Pulmonary embolism (PE) can be detected and investigated through several tests:
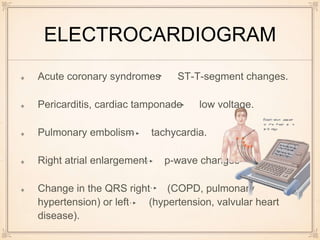
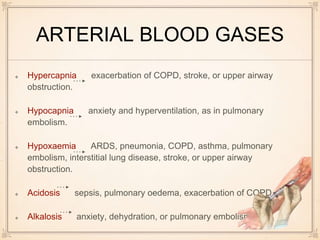
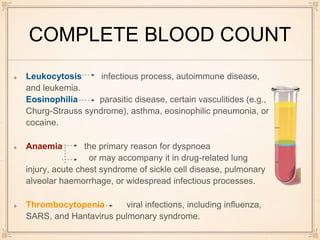
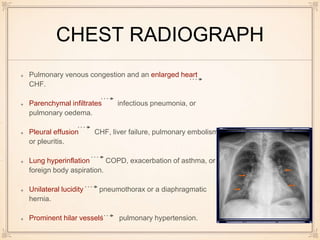
Pulse oximetry monitors for hypoxemia and oxygen supplementation is initiated, while further tests are done. Electrocardiograms can show changes indicating conditions like pulmonary embolism or right heart strain. Arterial blood gases may demonstrate hypoxemia, hypocapnia, or acidosis in PE. Chest x-rays can reveal signs of PE like enlarged heart size or perfusion deficits on lung scans. D-dimer tests if elevated suggest a thrombus, while normal levels rule out recent clots. CT pulmonary angiograms are best to diagnose or rule out PE due to speed, availability and ability to detect other lung abnormalities