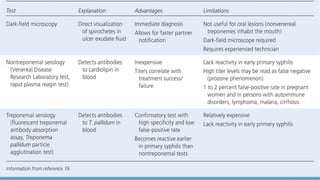
Syphilis is caused by the bacterium Treponema pallidum and is primarily transmitted through sexual contact or from mother to child during pregnancy. The disease progresses through four stages: primary, secondary, latent, and tertiary, each characterized by different symptoms and lesions. Diagnosis involves methods such as darkfield microscopy, serologic tests, and histopathological examination, while treatment primarily consists of antibiotics, especially penicillin.





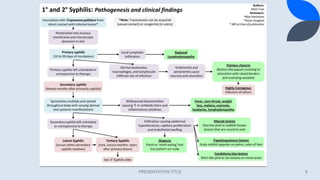










![Nontreponemal tests
Syphilitic infection leads to the production of
nonspecific antibodies that react to cardiolipin. This
reaction is the foundation of “nontreponemal” assays
such as the VDRL (Venereal Disease Research
Laboratory) test and Rapid Plasma Reagin (RPR) test.
Both these test are flocculation type tests that use
an antigen-antibody interaction. The complexes remain
suspended in solution and therefore visible due to
the lipid based antigens.[3][4]
All nontreponemal tests measure immunoglobulins G
(IgG) and M (IgM) anti-lipid antibodies formed by the
host in response both to lipoidal material released from
damaged host cells early in infection and to lipid from
the cell surfaces of the treponeme itself.
PRESENTATION TITLE 18](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ppt2-230614200446-f36af3a5/85/Syphilis-18-320.jpg)