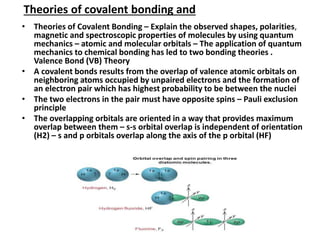
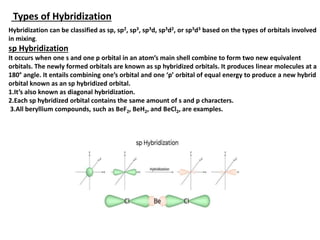
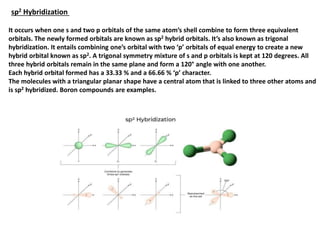
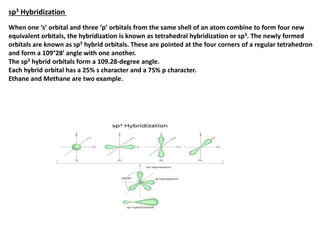
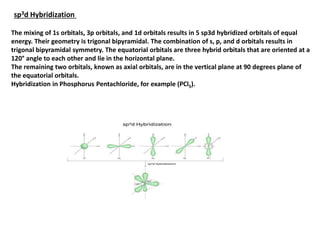
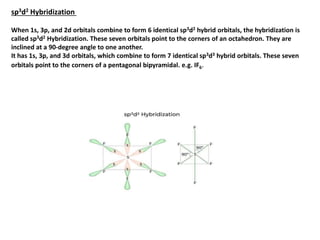
This document provides an overview of hybridization in chemistry. It defines hybridization as the mixing of atomic orbitals with the same energy level to form new hybrid orbitals. Hybridization can be classified as sp, sp2, sp3, sp3d, sp3d2, or sp3d3 based on the types of orbitals involved. Examples are provided for each type of hybridization, including their orbital orientations and molecular geometries. Common molecules that demonstrate different hybridizations, such as methane and phosphorus pentachloride, are described.