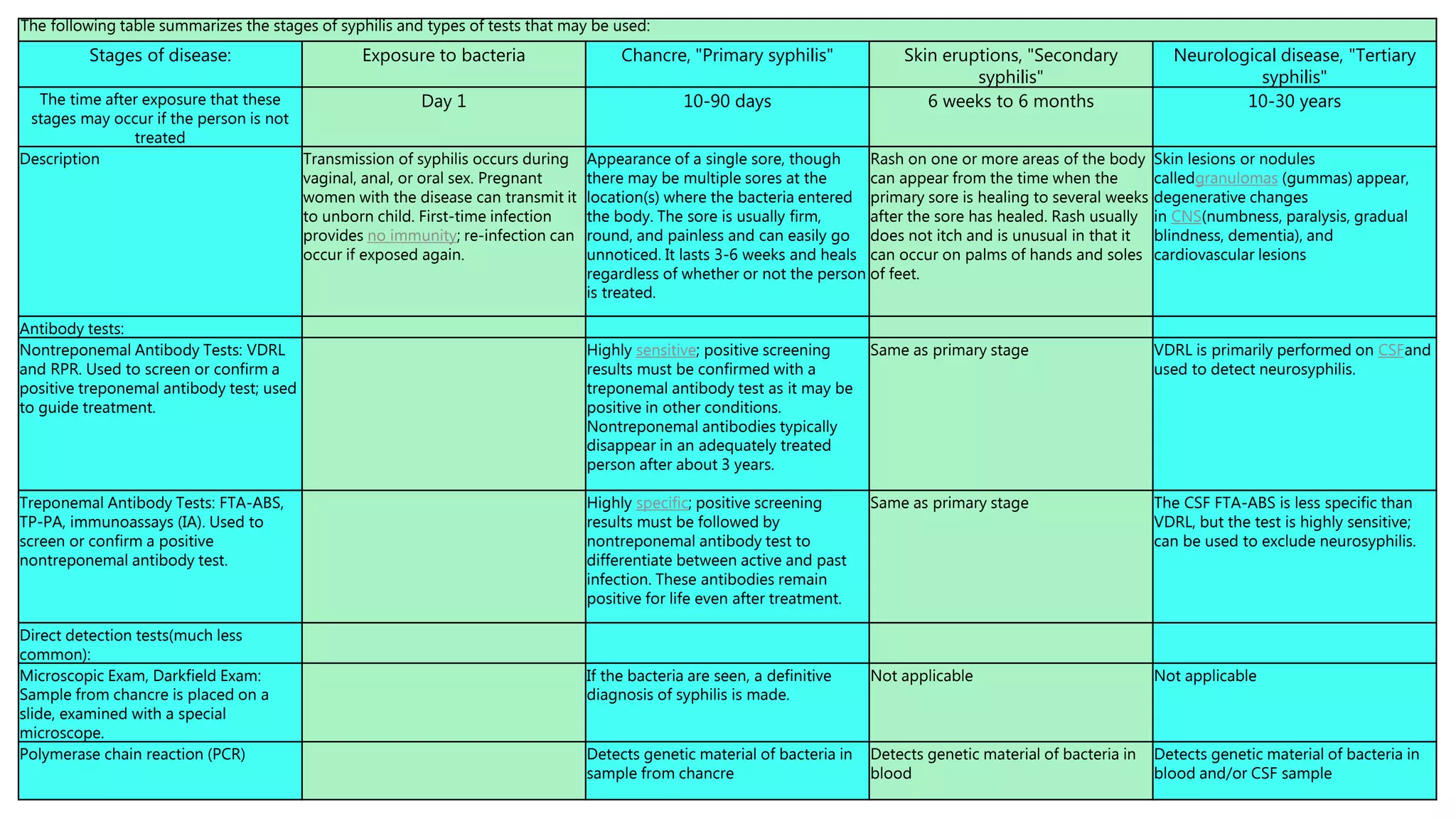
Syphilis is a chronic bacterial infection caused by the bacteria Treponema pallidum that is primarily transmitted through sexual contact. It progresses through three stages - primary, secondary, and tertiary - if left untreated. Primary syphilis involves skin sores, secondary syphilis involves rashes and mouth sores, and tertiary syphilis can damage internal organs. Syphilis is diagnosed through tests that detect antibodies produced in response to the infection. While antibiotics can cure it in its early stages, later stages may cause permanent damage without treatment.