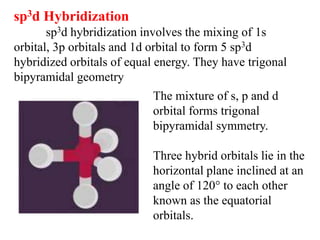
Hybridization is the concept of mixing atomic orbitals to form new hybrid orbitals during bond formation. It involves combining orbitals of similar energy, such as an s orbital mixing with p orbitals. This leads to hybrid orbitals with different energies, shapes, and orientations compared to the original orbitals. The type of hybridization depends on the number and type of orbitals that mix, with common examples being sp, sp2, and sp3 hybridization. Hybridization helps explain molecular geometry and bonding properties.