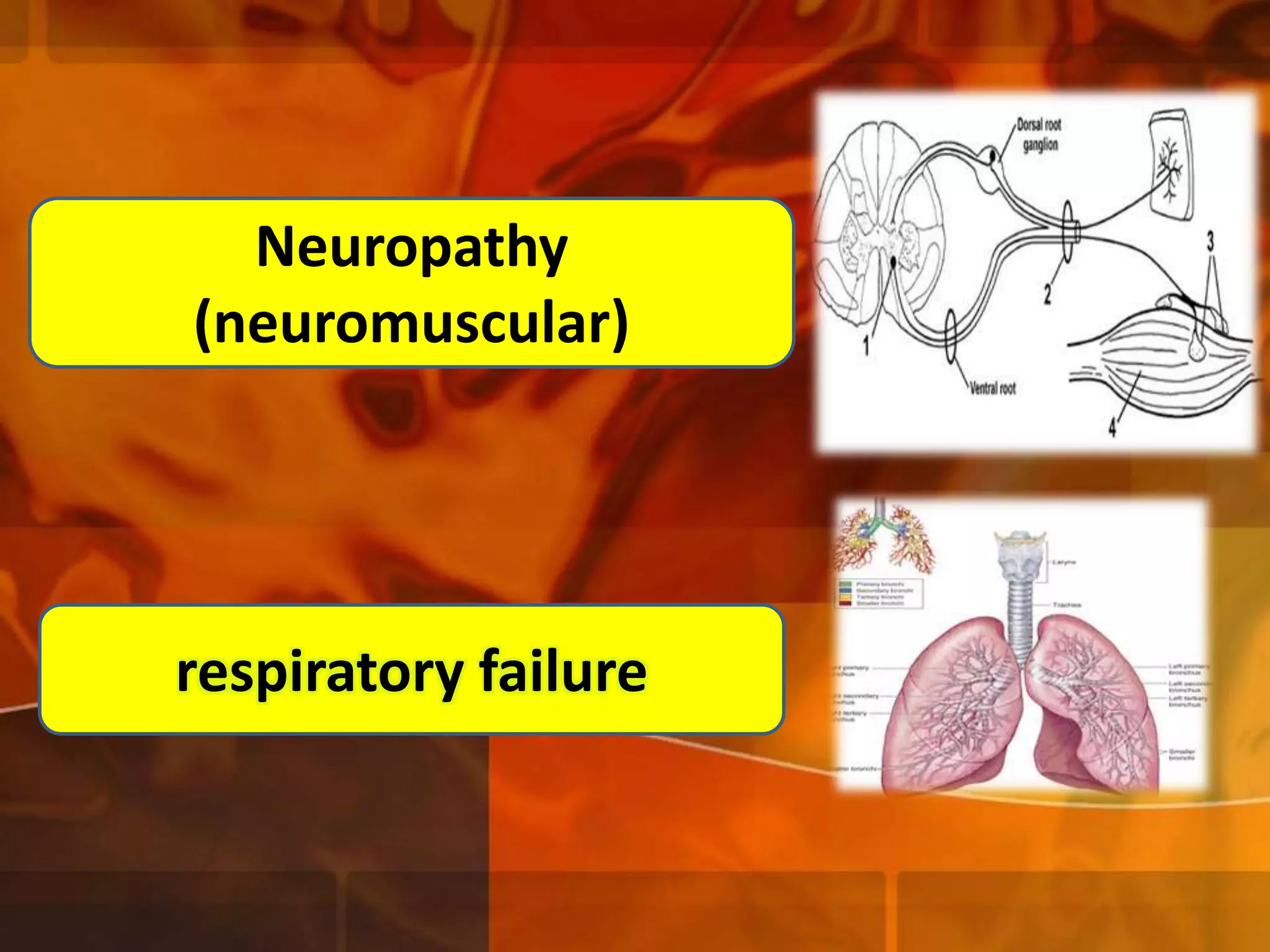
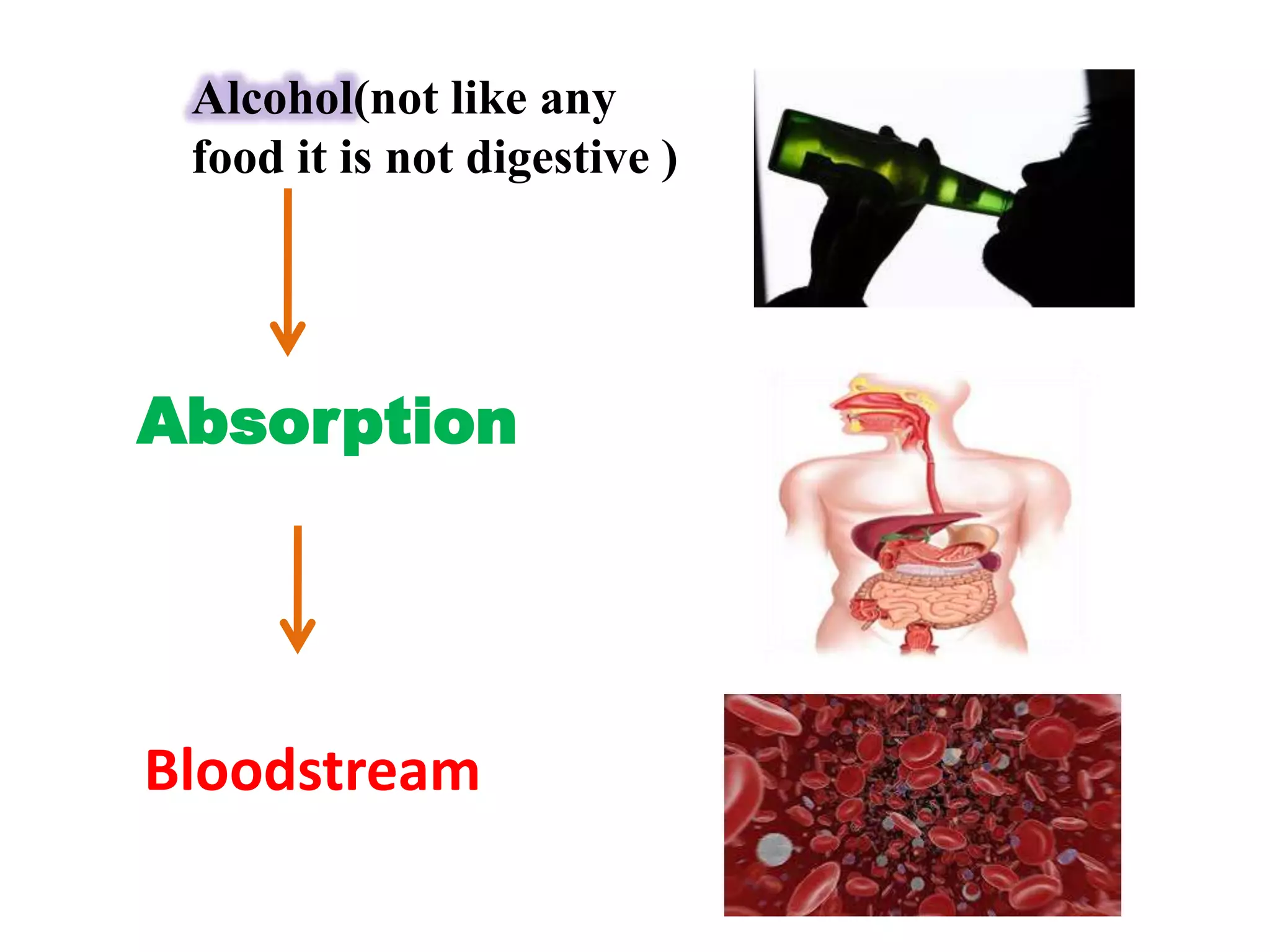
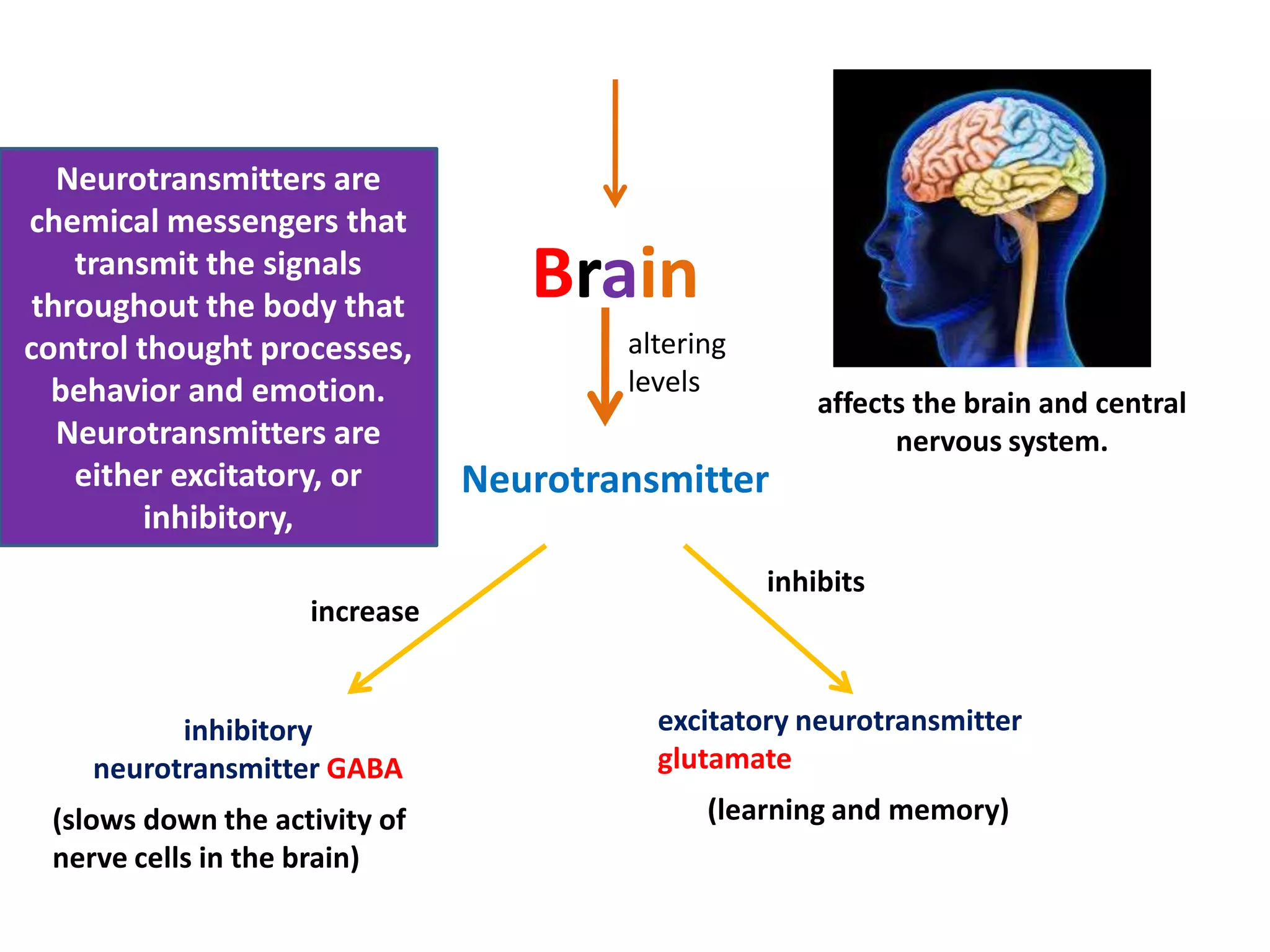
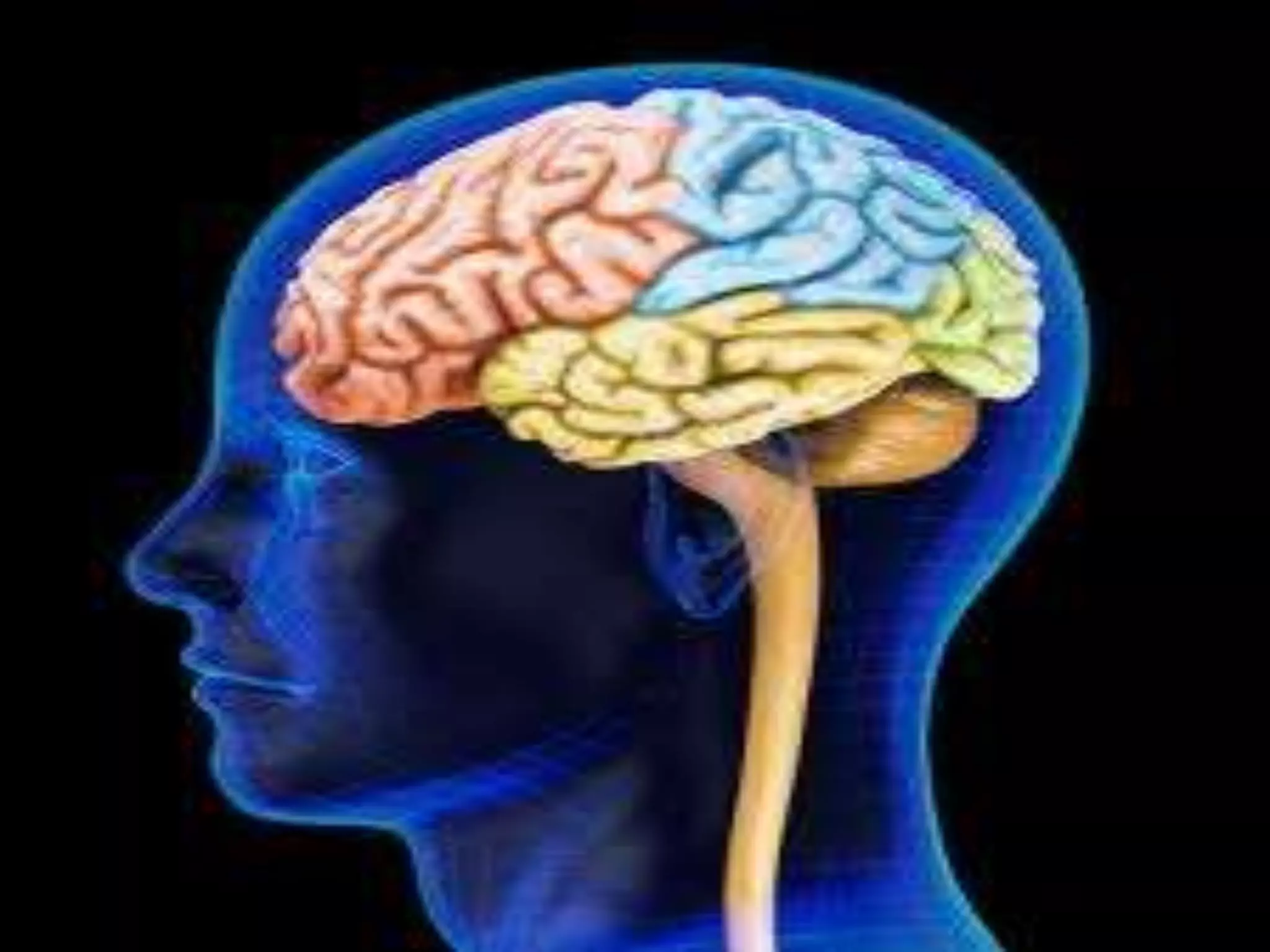
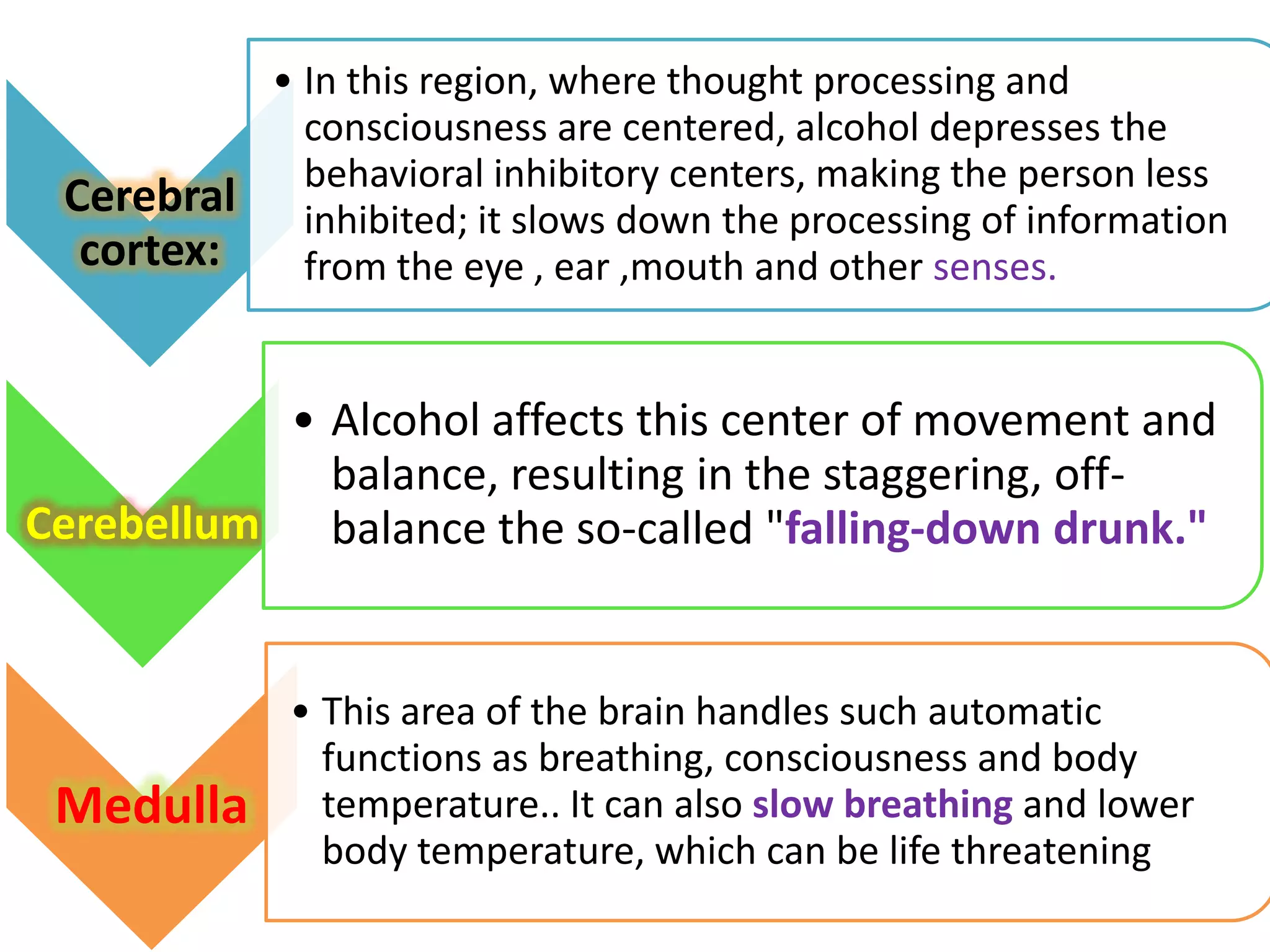
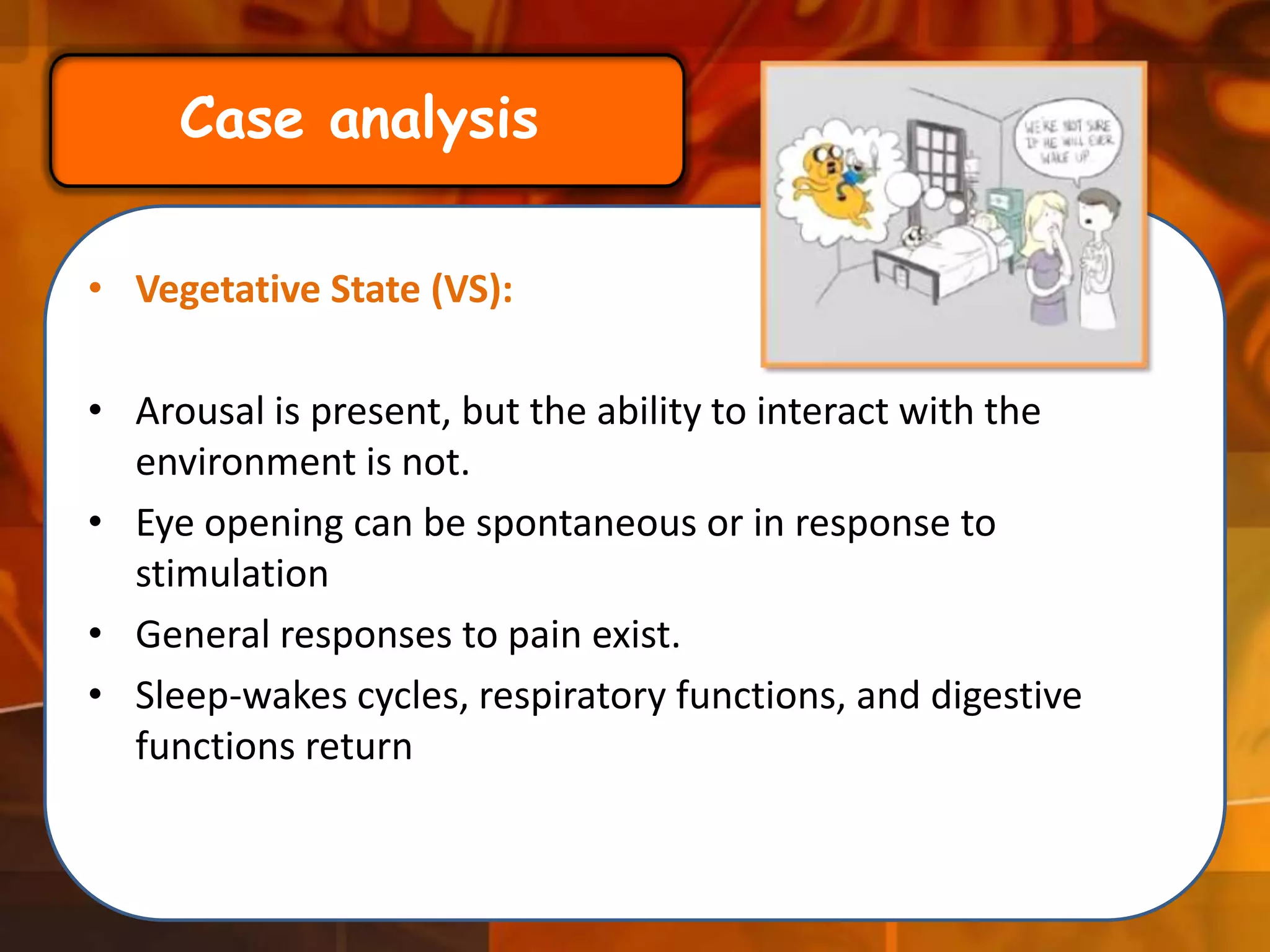
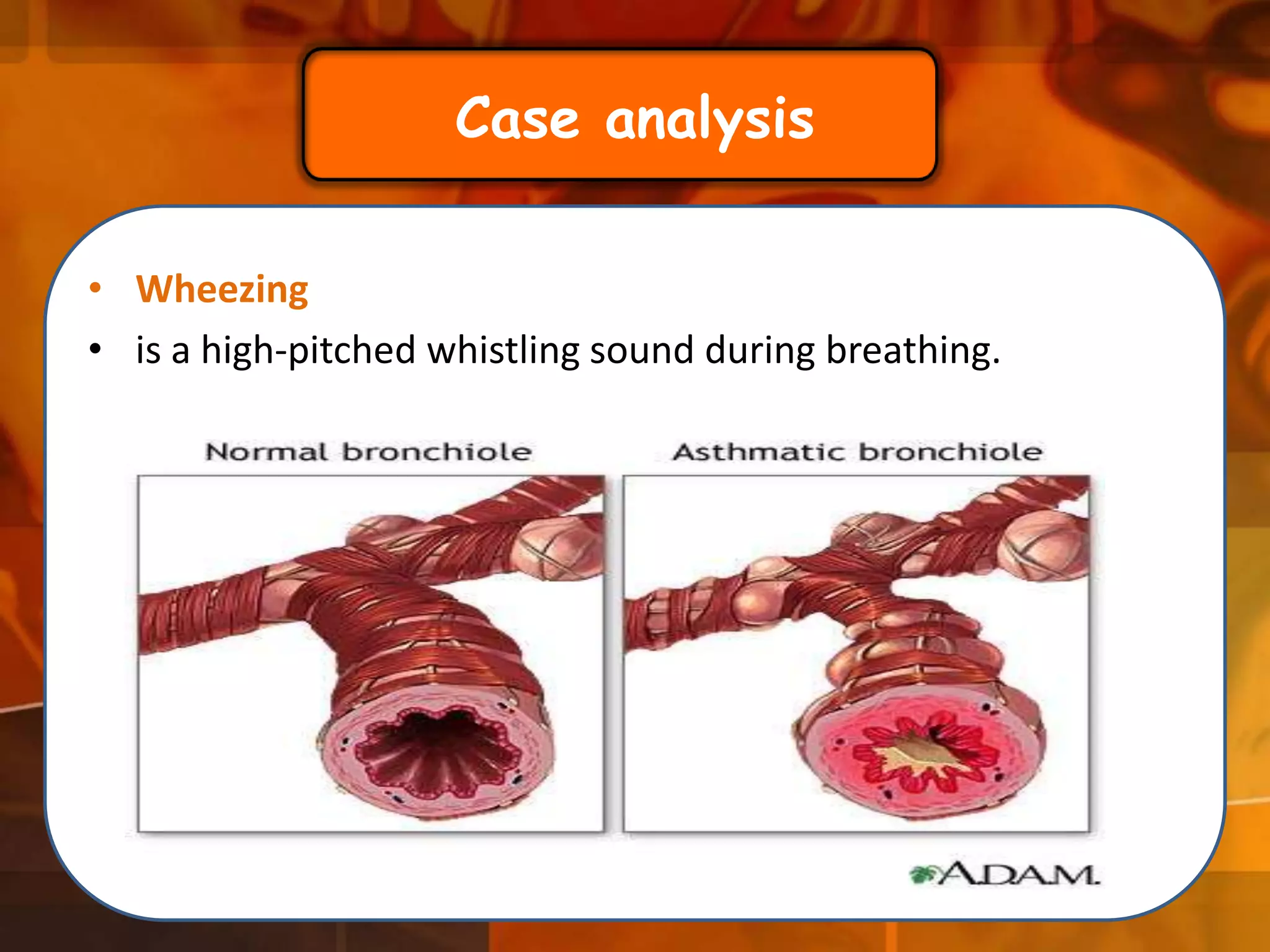
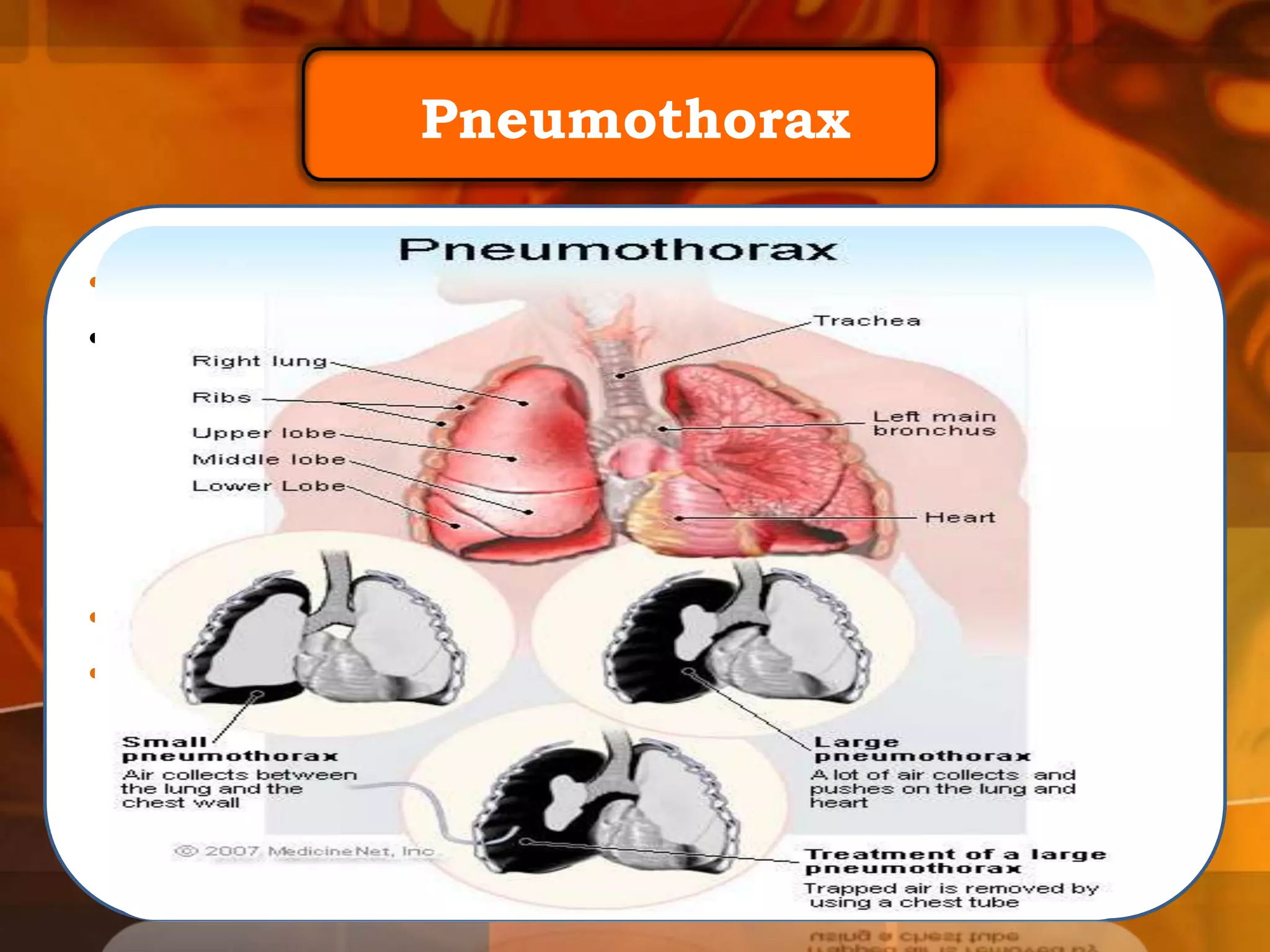
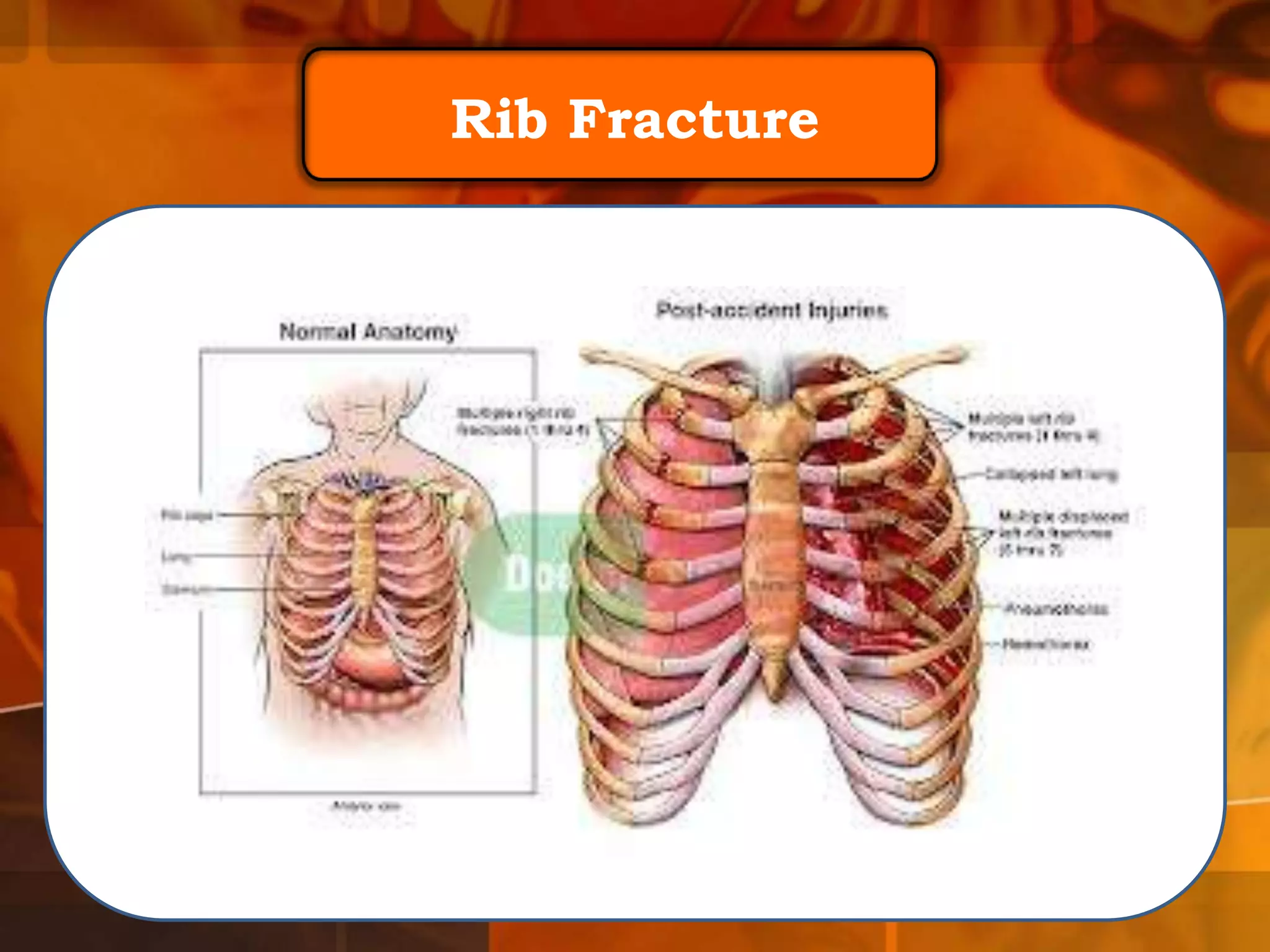
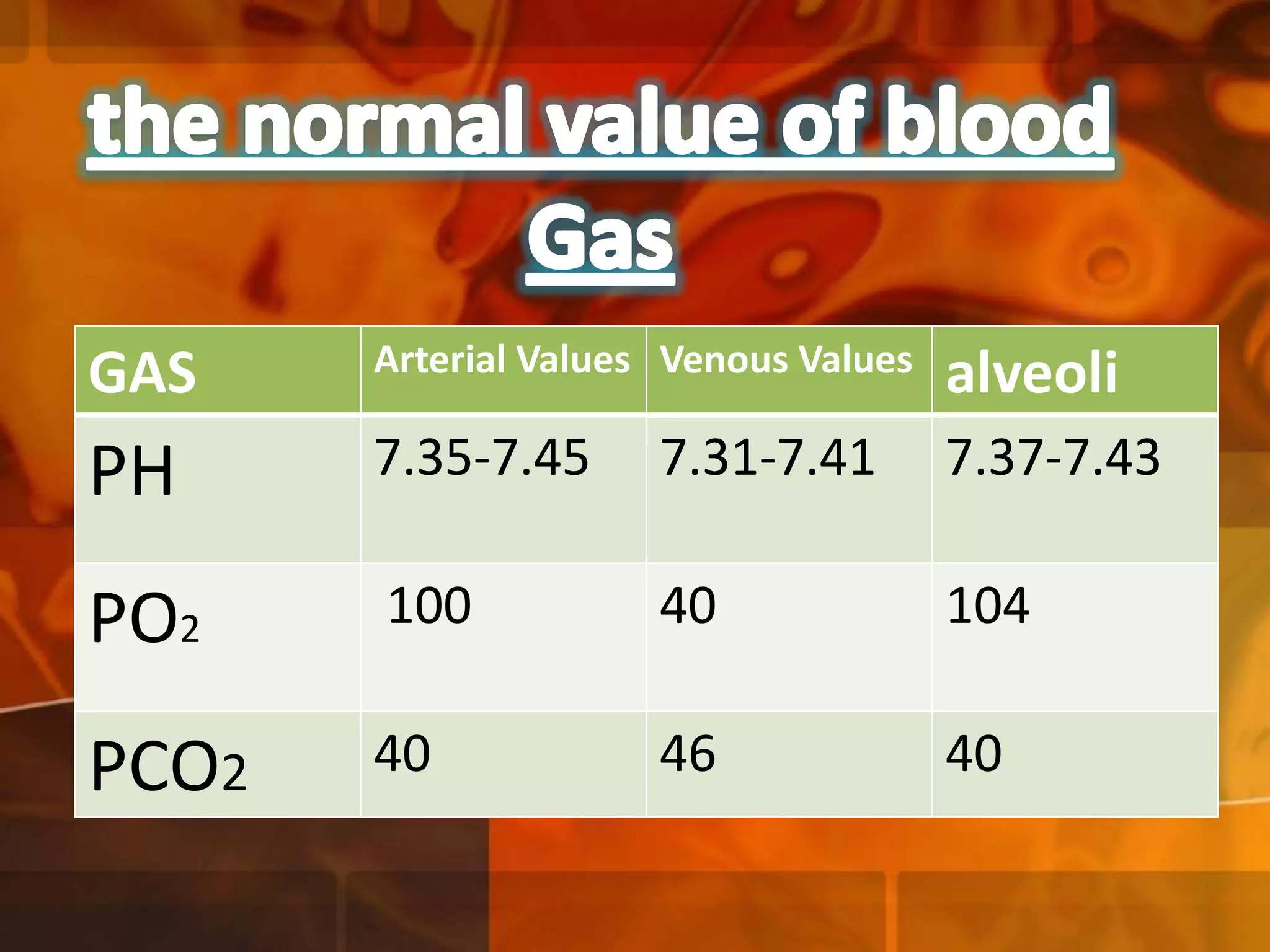
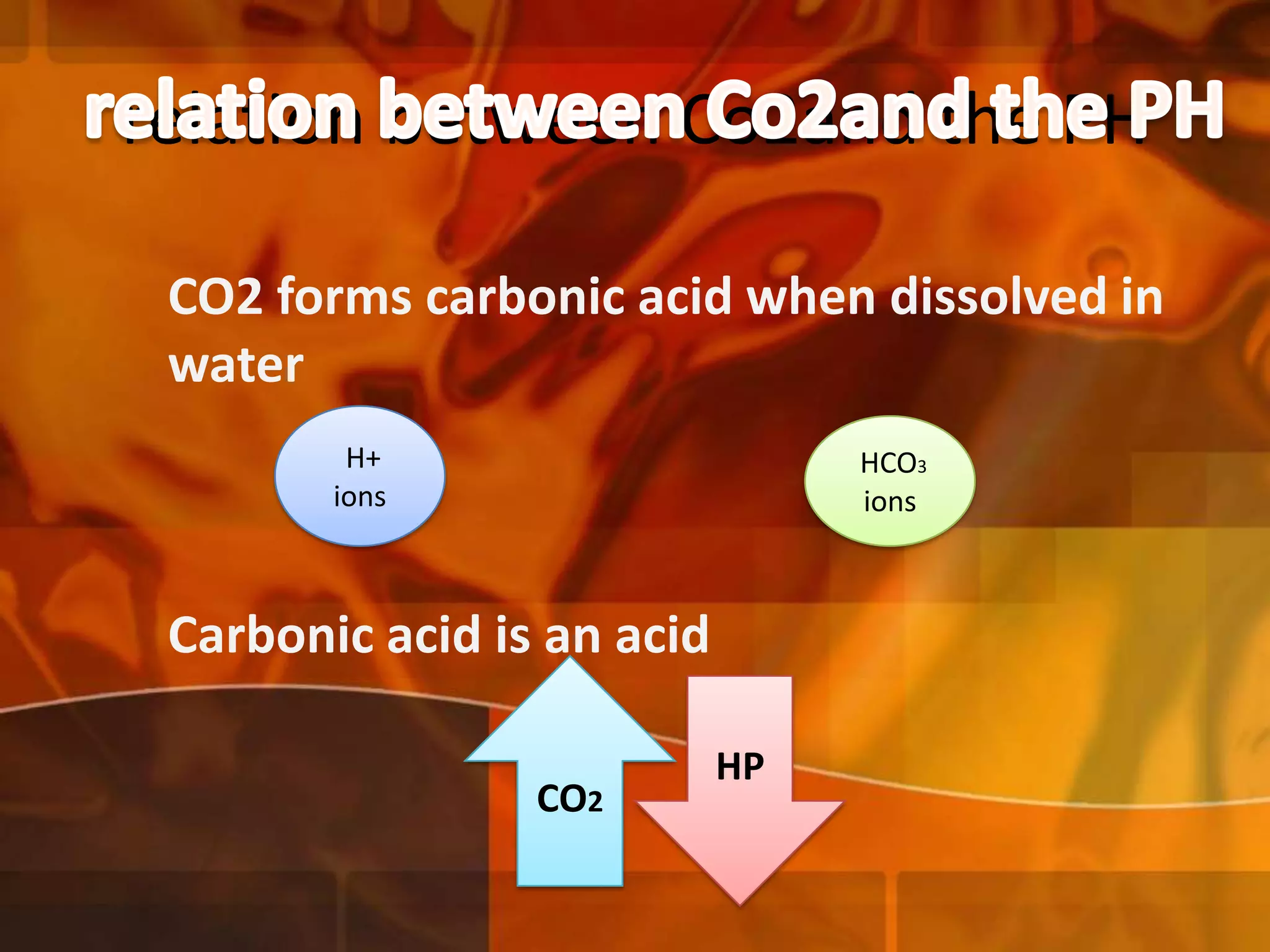
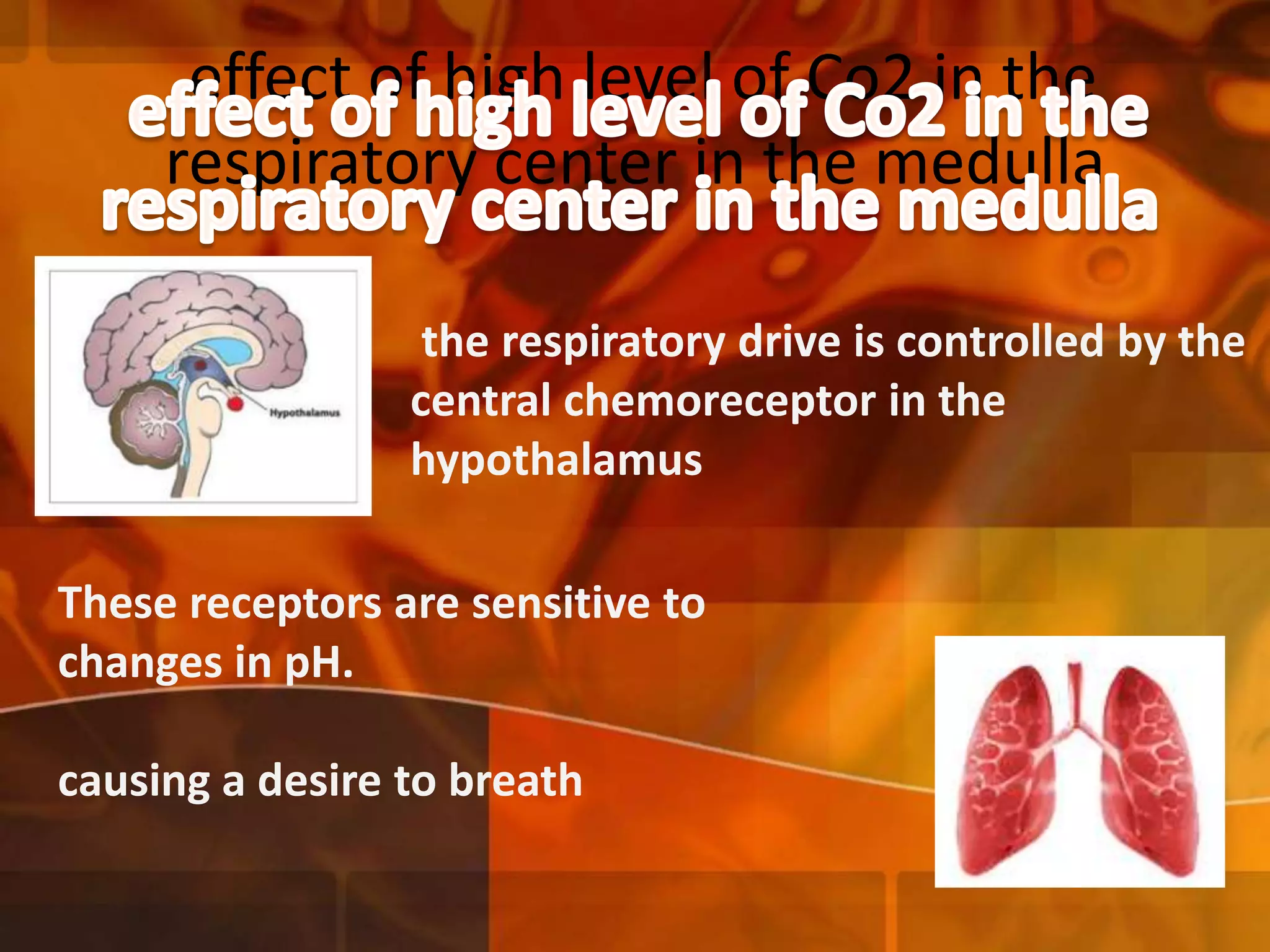
A 22-year-old man was brought to the emergency room after blacking out and falling at a coffee shop at 2am. On arrival, he smelled of alcohol and only responded to strong pain. He was wheezing with shallow, slow breathing and his left lung had minimal movement. Tests found low oxygen and high carbon dioxide levels in his blood. Examination revealed several fractured ribs on his left side. The man's condition and symptoms were likely due to alcohol intoxication leading to his fall, resulting in fractured ribs and a punctured lung causing shortness of breath.