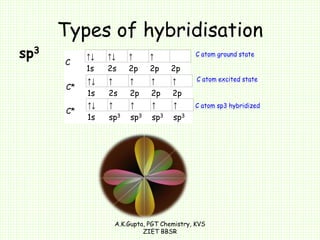
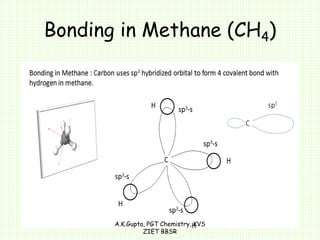
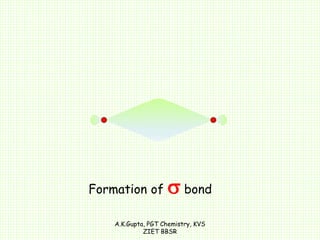
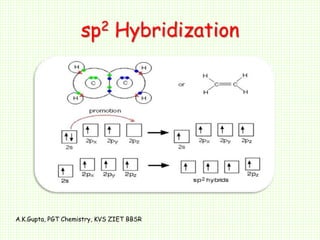
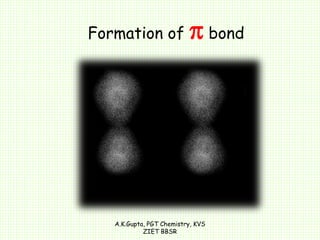
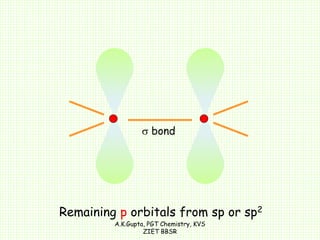
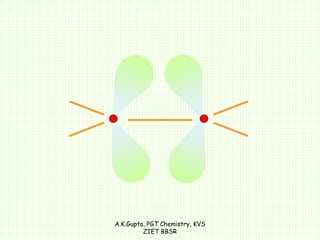
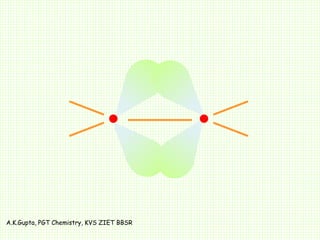
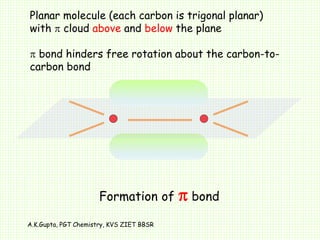
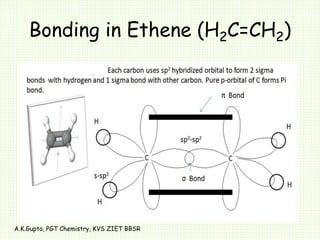
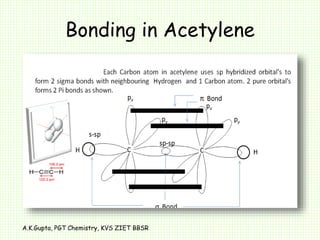
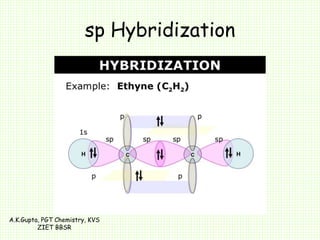
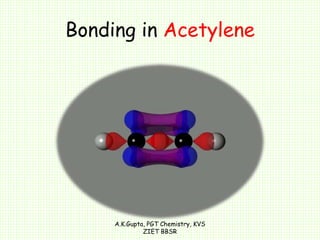
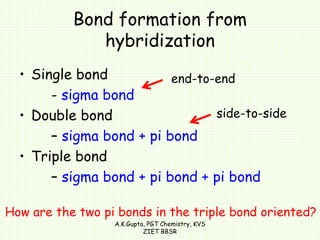
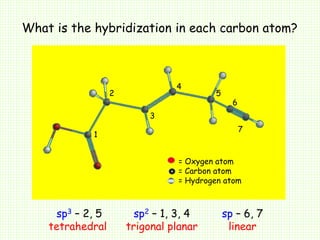
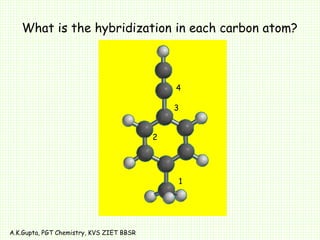
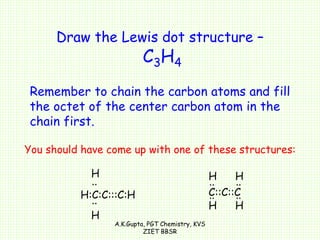
The document by A.K. Gupta discusses hybridization in chemistry, detailing types such as sp3, sp2, and sp along with their geometries and bond formation properties. It describes how hybrid orbitals are formed and their roles in sigma and pi bond creation, particularly in molecules like methane and ethene. The document emphasizes the importance of hybridization in understanding chemical bonding and molecular structure.