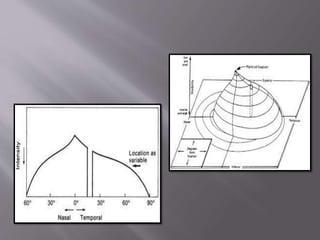
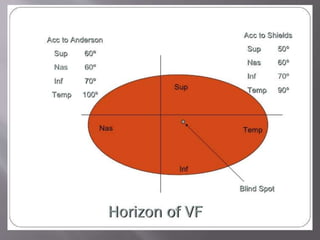
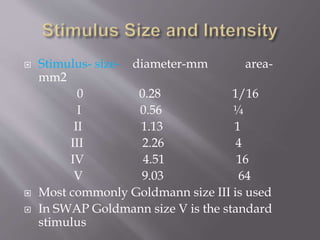
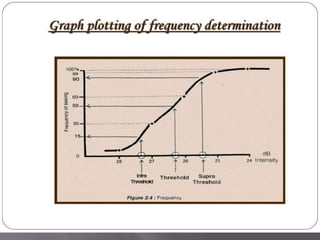
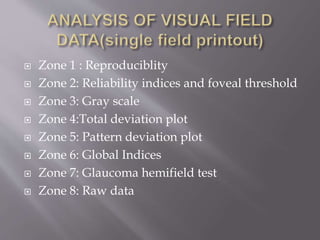
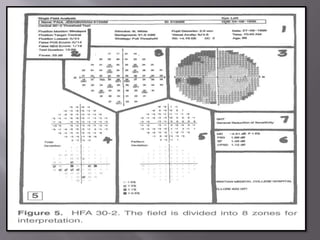
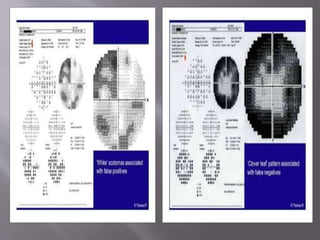
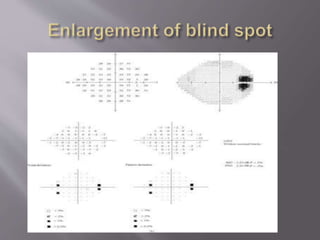
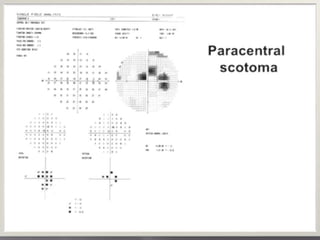
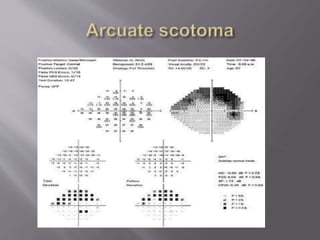
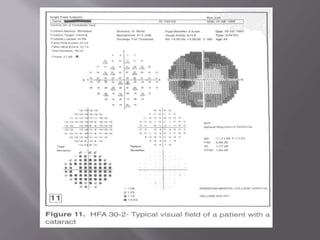
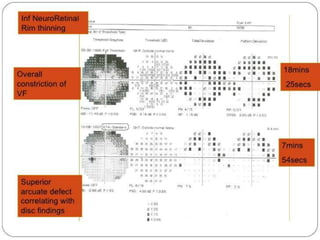
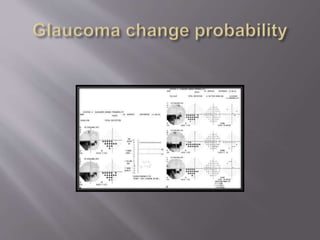
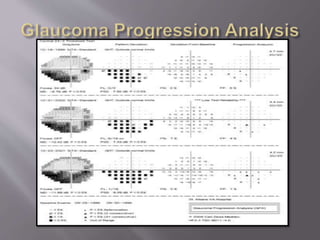
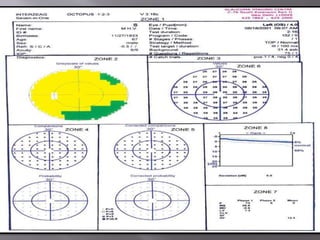
This document discusses visual field testing and perimetry. It defines visual field as the area that can be seen around a central point of fixation. Perimetry involves systematically measuring light sensitivity across the visual field using techniques like kinetic and static perimetry. Common perimetry devices include Humphrey, Octopus, and Goldmann perimeter. The document outlines stimulus parameters, test strategies, interpretation of results, and alternative perimetry techniques targeting different retinal pathways.
































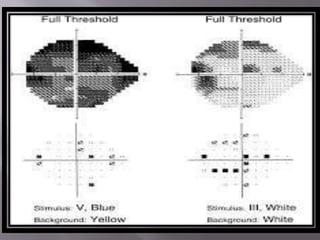
![ SWAP[Short Wave Automated Perimetry]
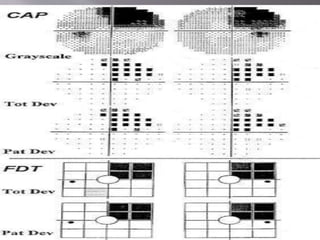
FDP[Frequency Doubling Perimetry]
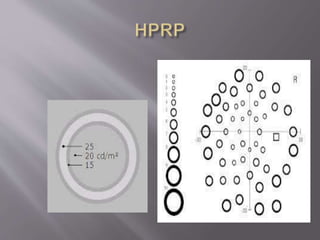
HPRP[High Pass Resolution Perimetry]
Flicker Perimetry
Multifocal Electroretinography
ACCUMAP[Multifocal Visual Evoked
Potential]
Motion Perimetry](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/automatedperimetry-160806125708/85/Automated-perimetry-50-320.jpg)