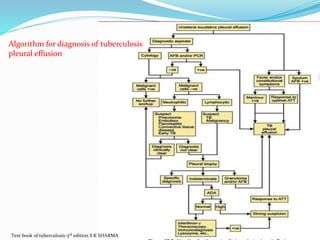
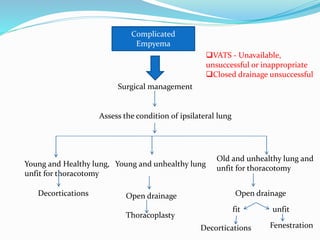
The document summarizes guidelines on the diagnosis and treatment of pleural tuberculosis. It discusses that pleural TB usually presents as a pleural effusion caused by the immune response to mycobacterial antigens in the pleural space. A diagnosis is made through diagnostic thoracentesis and examination of pleural fluid for characteristics of an exudative effusion as well as testing for adenosine deaminase levels and acid-fast bacilli. Treatment involves a standard 6-month course of anti-tubercular therapy. Complications can include fibrothorax, empyema, and bronchopleural fistula.




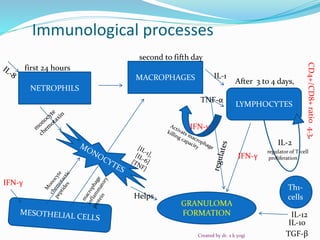
![ Nearly eight-fold increase in mycobactrial antigen sensitized T-
lymphocytes in pleural fluid than that found in the peripheral
blood
The ratio of CD4+ [helper-inducer] to CD8+
[suppressor/cytotoxic] lymphocytes is also much higher in TB
pleural fluid as compared to peripheral blood [3:4 vs 1:7] .
Significantly higher interferon-γ [IFN-γ] levels, suggestive of
predominantly T-helper cell type 1 [Th1] type immunity in the
pleural space.
Text book of tuberculosis-3rd edition S K SHARMA](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pleuraltb-200621163343/85/PLEURAL-TUBERCULOSIS-PLEURAL-EFFUSION-5-320.jpg)
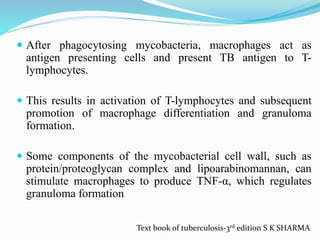
![CLINICAL MANIFESTATIONS
Tuberculosis pleural effusion is typically a disease Of young
men
< 1 month of duration
Non-productive cough [70%] and chest pain [75%] are the two
most common symptoms at presentation.
Fever, night sweats, weakness, weight loss, anorexia and
fatigue.
On physical examination
Non-specific signs of pleural effusion,
Dullness to percussion and the occasionally pleural rub at
auscultation
Text book of tuberculosis-3rd edition S K SHARMA](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pleuraltb-200621163343/85/PLEURAL-TUBERCULOSIS-PLEURAL-EFFUSION-8-320.jpg)



![Sputum samples for microscopy
In selected patients whenever concurrent pulmonary and pleural TB
is suspected.
Tuberculin Skin Test
In a patient with exudative pleural effusion , positive tuberculin skin
test [TST] strongly suggests the diagnosis of TB, in populations with
a low prevalence of TB infection,
Whereas the diagnostic value is lower in countries with a high
prevalence of TB.
NO Recommendation by INDEX –TB GUIDLINES](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pleuraltb-200621163343/85/PLEURAL-TUBERCULOSIS-PLEURAL-EFFUSION-14-320.jpg)


![Interferon-gamma
Estimation of pleural fluid IFN-γ levels is reported to be useful
in differentiating TB from other pleural fluids.
The IFN-γ can be estimated either by enzyme-linked
immunosorbent assay [ELISA] or radioimmunoassay [RIA].
IFN-γ levels in patients with TB pleurisy are high, with
sensitivity and specificity ranging from 90 to 100 per cent.
Expensive and still not widely available in india .
NO Recommendation by INDEX –TB GUIDLINES
Text book of tuberculosis-3rd edition S K SHARMA](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pleuraltb-200621163343/85/PLEURAL-TUBERCULOSIS-PLEURAL-EFFUSION-20-320.jpg)