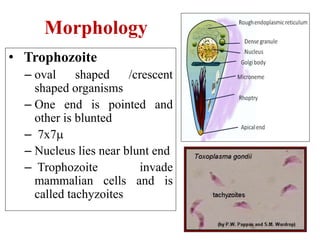
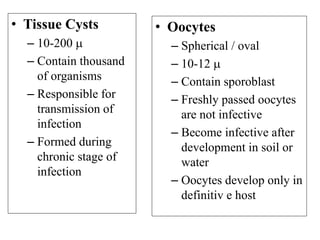
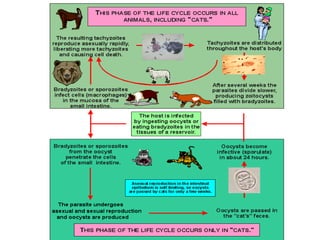
Toxoplasma gondii is an obligate intracellular parasite that can infect almost any mammal and has been found worldwide. It has a complex life cycle involving cats as the definitive host where it produces oocysts, and intermediate hosts where it produces tachyzoites and tissue cysts containing bradyzoites. Humans can be infected by ingesting oocysts from cat feces or tissue cysts in undercooked meat. While most infections are asymptomatic, it can cause serious issues in pregnant women and immunocompromised individuals like those with AIDS. Diagnosis involves serological tests or biopsy detection, and treatment consists of pyrimethamine and sulfadiazine antibiotics.