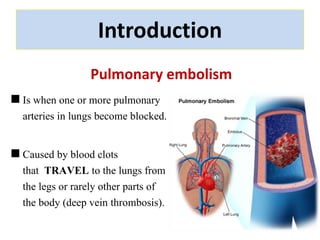
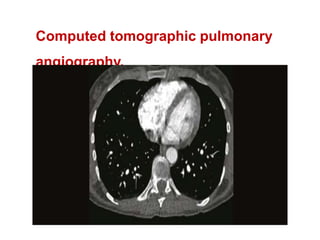
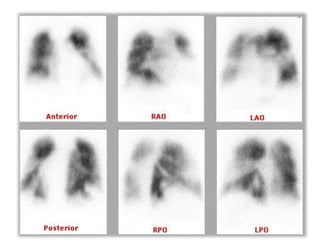
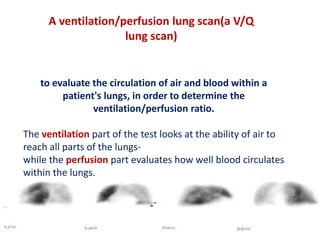
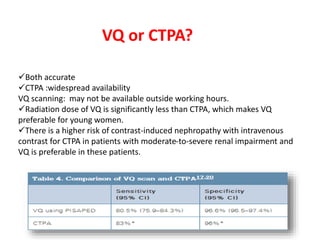
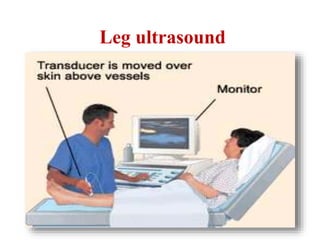
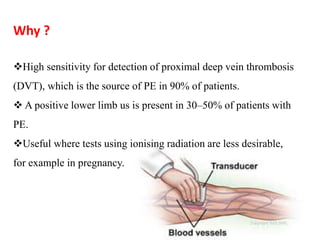
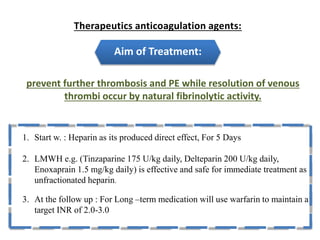
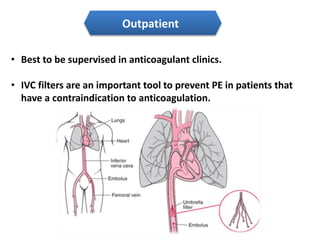
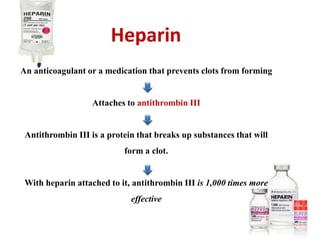
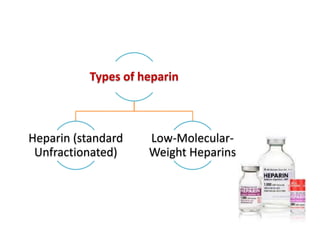
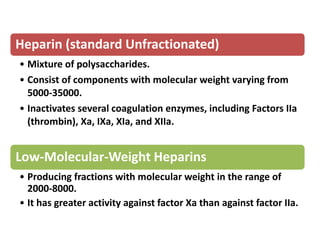
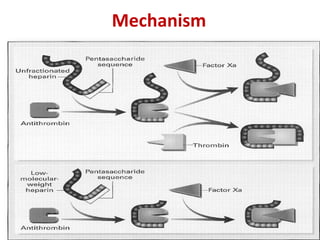
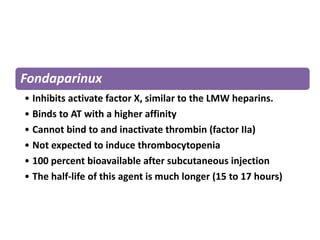
Maryam AL-Qahtani presented on pulmonary embolism. The key investigations for a PE patient are a D-dimer test, CT pulmonary angiography, isotope lung scanning, and leg ultrasound. For treatment, anticoagulants like heparin, low molecular weight heparins (LMWH), and warfarin are given as prophylaxis or therapy. The types of heparin are unfractionated heparin and LMWH, which differs in molecular weight, activity against coagulation factors, side effects, and half-life. Physicians consider effectiveness, safety and cost when deciding which type of heparin to use.