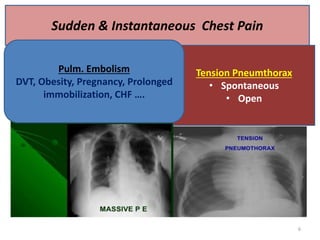
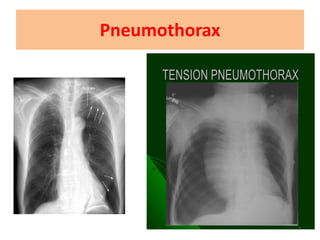
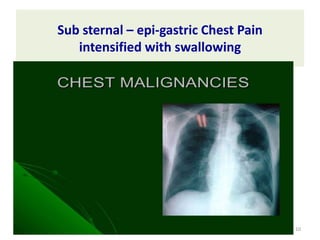
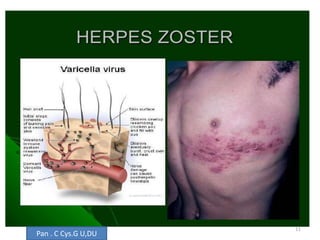
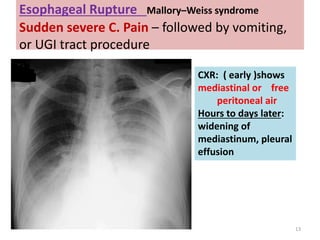
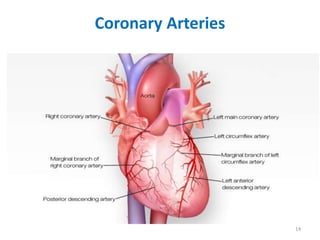
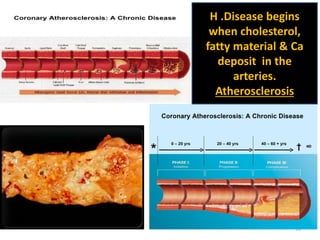
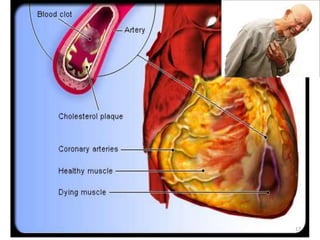
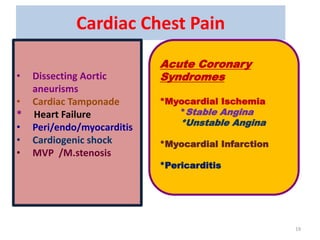
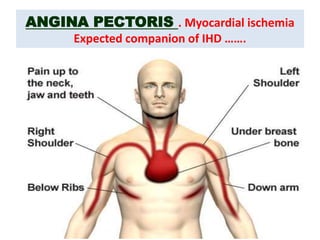
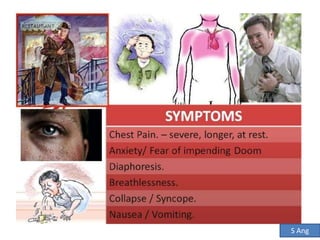
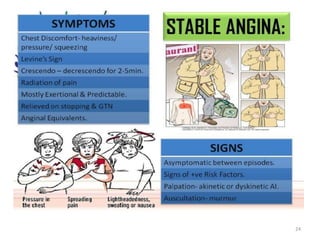
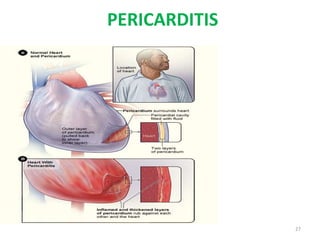
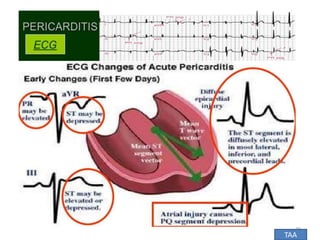
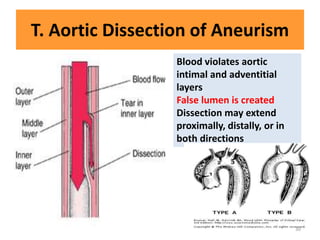
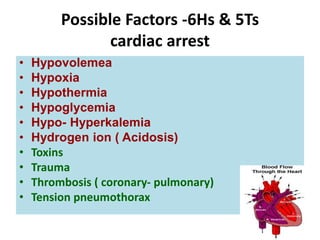
This document discusses the differential diagnosis of chest pain by describing various cardiac and non-cardiac causes. It outlines key factors in the history and physical exam that can help determine if chest pain is typical angina, atypical angina, or non-anginal. Common cardiac causes discussed include acute coronary syndromes, aortic dissection, and pericarditis. Common non-cardiac causes discussed include pulmonary embolism, pneumonia, gastrointestinal issues like pancreatitis and peptic ulcer disease. Diagnostic tests for different conditions are also mentioned.