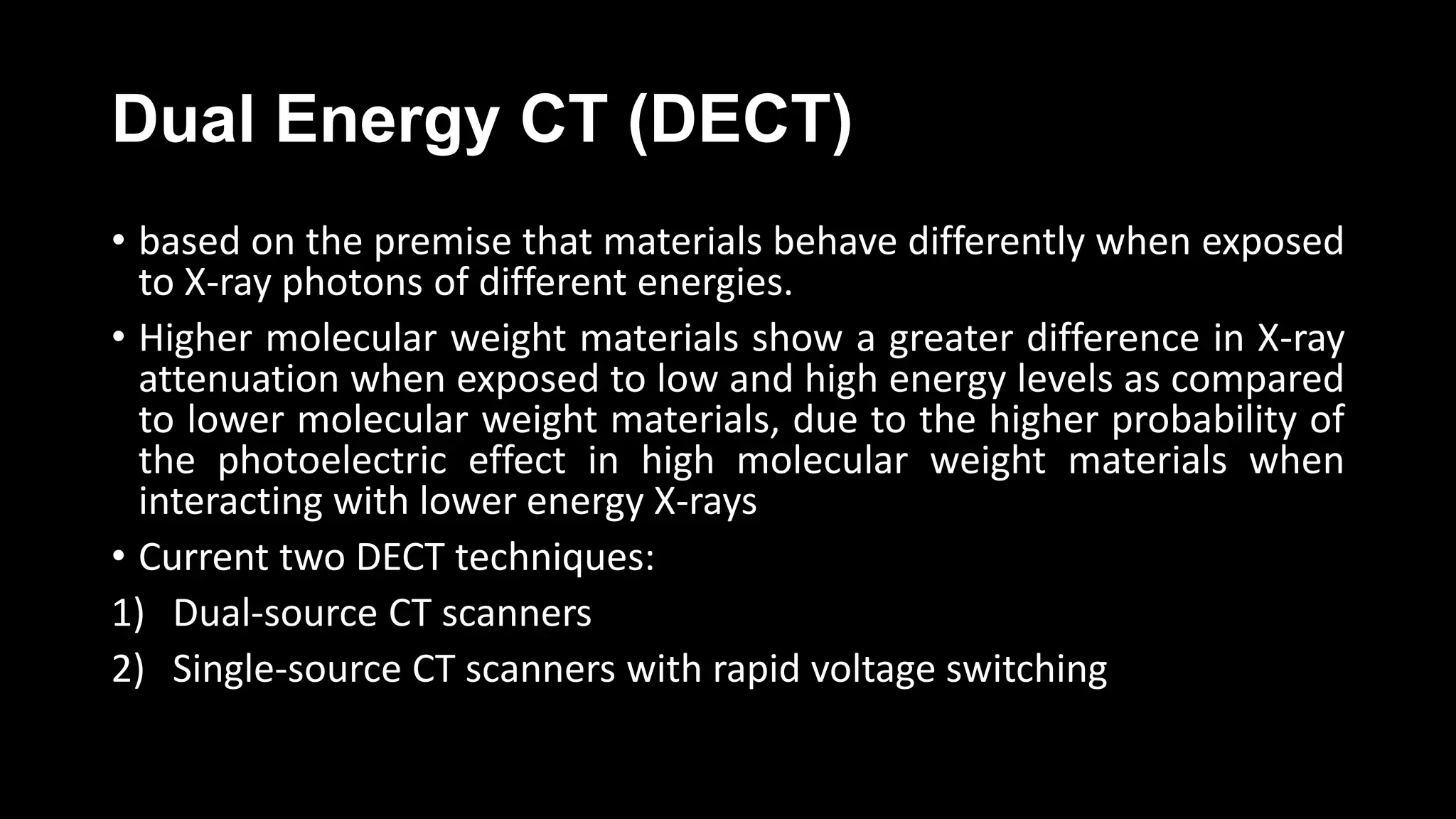
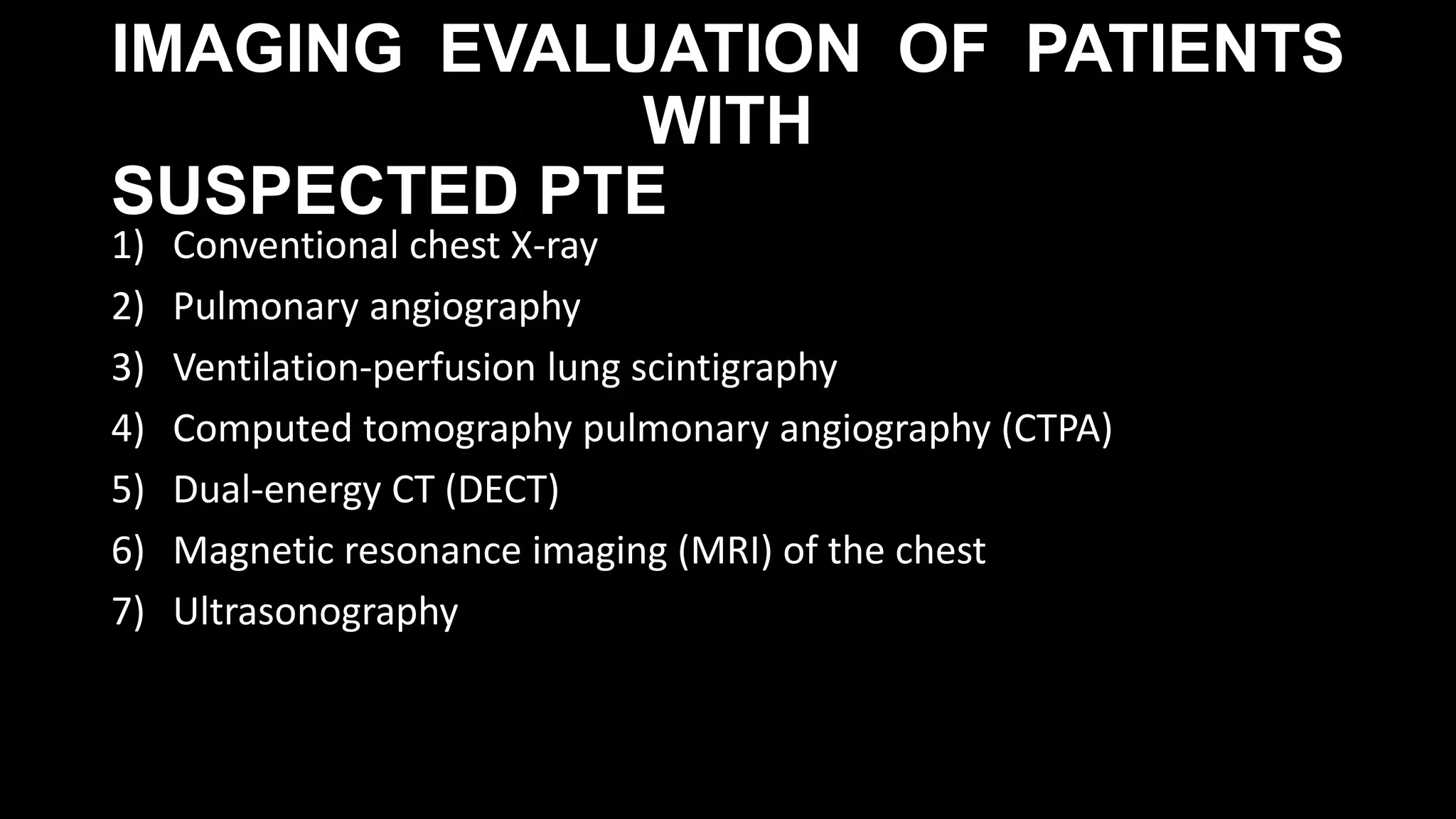
1) Pulmonary embolism occurs when a blood clot lodges in the pulmonary arteries, often originating from deep vein thromboses. It can be difficult to diagnose due to non-specific symptoms.
2) Evaluation involves assessing clinical probability, D-dimer levels, and imaging. D-dimers are elevated in pulmonary embolism but nonspecific. Imaging options include CT pulmonary angiography, ventilation-perfusion scanning, and pulmonary angiography.
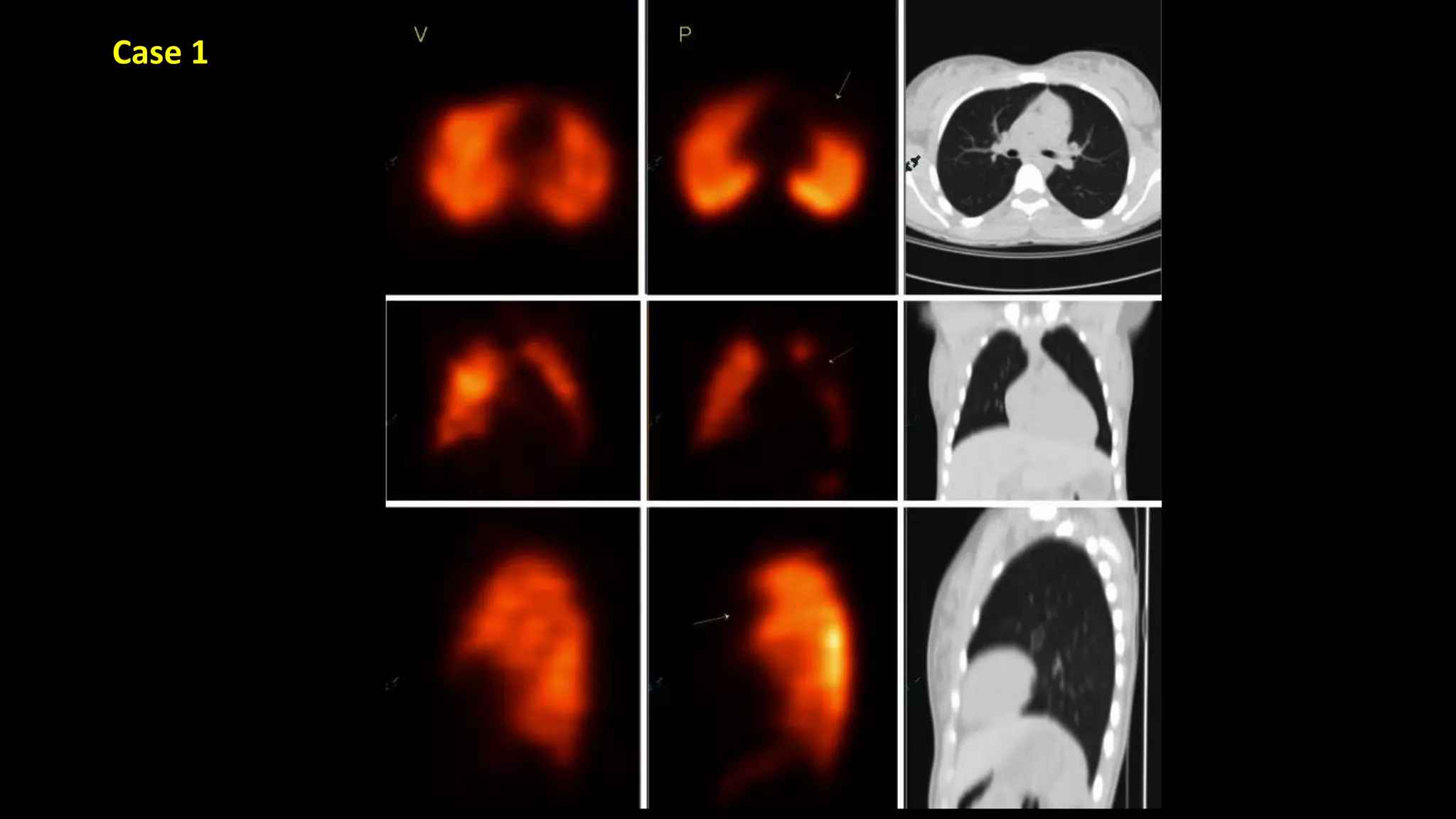
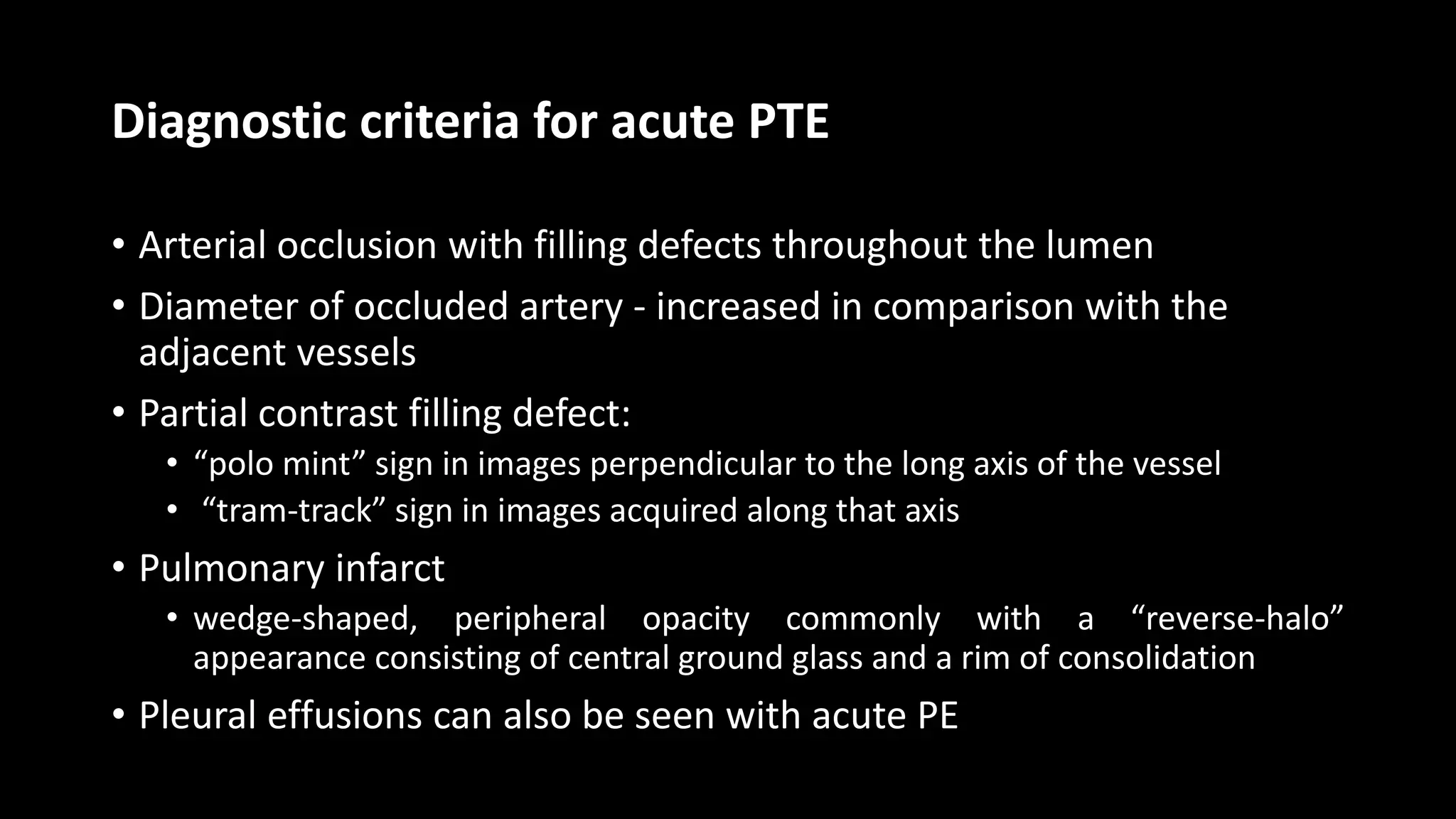
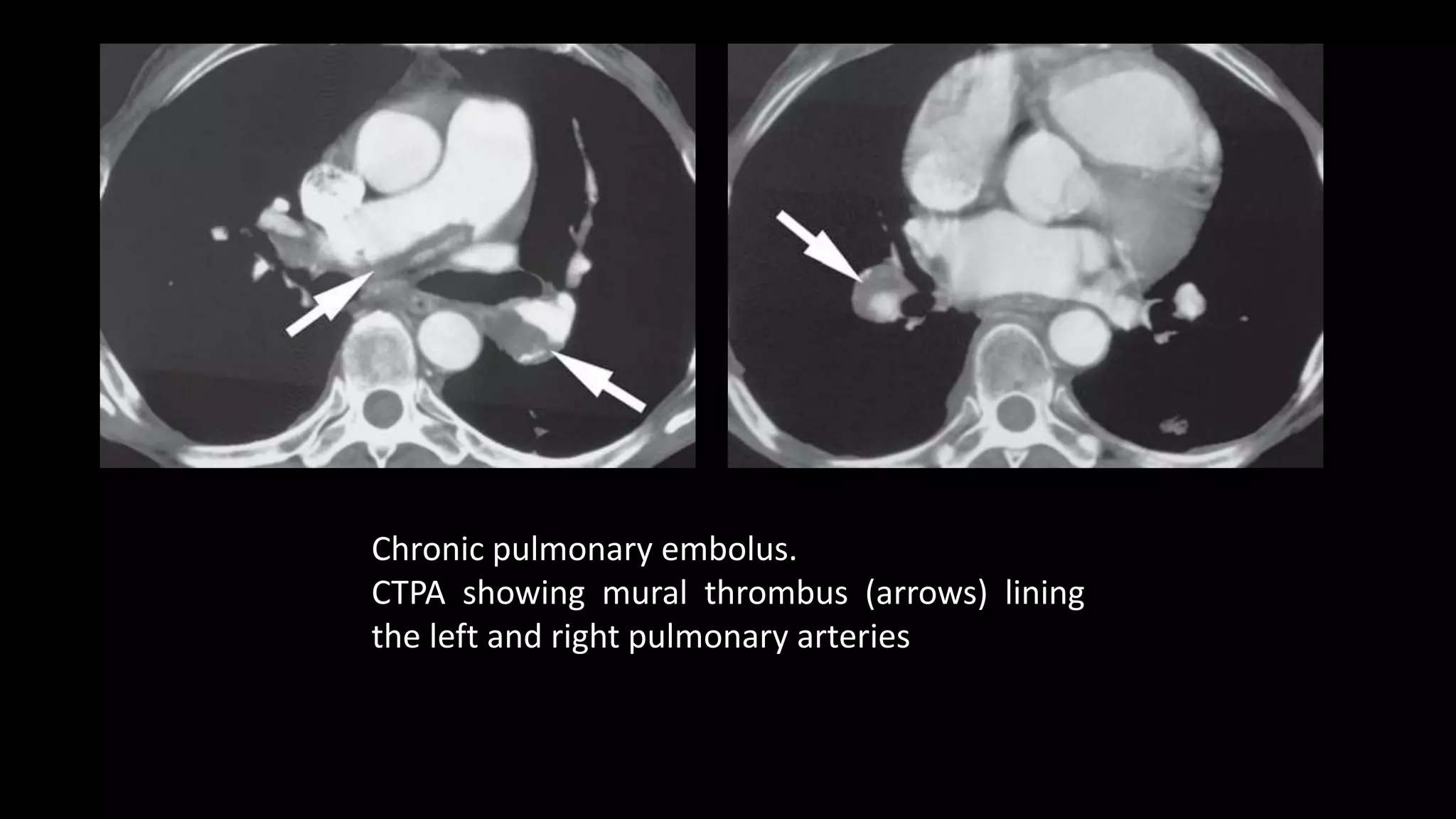
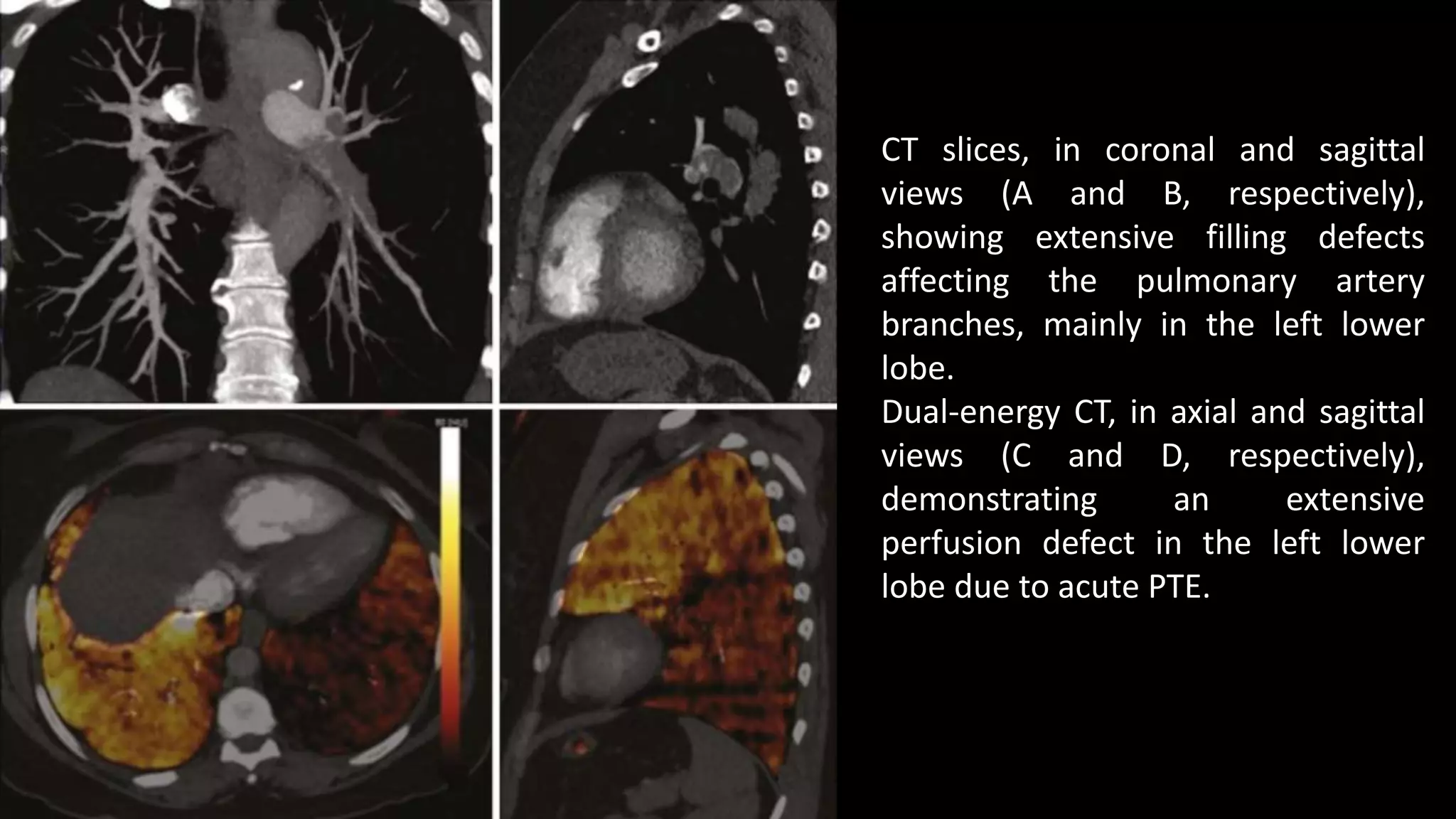
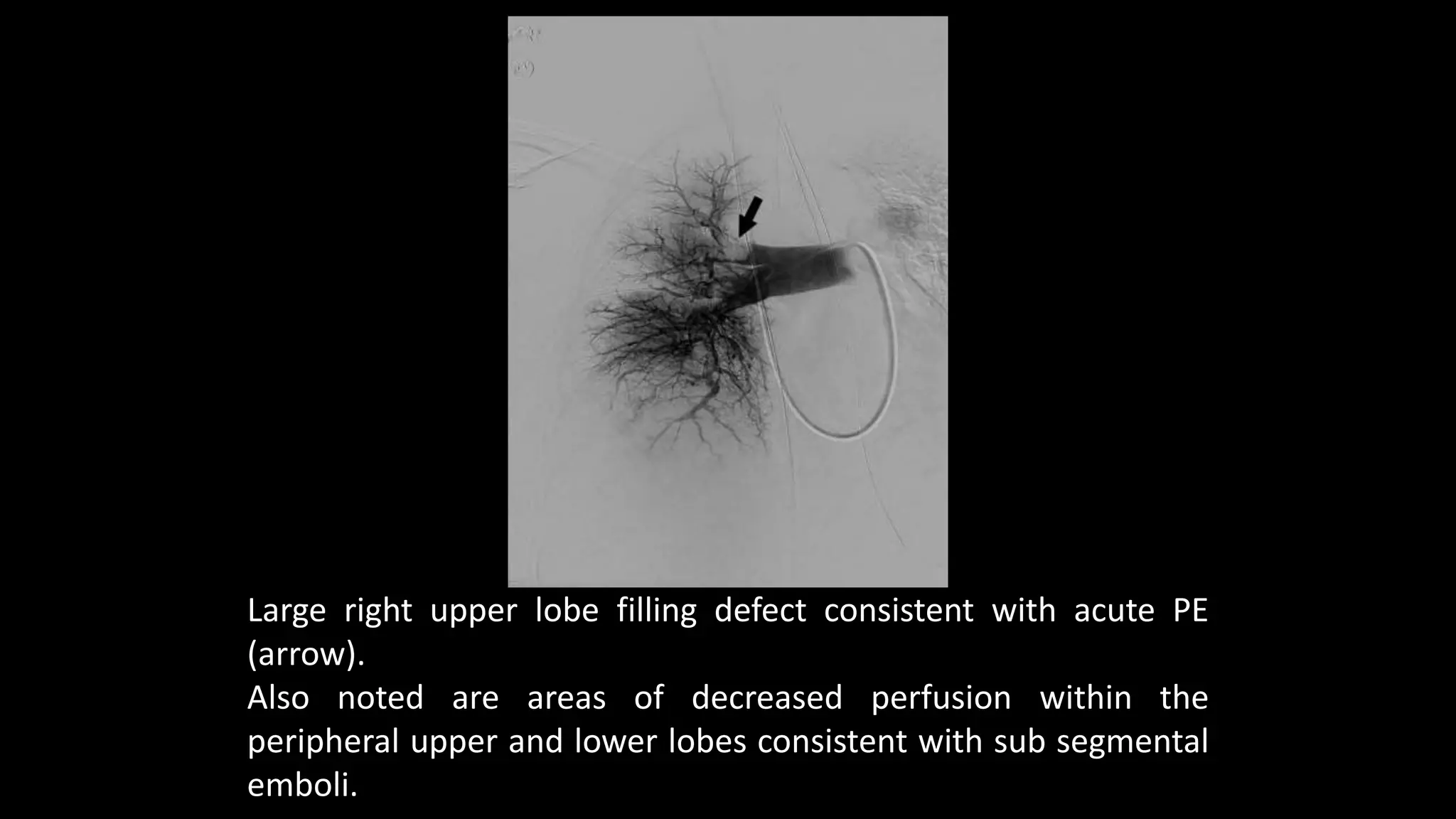
3) CT pulmonary angiography has become the initial test of choice due to its high sensitivity and specificity for detecting emboli as well as being readily available and minimally invasive. Ventilation-perfusion scanning provides functional information and has a lower radiation dose

















![Ventilation-perfusion lung
scintigraphy
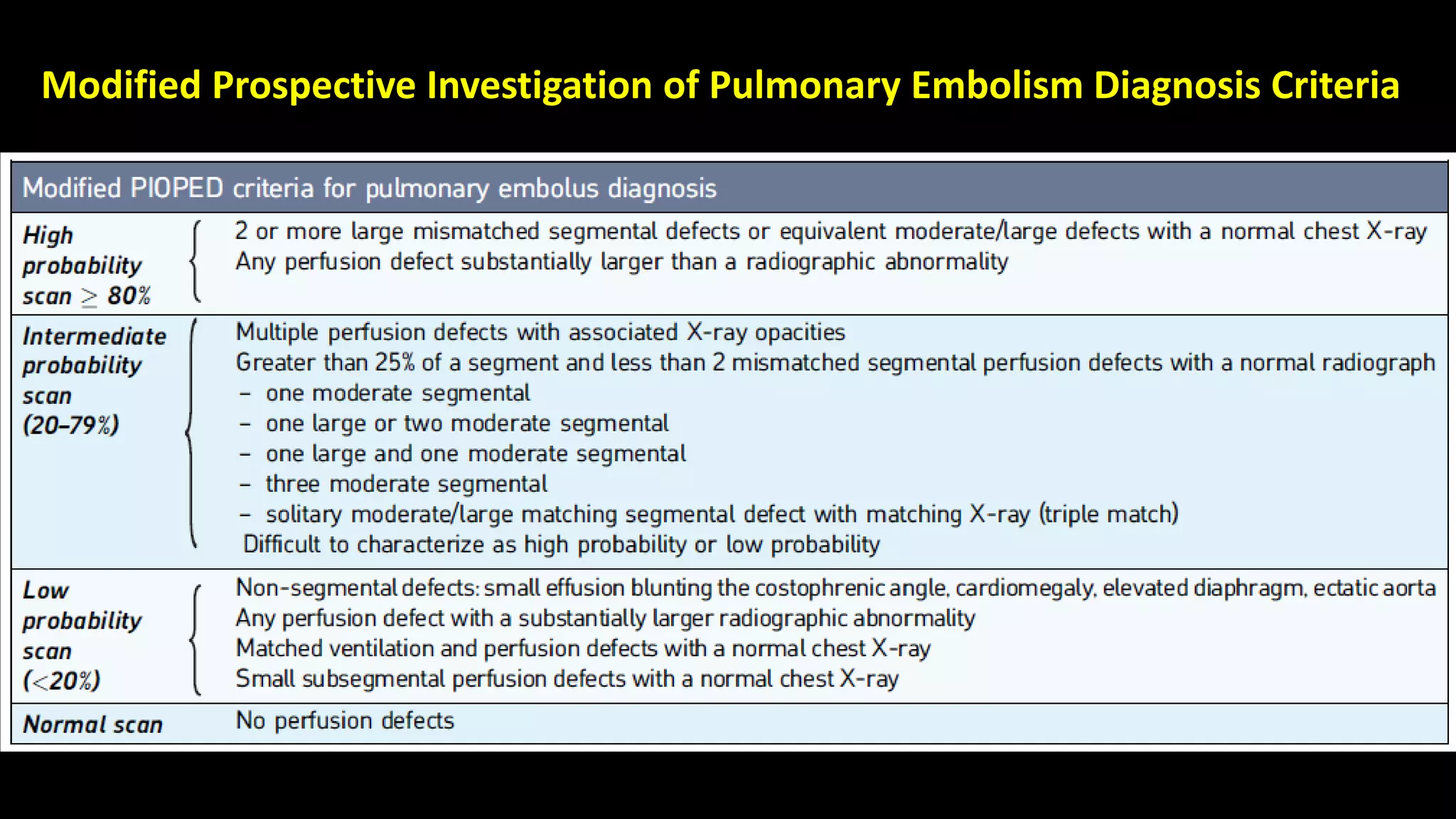
• Although CTPA is the current gold standard, VQ scan is preferred,
particularly renal failure, contrast material allergies, young females, and
patients who cannot fit into the CT scanner.
• VQ scan has 50-fold lower radiation dose to the breast (0.28–0.9 vs. 50–80
mSv in 64 slice CT) , which makes it useful in young females, including
those who are pregnant.
• Ventilation agents
• aerosolized technetium-99m (Tc-99m) labeled agents [diethylene-
triamine-penta-acetic acid (DTPA), sulfur colloid, and ultrafine carbon
suspensions] and
• radioactive noble gases [Krypton-81m and Xenon-133
• Perfusion portion is performed following the intravenous injection of
200,000–700,000 particles of Tc-99m labeled macro-aggregated albumin
(MAA).](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pulmonaryembolismimaging-190505165517/75/Pulmonary-embolism-imaging-23-2048.jpg)






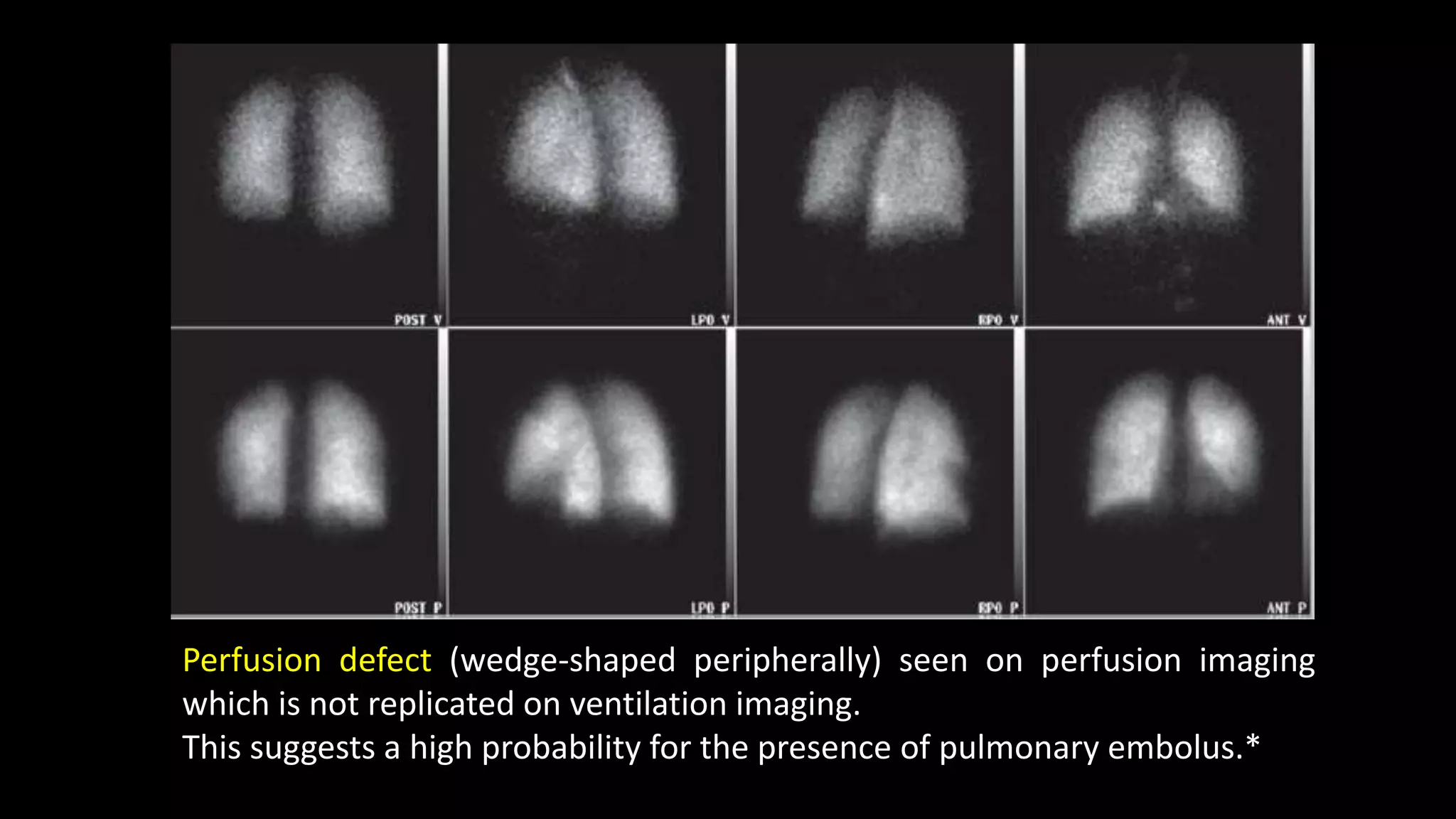
![Normal V/Q study
Ventilation [v] images on top row and perfusion [p] images beneath.
No defects are seen in either series.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pulmonaryembolismimaging-190505165517/75/Pulmonary-embolism-imaging-31-2048.jpg)