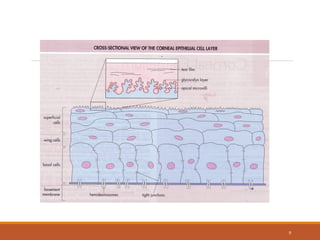
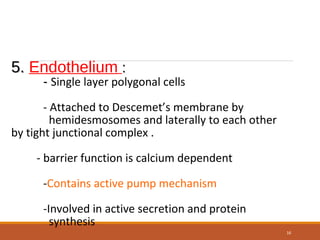
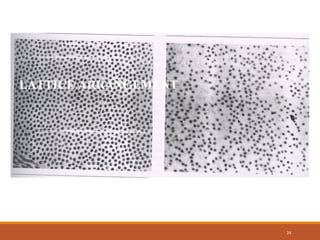
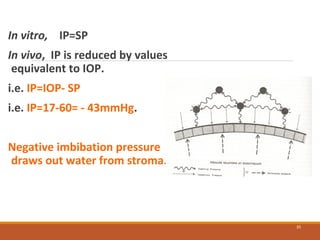
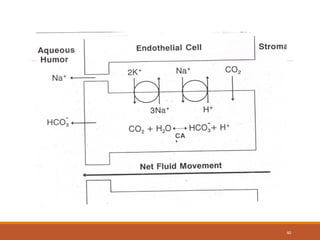
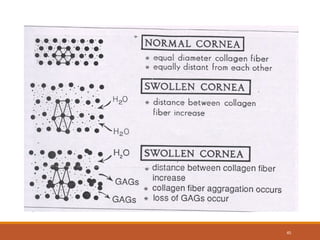
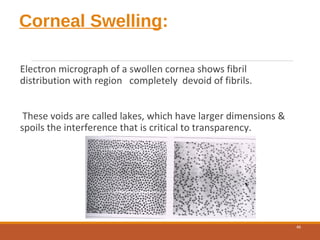
The cornea is a transparent tissue that forms the outer protective layer of the eye. It has five layers - epithelium, Bowman's layer, stroma, Descemet's membrane, and endothelium. The stroma makes up most of the corneal thickness and contains regularly arranged collagen fibrils that prevent light scattering through optical interference. The corneal endothelium actively pumps fluid out of the stroma to maintain corneal dehydration and transparency. Any disruption to the regular arrangement of collagen fibrils or the endothelial pump can compromise corneal transparency.