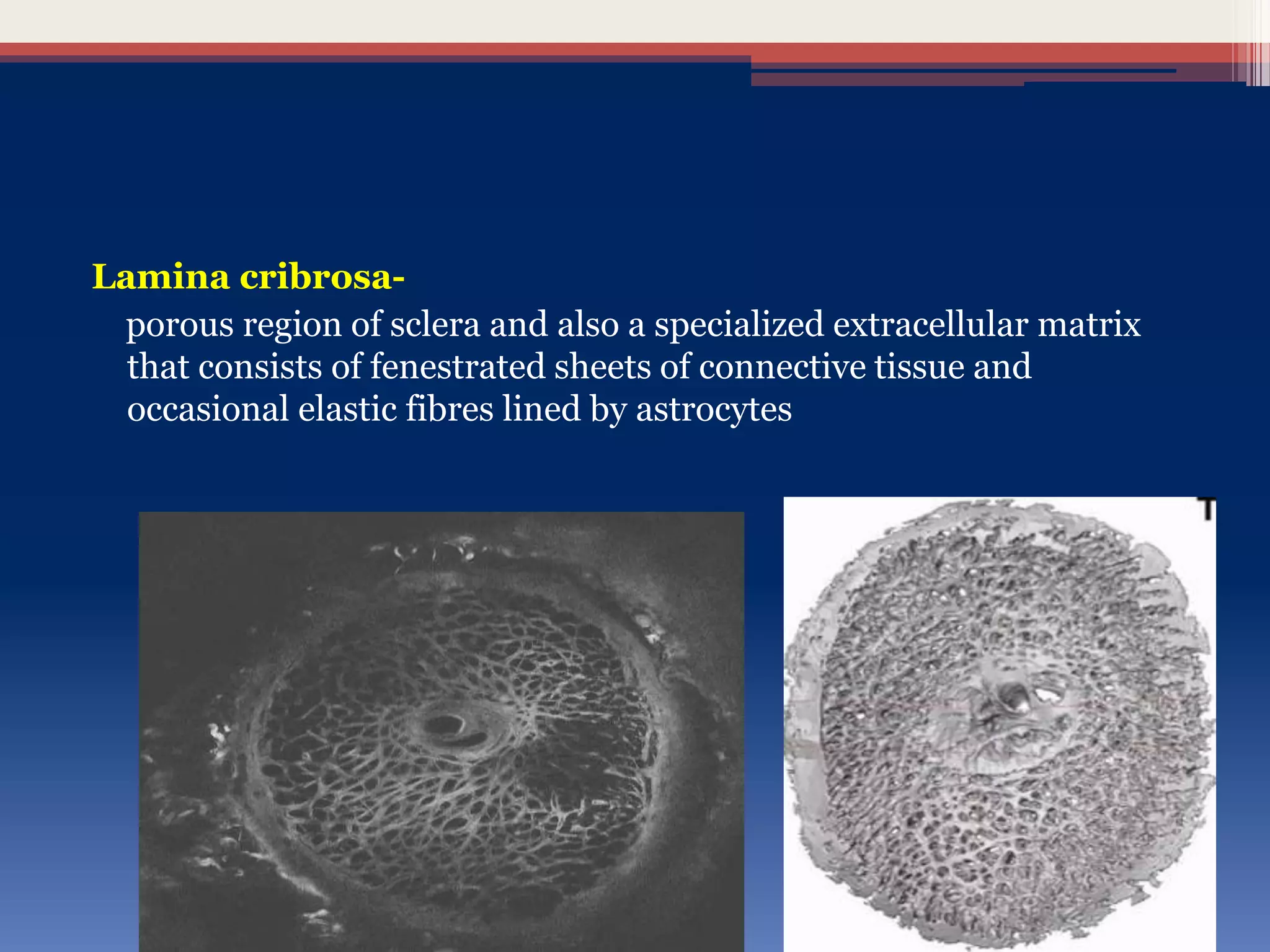
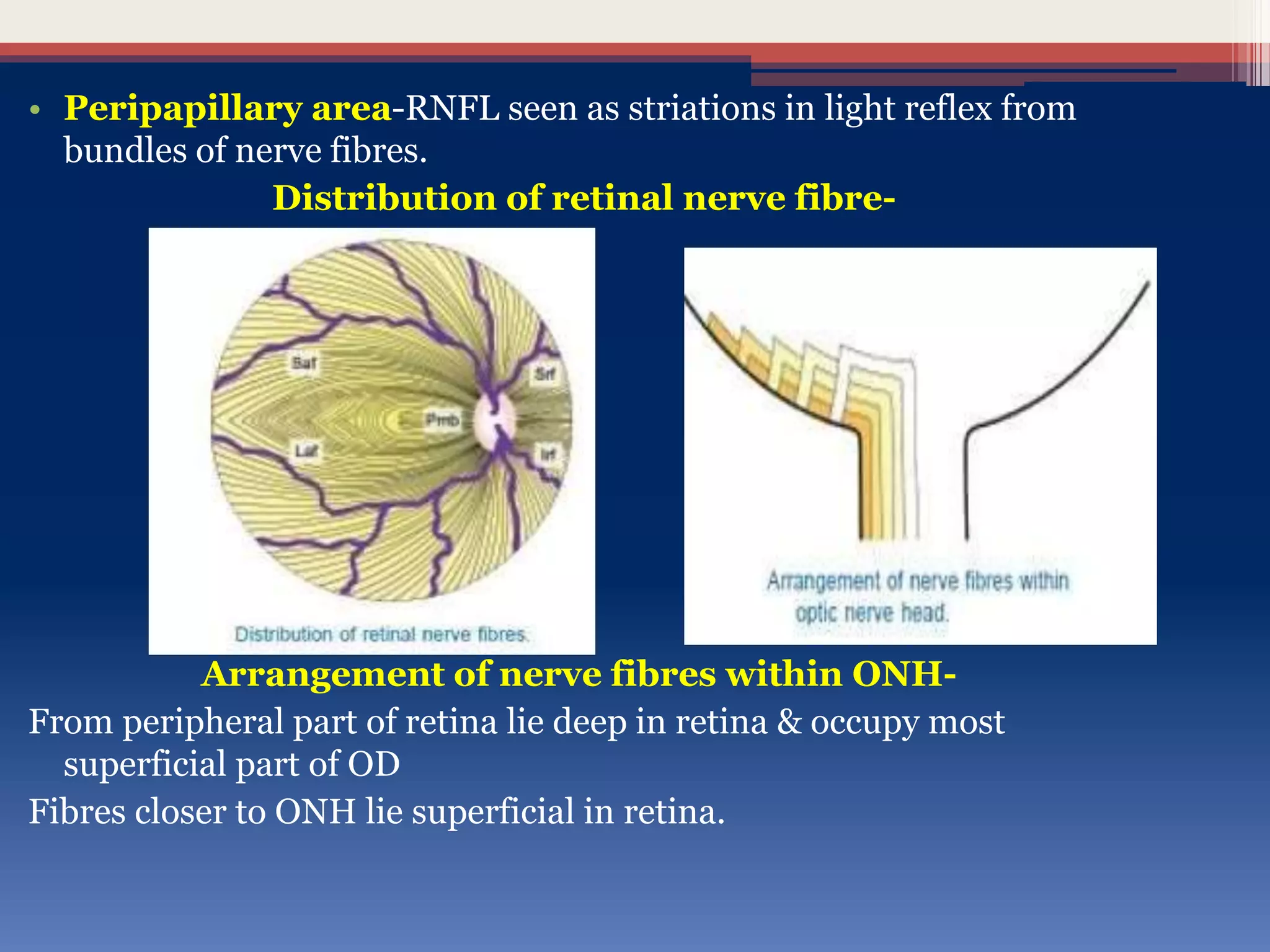
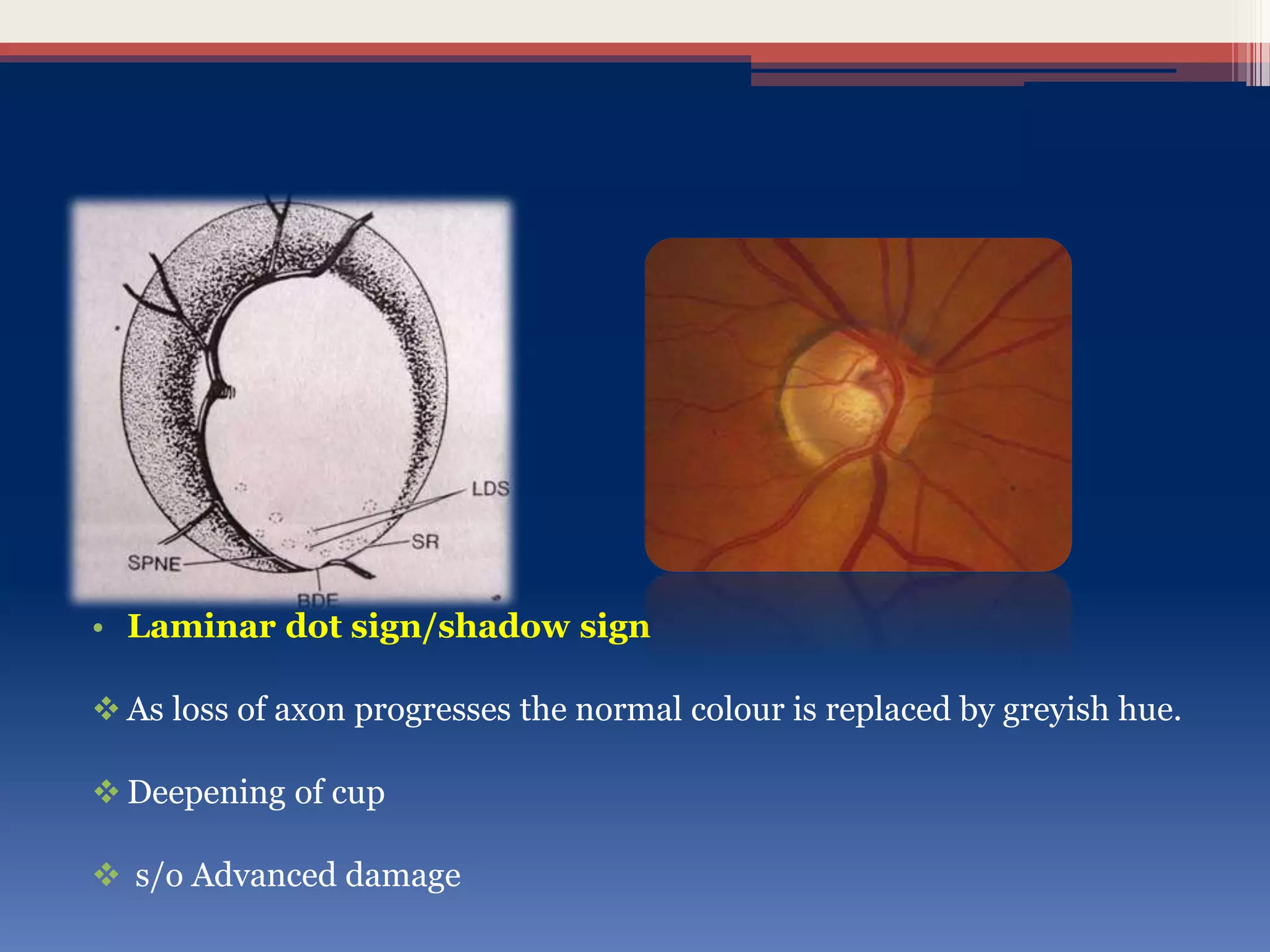
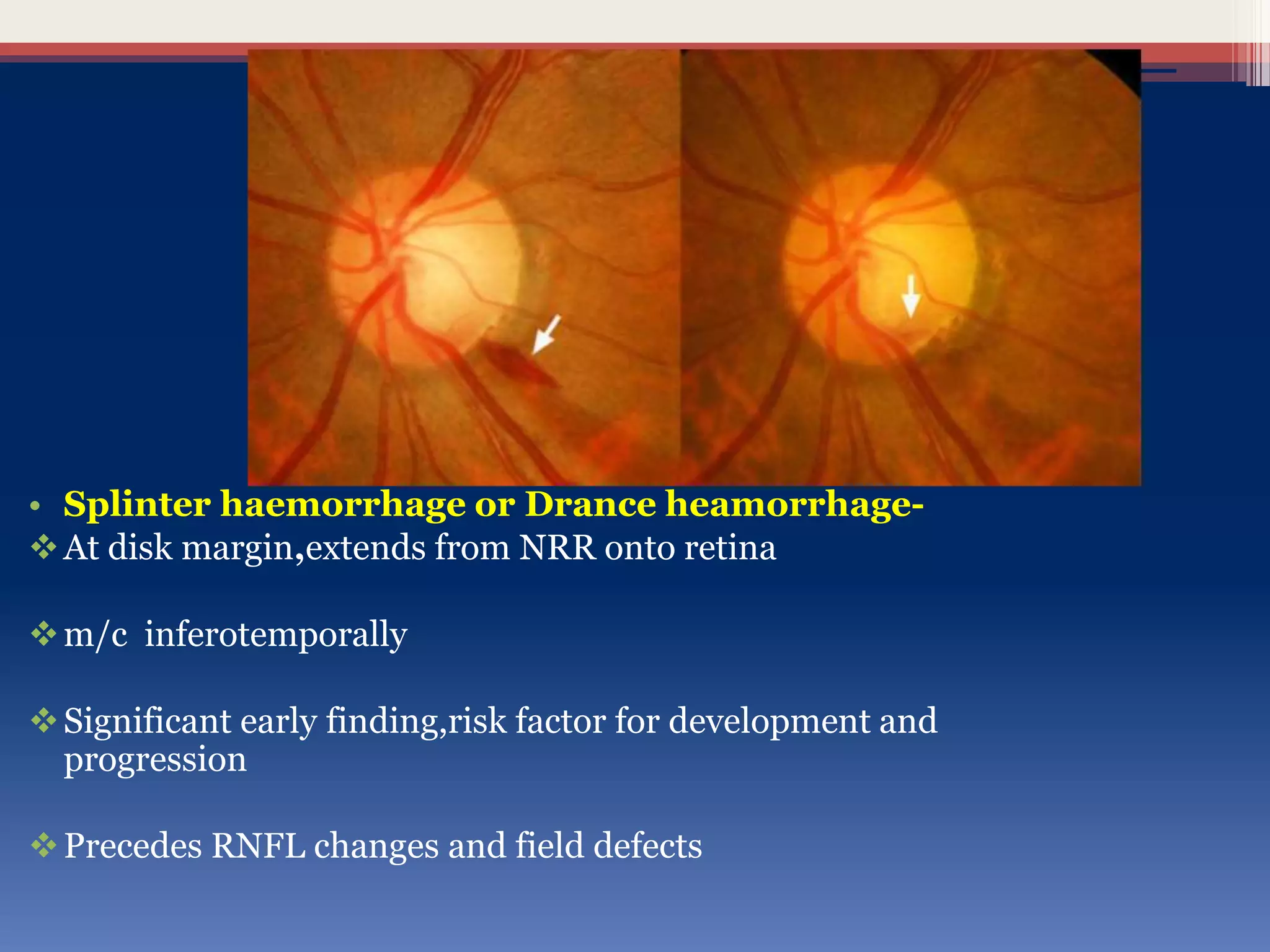
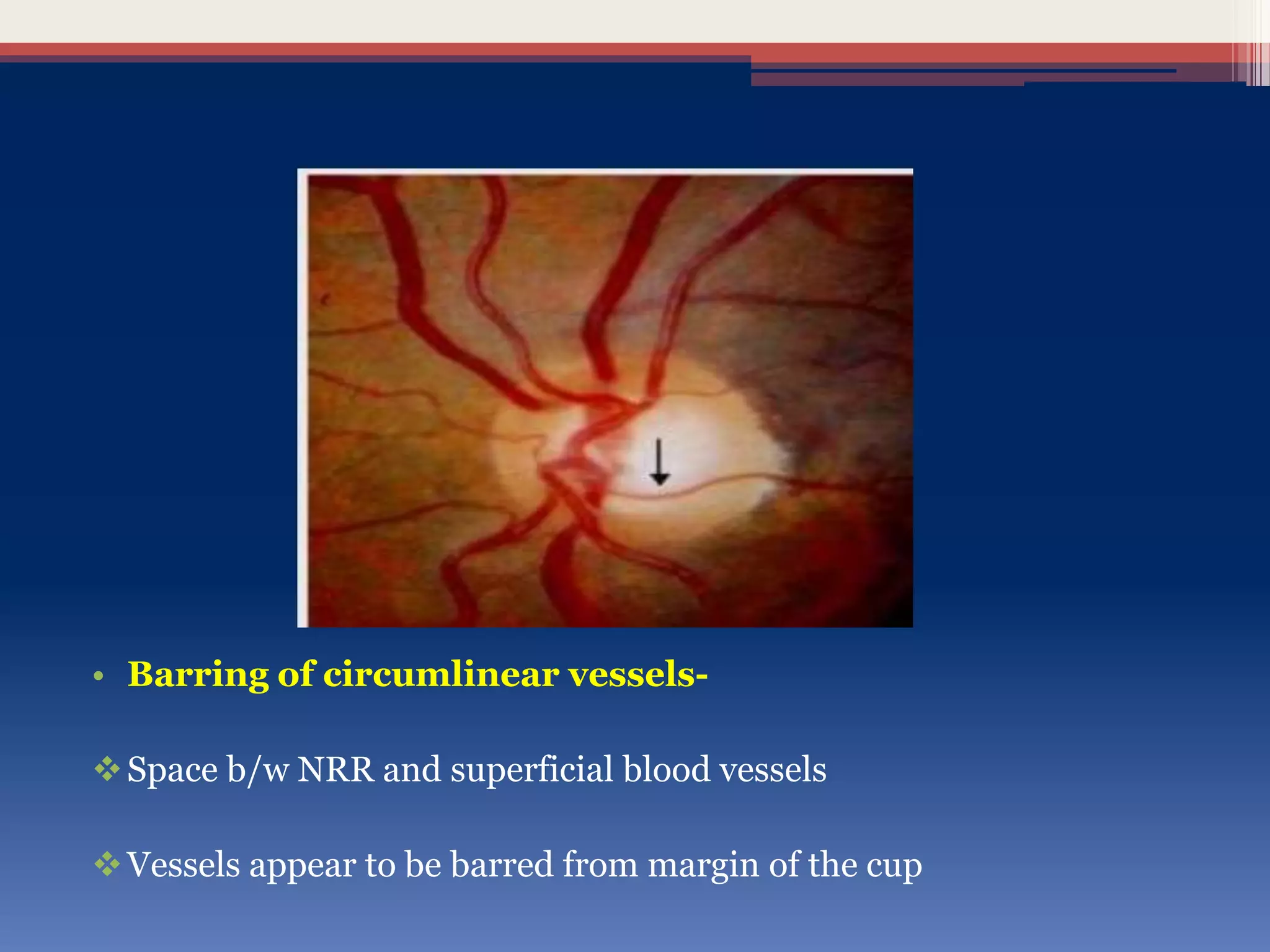
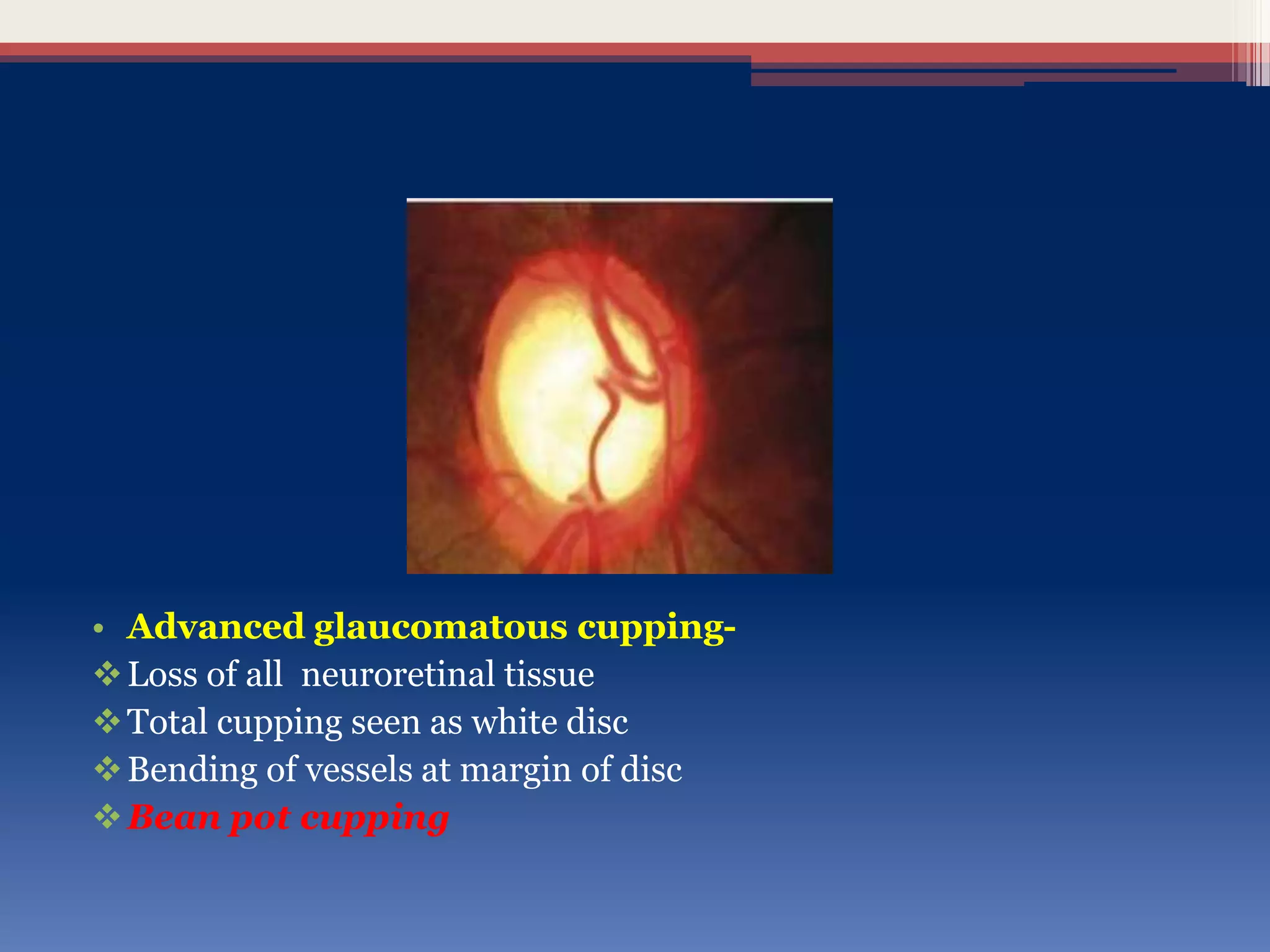
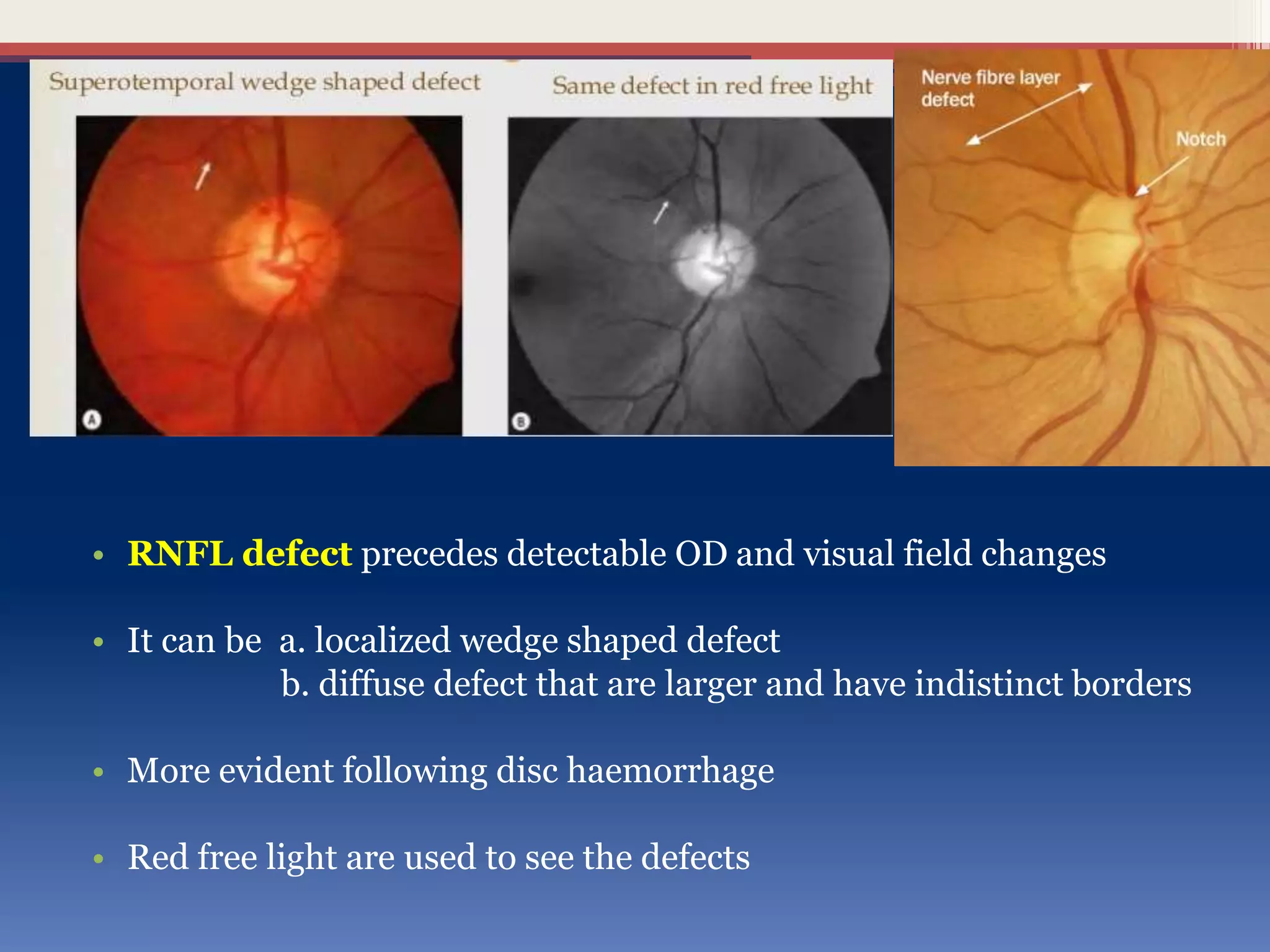
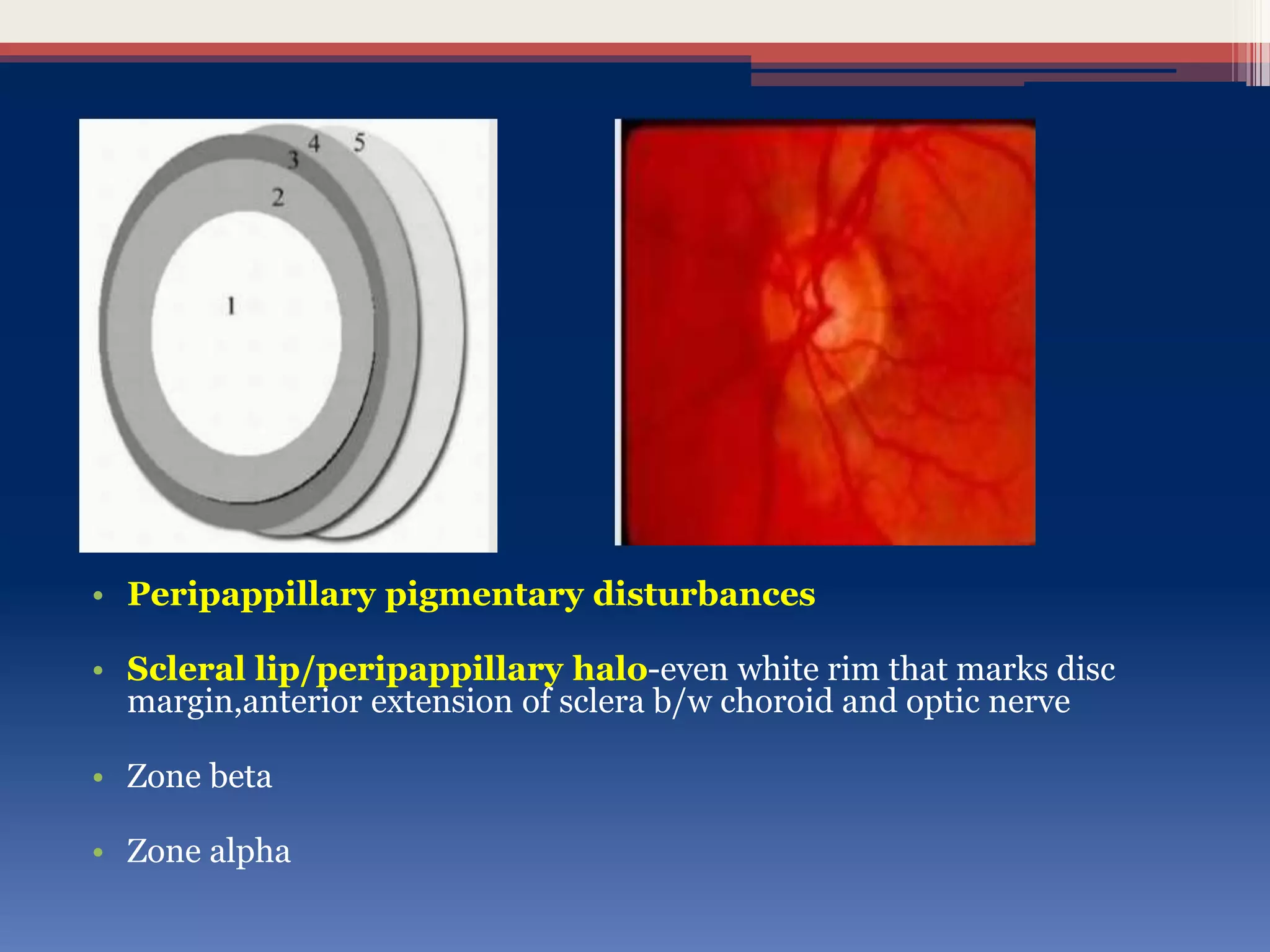
This document discusses optic disc changes in glaucoma. It defines key terms like optic nerve head and lamina cribrosa. It describes physiological cupping and normal cup-to-disc ratios. Pathogenesis of optic nerve head changes in glaucoma involves mechanical effects of increased intraocular pressure and vascular effects of ischemia. Signs suggestive of glaucoma include increased cup size, asymmetry between eyes, thinning of the neuroretinal rim, notches, splinter hemorrhages, and retinal nerve fiber layer defects preceding other changes. Advanced glaucoma shows total cupping and bending of retinal vessels at the disc margin.