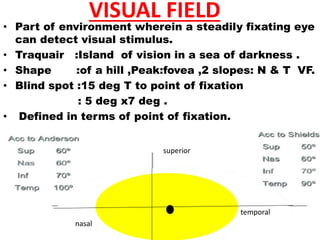
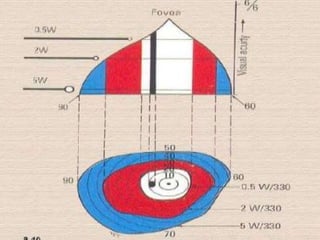
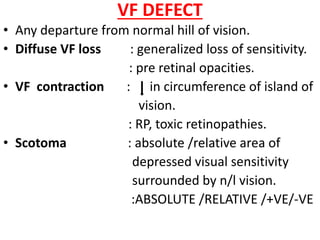
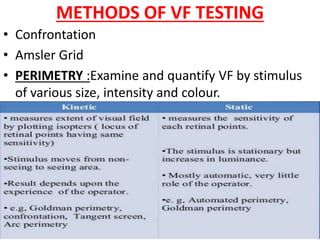
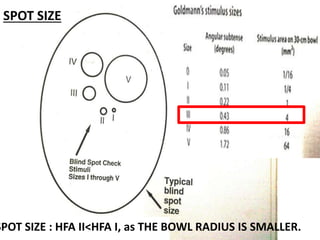
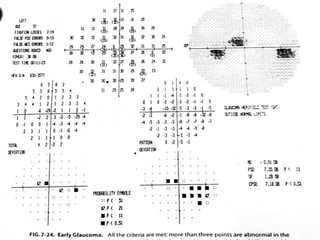
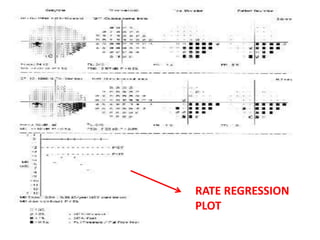
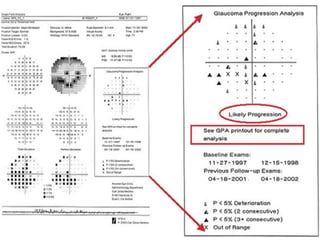
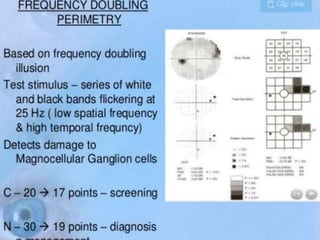
This document discusses visual field testing and perimetry. It defines the visual field and describes common visual field defects. It then covers the indications, methods, and terminology of visual field testing. Specific details are provided on threshold testing strategies, reliability indices, and how to interpret visual field printout maps and global indices. Criteria for diagnosing glaucomatous visual field loss and detecting progression over time are also outlined.