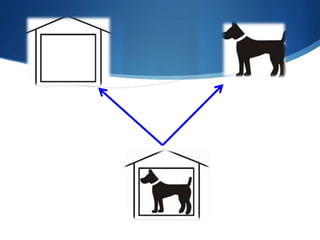
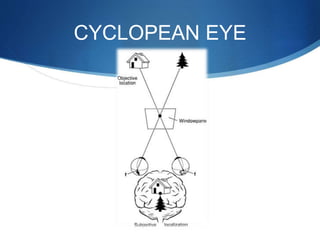
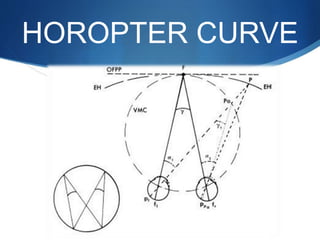
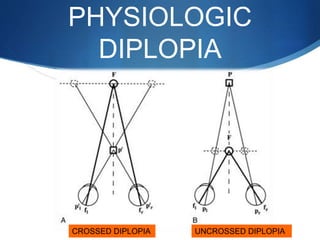
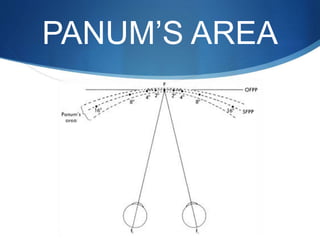
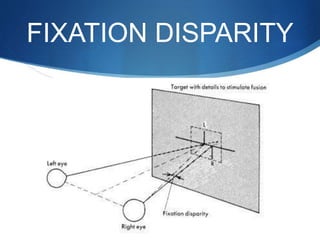
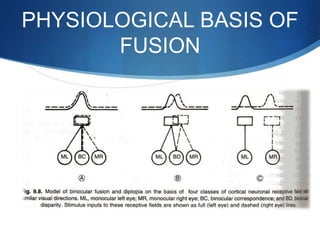
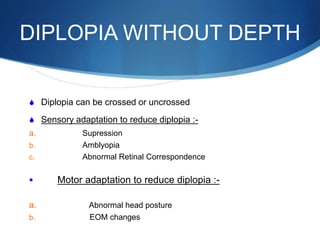
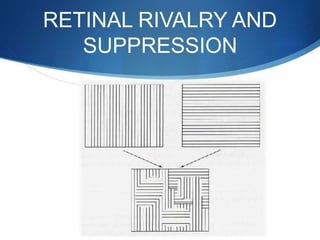
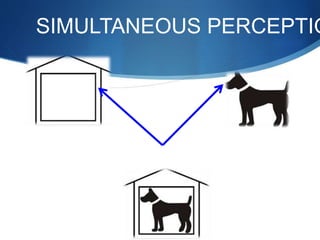
Binocular single vision refers to simultaneous vision with two eyes that occurs when an individual fixates on an object. There are three grades of binocular vision: simultaneous perception, fusion, and stereopsis. Fusion is the ability to see a composite picture from two similar images, while stereopsis provides the impression of depth by superimposing images from slightly different angles. Tests for binocular vision include those for simultaneous perception, fusion, and stereopsis using instruments like the synaptophore. Binocular vision develops through infancy and childhood as the visual axes become coordinated to direct each fovea at the object of regard.