Embed presentation
Downloaded 280 times

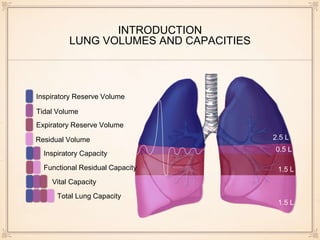
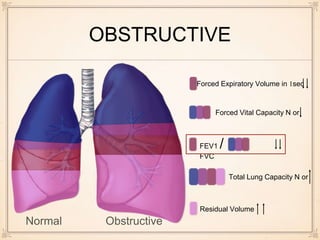
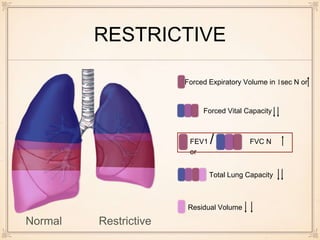



This document discusses the differences between restrictive and obstructive lung diseases. Restrictive lung diseases are characterized by a reduction in total lung capacity below 80% of predicted value, while obstructive lung diseases are characterized by a reduction in airflow, seen through a decreased forced expiratory volume in 1 second and ratio of forced expiratory volume to forced vital capacity. Key lung volumes and capacities such as tidal volume, inspiratory reserve volume, and residual volume are also defined.





