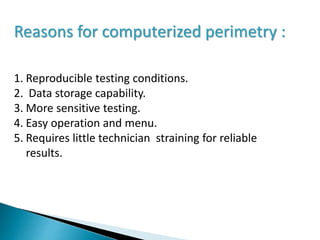
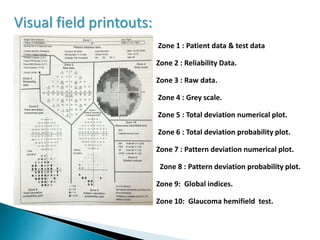
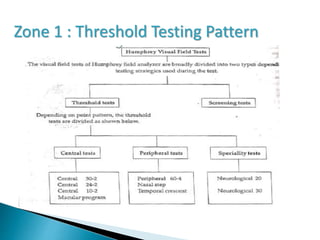
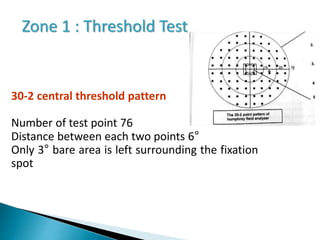
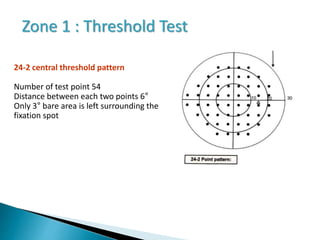
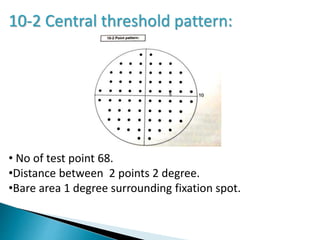
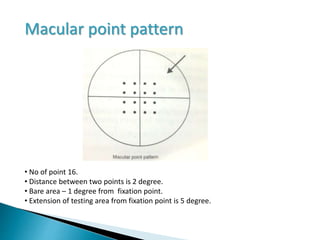
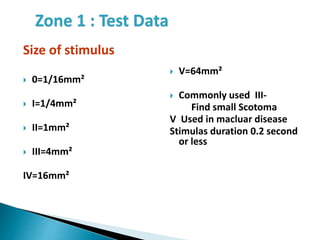
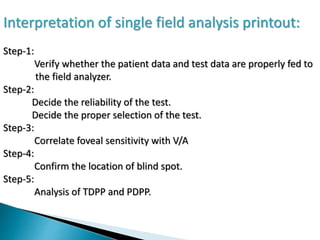
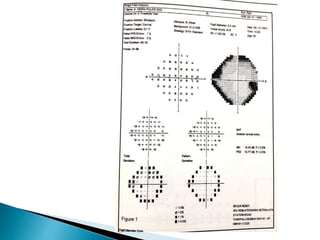
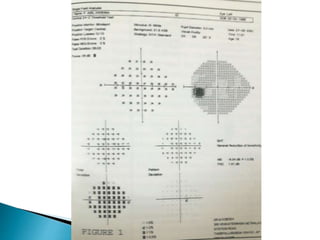
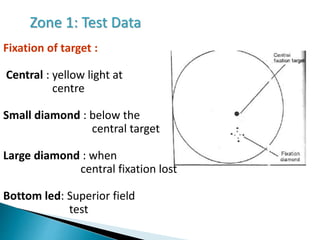
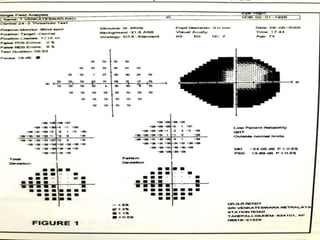
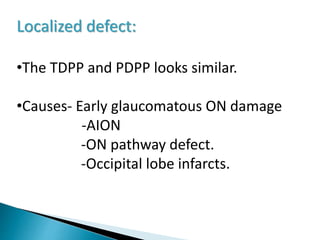
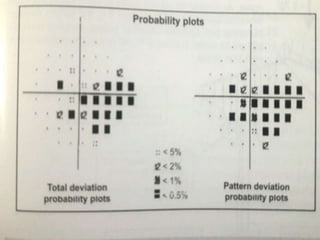
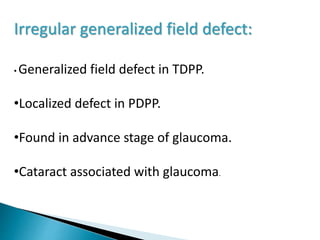
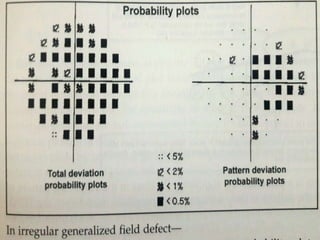
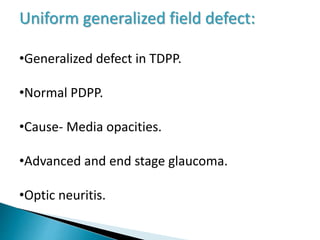
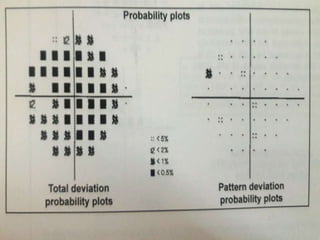
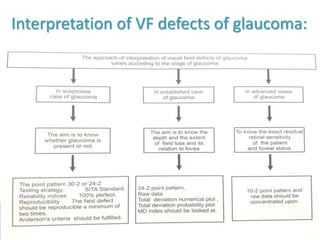
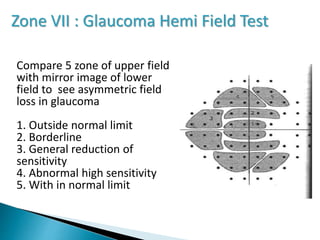
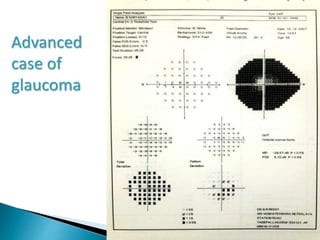
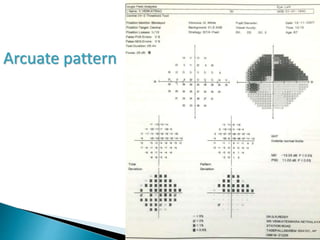
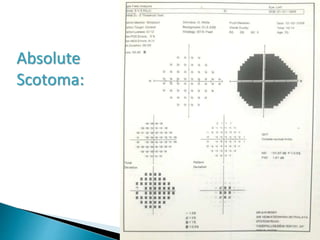
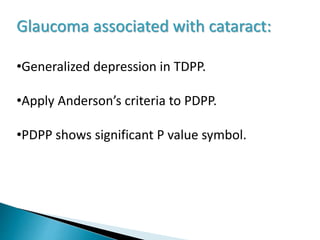
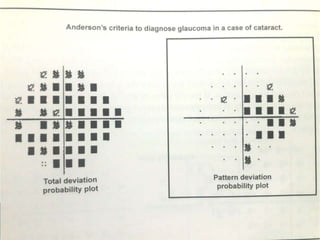
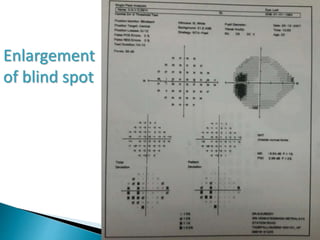
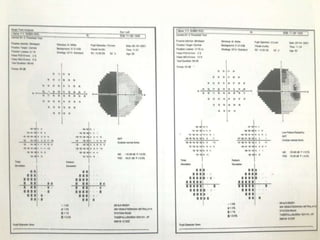
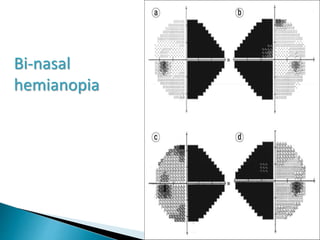
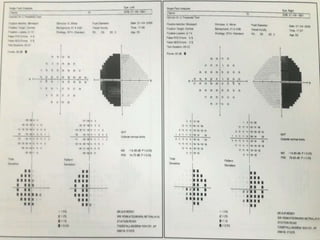
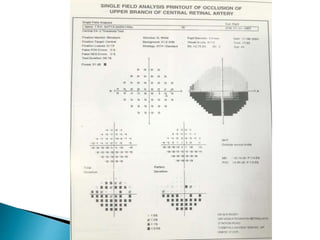
This document discusses perimetry and visual field testing. It begins by introducing the presenters and moderator of the discussion on perimetry. It then defines visual field and normal visual field limits. Perimetry is defined as the study of the visual field using an instrument called a perimeter. The document outlines the history of computerized perimetry and reasons for its use. Visual field testing is used to diagnose ocular and neurological conditions like glaucoma and brain tumors. Printouts from visual field tests are described and various visual field defects are interpreted. Factors like stimulus size, fixation, and refractive error and their effects on tests are covered. The role of visual field analysis in diagnosing neurological diseases and interpreting glaucom